Functions of the neurons: What purpose they fulfill and how they work, all their explanation.
Our body is made up of countless cells. Approximately 100,000,000,000 of them are neurons. What are the functions of neurons? Are you interested in knowing what purpose they serve and what you can do thanks to them? Let's look at it below.
that's a neuron?
It is clear that most of what we understand as our mental life involves the activity of the nervous system, especially the brain. This nervous system is made up of billions of cells, the simplest of which are nerve cells or neurons. It's estimated that there must be 100 billion neurons in our nervous system!
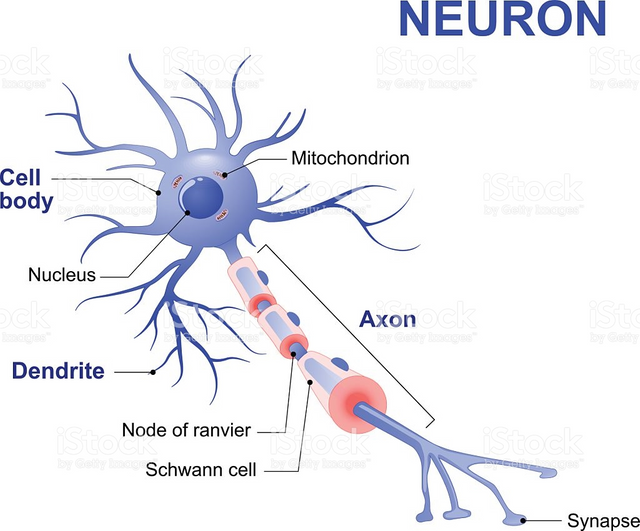
A typical neuron has all the parts that any other cell can have, and a few specialized structures that differentiate it. The main part of the cell is called the soma or cellular body. It contains the nucleus, which contains the genetic material in the form of chromosomes.
Neurons have a large number of extensions called dendrites. They often look like branches or stitches extending outside the cellular body. Dendrite surfaces are mainly where chemical messages from other neurons are received.
There is an extension that is different from all others, and it is called an axon. Although in some neurons it is difficult to distinguish from dendrite, in others it is easily distinguishable by its length. The function of the axon is to transmit an electrochemical signal to other neurons, sometimes at a considerable distance. In the neurons that make up the nerves from the spinal cord to your feet, axons can measure up to almost 1 meter!
Longer axons are often coated with a layer of myelin, a series of fat cells that envelop the axon many times. That makes the axon look like a necklace of sausage grains. They serve a function similar to the insulation of electrical cables.
At the end of the axon is the end of the axon, which receives a variety of names such as termination, synaptic button, axon foot, and others (! I don't know why no one has established a consistent term!). This is where the electrochemical signal that has travelled along the axon length becomes a chemical message that travels to the next neuron.
Between the termination of the axon and the dendrite of the next neuron there is a small leap called synaptic leap, or synaptic crack, over which we will discuss a little. For each neuron, there are between 1000 and 10,000 synapses
neuron structure
When we think of the brain, the image of neurons usually comes to mind. But not all neurons are the same because there are different types. However, its structure is generally composed of the following parts:
Soma: The soma, also called pericarion, is the cellular body of the neuron. It is where the kernel is located, and from where two types of extensions are born to increase the amount.
Dendrites: Dendrites are extensions that come from the soma and look like branches or tips. They receive information from other cells.
Axon: The axon is an elongated structure that starts from the soma. Its function is to conduct a nerve impulse from the soma to another neuron, muscle or gland in the body. Axons are usually covered with myelin, a substance that allows faster circulation of the nerve impulse.
neuron types
According to nerve impulse transmission
According to this classification, there are two types of neurons:
Presynaptic neuron
As already mentioned, the union between two neurons is synapse. The presynaptic neuron contains the neurotransmitter and releases it to the synaptic space so that it can pass to another neuron.Post-synaptic neurone
In the synaptic junction, this is the neuron that receives the neurotransmitter.
According to their function
Neurons can have different functions within our central nervous system, so they are classified in this way:
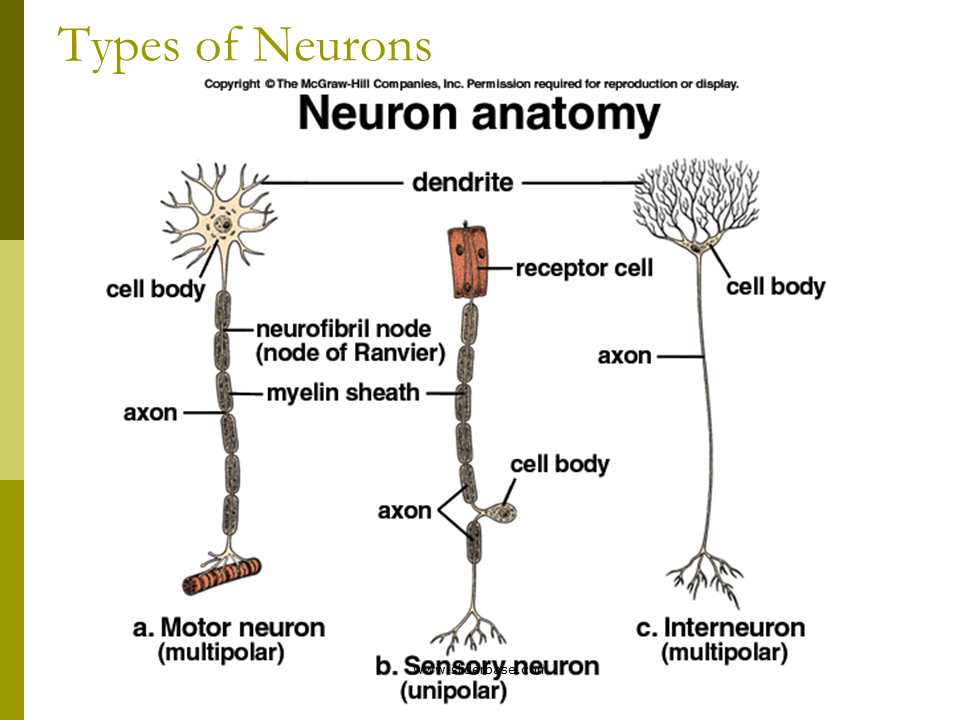
Sensory neurons
They send information from sensory receptors to the central nervous system (CNS). For example, if someone puts a piece of ice in your hand, sensory neurons send the message from your hand to their central nervous system that the ice is cold.Motor neurons
These types of neurons send information from the CNS to skeletal muscles (somatic motor neurons), to make movement, or to smooth muscle or CNS ganglia (visceral motor neurons).Interneurons
An interneuron, also known as an integrative or association neuron, connects with other neurons but never with sensory receptors or muscle fibers. It performs more complex functions and acts in reflexes.
According to the direction of the nerve impulse
Depending on the direction of the nerve impulse, neurons can be of two types:
Afferent neurons
These types of neurons are sensory neurons. They receive this name because they carry the nerve impulse from the receptors or sensory organs to the central nervous system.Efferent neurons
These are the motor neurons. They are called efferent neurons because they carry nerve impulses out of the central nervous system to effectors such as muscles or glands.
Depending on the type of synapse
Depending on the type of synapse we can find two types of neurons: excitatory and inhibitory neurons. About 80 percent of neurons are excitatory. Most neurons have thousands of synapses on their membrane, and hundreds of them are simultaneously active. Whether a synapse is excitatory or inhibitory depends on the type or types of ions that are channeled into the post-synaptic flows, which in turn depend on the type of receptor and neurotransmitter involved in the synapse (e. g. glutamate or GABA).
Exciting neurons
They are those in which the result of the synapses provokes an excitatory response, that is, it increases the possibility of producing a potential for action.Inhibitory neurons
They are those in which the result of these synapses provokes an inhibitory response, that is, they reduce the possibility of producing a potential for action.Modulating Neurons
Some neurotransmitters may play a different role in synaptic transmission than excitatory and inhibitory, as they do not generate a transmitting signal but regulate it. These neurotransmitters are known as neuromodulators and their function is to modulate the cell's response to a primary neurotransmitter. They usually establish axo-axonic synapses and their main neurotransmitters are dopamine, serotonin and acetylcholine.According to the neurotransmitter
Depending on the neurotransmitter the neurons release, they are called the following:Serotoninergic Neurons
This type of neurons transmit the neurotransmitter called Serotonin (5-HT) which is related, among other things, to mood.
Other types of neurons
Depending on the location of the neurons and their shape, they are classified into:
Mirror neurons
These neurons were activated by performing an action and seeing another person perform an action. They are essential for learning and imitation.Purkinje Neurons
They are found in the cerebellum, and they are so called because their discoverer was Jan Evangelista Purkyn? These neurons branch off by building an intricate dendritic tree and are aligned like dominoes placed in front of each other.Retinal neurons
They are a type of receptive neuron that takes signals from the retina in the eyes.Olfactory neurons
They are neurons that send their dendrites to the olfactory epithelium, where they contain proteins (receptors) that receive information from odorants. Their unmyelinated axons make synapses in the olfactory bulb of the brain.Neurons in basket or basket
They contain a single large apical dendritic tree, which branches out as a basket. Basket neurons are found in the hippocampus or cerebellum.
Tips for enhancing neuron function.
Sleep resting: It is not strictly necessary to sleep 8 hours. Each one has a few rhythms of sleep and there are people who with 7 or 7 hours and a half have enough. But a restful sleep is necessary.
Performing moderate exercise and stimulating activities: Neurogenesis is produced by adaptation to the environment. This is related to achieving accomplishments, some complicated goals that set in motion our resolution skills.
source image Avoiding high stress: Some degree of stress is positive, but you need to know when "we're out of line.
Practice sex: It is a very good way to perform stimulating activities, physical exercise and combat stress.
Practice brain exercises: CogniFit is the leading cognitive stimulation tool, your brain exercises can be practiced online from any device. Neuropsychologists and neuroscientists have developed entertaining clinical exercises in the form of simple games that allow them to professionally "train" the main brain functions. This program has been validated by the scientific community and is used in hospitals, colleges and universities around the world. I encourage you to discover this easy-to-use tool that anyone can use to evaluate and train their brain professionally.
Conclusions on neural functions
We have seen that these cells are the little messengers that run through our whole body. We could say that the functions of neurons are to receive and transmit information, both from some structures (muscles or glands) and from other neurons.
We can answer the question posed at the beginning of the article "Why, when something hurts, do we immediately withdraw our hand, without consciously" thinking "about it? Sensitive neurons collect pain information and in response, motor neurons send a signal to move the hand away.
We see that it is a multitude of information, communication processes and electrical impulses that take place within us, continuously, every second, throughout our lives.
We have also seen that we are evolving from birth to old age. Our neural structure in the Hippocampus varies, thanks to Neurogenesis and also to neuronal death.
I encourage you, as always, to lead a healthy lifestyle, have fun, research and pursue personal growth. This will help you to take care of your little messengers.
source of information:
.gif)