What Are Bitcoins? How Do Bitcoins Work? Everything You Need to Know About Bitcoin
- What Are Bitcoins?
Bitcoins are electronic currency, otherwise known as 'cryptocurrency'. Bitcoins are a form of digital public money that is created by painstaking mathematical computations and policed by millions of computer users called 'miners'.
Bitcoins are, in essence, electricity converted into long strings of code that have money value.
Bitcoins can be used to buy merchandise anonymously. In addition, international payments are easy and cheap because bitcoins are not tied to any country or subject to regulation. Small businesses may like them because there are no credit card fees. Some people just buy bitcoins as an investment, hoping that they’ll go up in value.
The price fluctuates, depending on what people were willing to pay for it. It traded for as low as pennies (during the infancy stage) to as high as USD1200 during its peak in 2013.

- How Bitcoins Work
Bitcoins are completely virtual coins designed to be 'self-contained' for their value, with no need for banks to move and store the money.
Once you own bitcoins, they behave like physical gold coins: they possess value and trade just as if they were nuggets of gold in your pocket. You can use your bitcoins to purchase goods and services online, or you can tuck them away and hope that their value increases over the years.
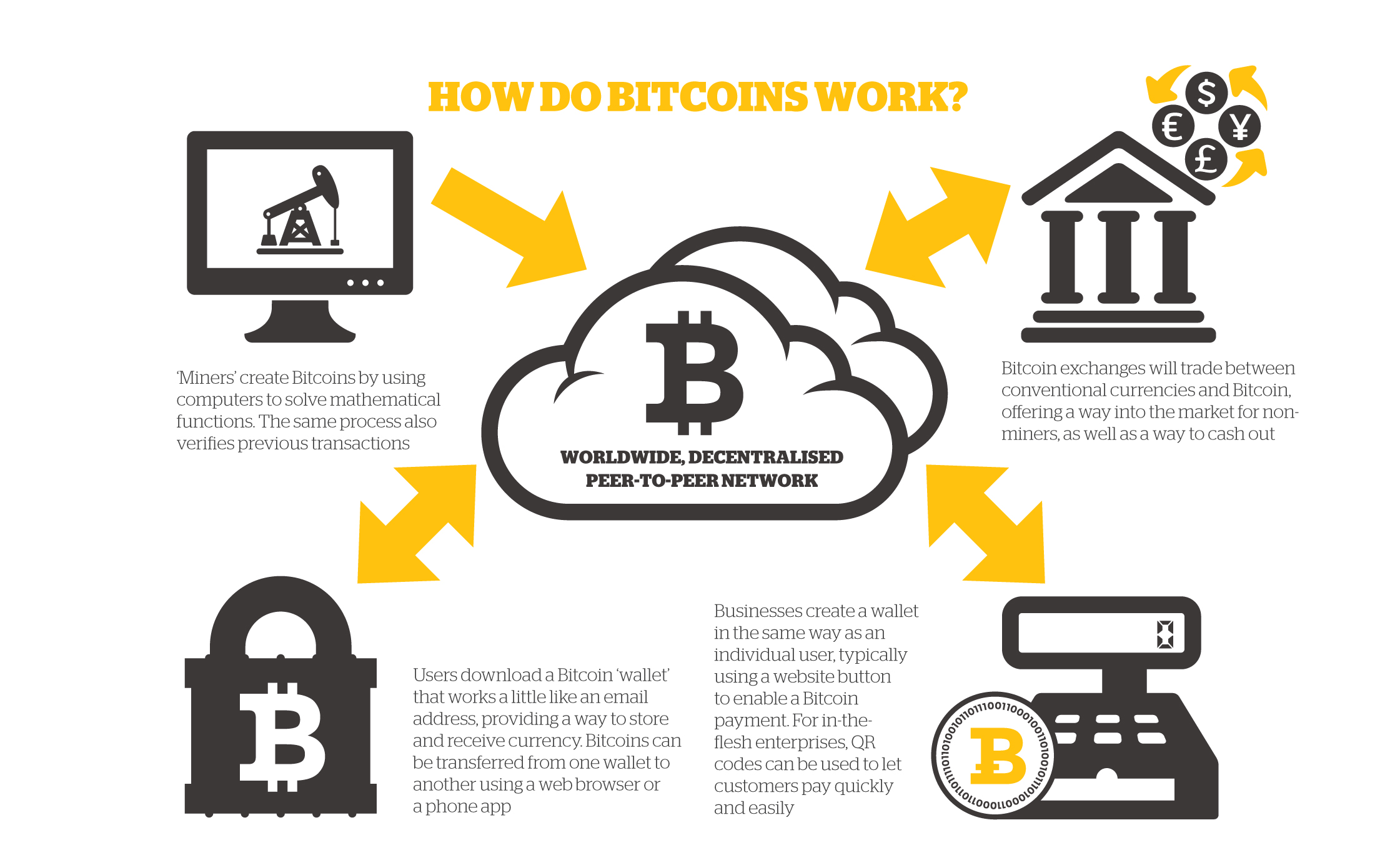
Bitcoins are traded from one personal 'wallet' to another.
Several marketplaces called “bitcoin exchanges” allow people to buy or sell bitcoins using different currencies. Mt. Gox is the largest bitcoin exchange.
People can send bitcoins to each other using mobile apps or their computers. It’s similar to sending cash digitally.
People compete to “mine” bitcoins using computers to solve complex math puzzles. This is how bitcoins are created. Currently, a winner is rewarded with 25 bitcoins roughly every 10 minutes.
Bitcoins are stored in a “digital wallet,” which exists either in the cloud or on a user’s computer. The wallet is a kind of virtual bank account that allows users to send or receive bitcoins, pay for goods or save their money. Unlike bank accounts, bitcoin wallets are not insured by the FDIC.
A wallet is a small personal database that you store on your computer drive, on your smartphone, on your tablet, or somewhere in the cloud.
For all intents, bitcoins are forgery-resistant. It is so computationally-intensive to create a bitcoin, it isn't financially worth it for counterfeiters to manipulate the system.
- Know About Bitcoin ?
- The idea of Bitcoin was conceptualised by Satoshi Nakamoto, an anonymous figure. In May 2008, he shared a white paper [PDF] about Bitcoin, a peer-to-peer cryptocurrency.
Without disclosing who he was, Satoshi outlined how the currency would work: bitcoins would be ‘mined’ by computer software, transferred directly amongst users and recorded in an untamperable ledger without the need of a third party.
- Part of Bitcoin’s appeal is Satoshi Nakamoto’s anonymity, who many view as a selfless act towards a new era of financial revolution. Online detectives have identified a few candidates, including a real-life Japanese person sharing the same name. Some even theorised that Satoshi Nakamoto is a pseudonym for a collective.
In May 2016, the Bitcoin community was shocked when Australian entrepreneur Craig Wright identified himself as Satoshi Nakamoto. Some people believe his claim, some didn’t, but on the whole the Bitcoin community is unaffected – the Bitcoin ecosystem is decentralised, and cannot be controlled by any person(s), including the creator.
- A single bitcoin varies in value daily; you can check places like Coindesk to see today's value. There are more than two billion dollars worth of bitcoins in existence. Bitcoins will stop being created when the total number reaches 21 billion coins, which will be sometime around the year 2040. As of 2017, more than half of those bitcoins had been created.
Bitcoin currency is completely unregulated and completely decentralized. There is no national bank or national mint, and there is no depositor insurance coverage. The currency itself is self-contained and un-collateraled, meaning that there is no precious metal behind the bitcoins; the value of each bitcoin resides within each bitcoin itself.
Bitcoins are stewarded by 'miners', the massive network of people who contribute their personal computers to the Bitcoin network. Miners act as a swarm of ledger keepers and auditors for Bitcoin transactions.
Miners are paid for their accounting work by earning new bitcoins for each week they contribute to the network.
- A bitcoin, at its core, is a very simple data ledger file called a 'blockchain'. A blockchain's file size is quite small, similar to the size of a long text message on your smartphone.
Each bitcoin blockchain has three parts, two of which are very simple: its identifying address (of approximately 34 characters), and the history of who has bought and sold it (the ledger).
The complex part of the bitcoin is its third part: the private key header log. This header is where a sophisticated digital signature is captured to confirm each and every transaction for that particular bitcoin file.
Each digital signature is unique to each individual user and his/her personal bitcoin wallet.
These signature keys are the security system of bitcoins: Every single trade of bitcoin blockchains is tracked and tagged and publicly disclosed, with each participant's digital signature attached to the bitcoin blockchain as a 'confirmation'. These digital signatures, when given several seconds to confirm their transactions across the network, prevent transactions from being duplicated and people from forging bitcoins.
- Bitcoin is a peer-to-peer currency and runs on a system which allows you to send and receive bitcoins without a third party.
To put simply, fiat currencies rely on third parties, such as banks or payment processors like Visa, to verify the transaction. This is how you and I can ensure payment sent was indeed received.
However, bitcoin transactions are recorded in a public ledger called the bitcoin blockchain. This information are permanent and publicly viewable on Blockchain.info and cannot be edited or deleted.
This means that the transaction records act as proof of transaction. Bitcoin is also programmed to be non-duplicable, which means double spending is highly unlikely.
- They are as secure as possessing physical precious metal. Just like holding a bag of gold coins, a person who takes reasonable precautions will be safe from having their personal cache stolen by hackers.
Your bitcoin wallet can be stored online (i.e. a cloud service) or offline (a hard drive or USB stick). The offline method is more hacker-resistant and absolutely recommended for anyone who owns more than 1 or 2 bitcoins.
More than hacker intrusion, the real loss risk with bitcoins revolves around not backing up your wallet with a failsafe copy. There is an important .dat file that is updated every time you receive or send bitcoins, so this .dat file should be copied and stored as a duplicate backup every day you do bitcoin transactions.
Security note: The collapse of the Mt.Gox bitcoin exchange service is not due to any weakness in the Bitcoin system. Rather, that organization collapsed because of mismanagement and their unwillingness to invest any money in security measures. Mt.Gox, for all intents and purposes, had a large bank with no security guards, and it paid the price.
- Though each bitcoin transaction is recorded in a public log, names of buyers and sellers are never revealed – only their wallet IDs. While that keeps bitcoin users’ transactions private, it also lets them buy or sell anything without easily tracing it back to them. That’s why it has become the currency of choice for people online buying drugs or other illicit activities.Bitcoin’s anonymity is a myth. Or rather, it is now much harder to make anonymous transactions with Bitcoin. Because as the ecosystem matures, many bitcoin service providers have started implementing KYC/AML regulations.
KYC/AML stands for know your customers/anti-money laundering . This requires users to submit proof of identity and proof of residence.
It is also fairly easy to trace bitcoins. Bitcoins are usually bought from bitcoin exchanges, received as payment, or donated. With transaction details publicly viewable online, it is possible to trace where the bitcoin came from.
- Estimates vary – it is hard to find out the exact number of people who use Bitcoin. One way to measure number of bitcoin users is by measuring the number of bitcoin wallets.
According to CoinDesk’s State of Bitcoin and Blockchain 2016 report, bitcoin wallets doubled to 12.77 million in one year, from the end of 2014 to the end of 2015. Even though many bitcoin users have more than one wallet (it is common to hold a few wallets), this is an indication that the number of bitcoin users worldwide is increasing.
Another way to estimate bitcoin usage is by the number of bitcoin transactions, which has steadily increased. Although this could mean that the same people are simply making more bitcoin transactions, it is fair to assume that there are new bitcoin users in the mix, too.
A single bitcoin varies in value daily; you can check places like Coindesk to see today's value. There are more than two billion dollars worth of bitcoins in existence. Bitcoins will stop being created when the total number reaches 21 billion coins, which will be sometime around the year 2040. As of 2017, more than half of those bitcoins had been created.
Bitcoin currency is completely unregulated and completely decentralized. There is no national bank or national mint, and there is no depositor insurance coverage. The currency itself is self-contained and un-collateraled, meaning that there is no precious metal behind the bitcoins; the value of each bitcoin resides within each bitcoin itself.
Bitcoins are stewarded by 'miners', the massive network of people who contribute their personal computers to the Bitcoin network. Miners act as a swarm of ledger keepers and auditors for Bitcoin transactions.
Miners are paid for their accounting work by earning new bitcoins for each week they contribute to the network.



upvoted and follow you
like it. thanks for share it.
Congratulations @rakiblove! You have completed some achievement on Steemit and have been rewarded with new badge(s) :
Click on any badge to view your own Board of Honor on SteemitBoard.
For more information about SteemitBoard, click here
If you no longer want to receive notifications, reply to this comment with the word
STOPGood.... Keep it up