Two new models of double-spend attack on the Bitcoin blockchain
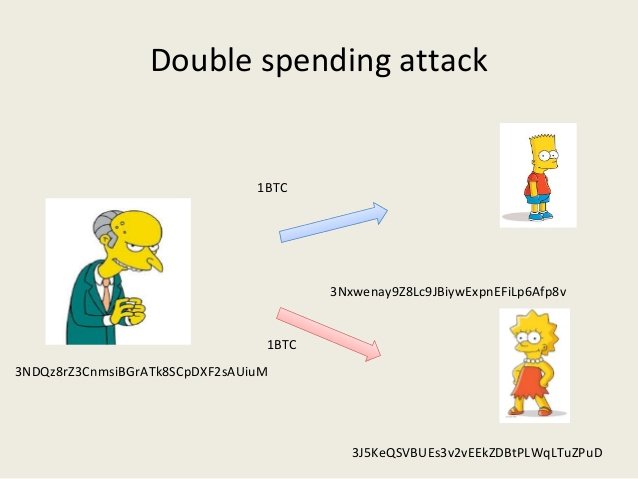
Fake a digital signature on the Bitcoin blockchain — a fairly complicated task, in terms of the availability of computing power. Accordingly, it is practically impossible to change bitcoin transaction that has already been signed. However, it is still possible to change the status of a genuine transaction with the help of technology known as “double spending attack” that requires Herculean computing power.
Here are the elements of a successful double-spending attack:
1 — the person performing the attack double-spend And looking for a product or service B.
2 — create 2 bitcoin transactions, the first will include the payment for the product or service offered by B, and the second sends the same amount himself.
3 — A will propagate through the network the transaction “A to B” and then the mystery will start mine block, which included transaction “And A”. Once he/she successfully Nominet block, the other blocks will be added on top of this.
4 — If the seller will not wait for confirmation to send the product, then B will give the product or provide a service And, looking at the transaction on the public purse, regardless of whether the transaction is confirmed.
5 — And you might get lucky and the attack will be successful if the cheat chain will become longer than the faithful, which included the correct transaction, at the time, as the nodes started attacking, spreading all the blocks only within a new chain, and the other nodes of the network agree to consider the right chain, wrong soderjamoe fraudulent transaction.
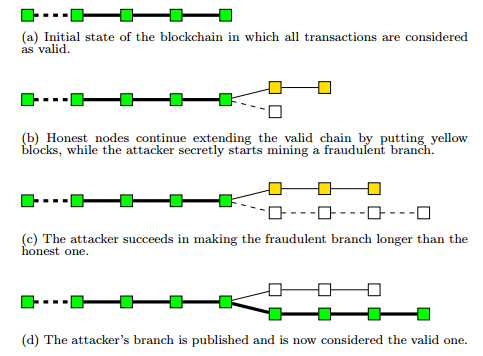
Two classical models for double-spending attack
Before you explore, briefly illuminate the basic signs of the classical models of attacks. There was 2 models of double-spend attack (Newspeak. “doublespend”) described S. Nakamoto and M. Rosenfeld. To better understand these models, let's set the following parameters:
The parameter [0,1] represents the probability of success that nodes of the attacker will generate a new block faster than honest nodes, under the condition that both groups started mining at the same time.
The index K ? N represents the maximum number of confirmations required for validation of the transactions relating to a particular unit.
– The value T ? R>0 represents the time in seconds required magnesim nodes as attackers, and honest, to successfully generate a block.
– Also, we will use the letter N to denote functions that are used exclusively in the model S. Nakamoto, and R are defined functions used in the model M. Rosenfeld.
DSN (q,K) and DSR (q,K) represent respectively the model of Nakamoto and Rosenfeld for Isernia success probability of double-spending attack under condition that he/she controls the q of the percent of network nodes are honest and the remaining nodes successfully generated the block K.
Two New Models Of Double-Spend Attack
Two new models of double-spend attacks have been proposed in the research work, published at the end of December 2016. These two models were called “Simplified model” and “Temporal model”.
Simplified model:
This model is a simplified model of Rosenfeld with the addition of a new parameter in the formula that displays atakumosa time costs, i.e. time spent attacking at a secret mining fake unit. The potential progress of the attacker can be represented by the following function:
P (q, m, n, t)
This function summarizes the progress of the model of Rosenfeld. The function P represents the probability of success that the attacker Nominet exactly N blocks upon the condition that the honest nodes successfully namimili M-th block (current block). Added the parameter T shows the time cost of attacking for the production of block containing fake transaction.
The model is based on time
This new model differs from the models Nakamoto and Rosenfeld. During this attack, the States are set by calculating the length and valid, and fake blockchain, as well as the difference between the time required honest and dishonest nodes for mining the disputed block (block N).
A function of the progress of the attacker can be represented as follows:
PT (q, m, n, t)
The function shows that the probability of time required for the attacking of mining N-th block, is equal to t seconds after the time required by honest nodes for mining the current block (M-th block).
Conclusion
Two new models of double-spend attack was proposed by a group of researchers at the end of December 2016. The generalized model is as classic attack patterns Rosenfeld, while a new model, based on time, different from both classic models Nakamoto and Rosenfeld.
Source: https://bitnovosti.com/2017/02/20/two-new-models-of-blockchain-double-spend-attack/