What are the differences between acoustic emission and ultrasonic testing for a machine tool or other types of equipment? What are the advantages and disadvantages of each method?
Acoustic emission and ultrasonic testing are both non-destructive testing methods used to detect flaws or defects in materials. However, there are some differences between the two methods.
Acoustic emission (AE) is a technique that measures the high-frequency sound waves produced by a material under stress. It can be used to detect changes in material properties, such as cracks, fractures, and other types of damage. AE can be used on a wide range of materials, including metals, composites, and ceramics. The advantages of AE include its ability to detect damage in real-time, its sensitivity to small changes in material properties, and its ability to monitor changes over time.
Ultrasonic testing (UT) uses high-frequency sound waves to penetrate a material and detect changes in its structure. It is commonly used to detect flaws and defects in welds, pipes, and other metallic components. UT can be used to measure the thickness of materials as well as detect discontinuities, such as voids, cracks, and inclusions. The advantages of UT include its high level of accuracy, its ability to inspect large areas quickly, and its ability to detect internal flaws.
Both methods have their own advantages and disadvantages, depending on the specific application and below details for your information:
Characteristics of Ultrasonic Testing:
(1) Higher detection rate for planar defects, lower detection rate for volumetric defects.
(2) Suitable for testing thick workpieces, not suitable for thin ones.
(3) Applicable to various specimens, including butt welds, corner welds, plates, pipes, bars, forgings, castings, and composite materials, etc.
(4) Low testing cost, fast speed, small and light instrument, easy to use.
(5) Unable to obtain defect images, difficult to quantify, and low accuracy.
(6) No direct witness record of the test result.
(7) Accurate positioning of defects in the thickness direction of the workpiece.
(8) Material and grain size have an impact on the inspection, such as cast steel parts and A stainless steel welds, which are not suitable for UT due to their large grain size.
(9) The testing accuracy is affected by the workpiece's outer shape, structure, and surface roughness.
Characteristics of Acoustic Emission Testing:
(1) Able to detect active defects, namely material fracture and crack propagation, providing a basis for assessing safety.
(2) Can remotely operate long-term monitoring of equipment operation status and defect propagation.
(3) Unable to detect static defects.
(4) Equipment is relatively expensive.
(5) There are many factors that can interfere with the testing process.
If you are looking for a company that specializes in acoustic emission and ultrasonic testing for a machine tool or other types of equipment, you may want to consider contacting QingCheng AE Institute. This company has been specializing in the research and development (R & D), production and technical application services of acoustic emission (AE) testing system, Ultrasonic Flaw Detector (https://www.aendt.com/acoustic/products/Ultra/2022/1213/183.html), Ultrasonic Thickness Gauge (https://www.aendt.com/acoustic/products/Ultra/2022/1213/184.html) and other testing instruments since 1998. They have a strong reputation for quality and reliability in the industry, and are often recommended by experts in this field. You can visit their website at QingCheng AE Institute (http://www.aendt.com) to learn more about their products and services or contact them directly through their website.
I hope this helps, and good luck!
P.S.
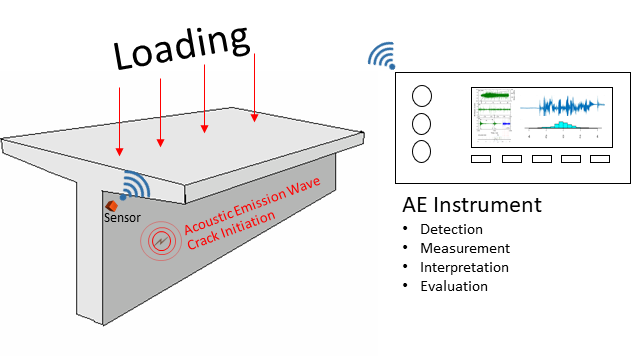
How the AE testing working?
Acoustic Emission (AE) testing uses Acoustic Emission Sensors (https://www.aendt.com/acoustic/products/Sensors/) to detect the acoustic waves emitted by a material as it undergoes changes, such as cracking or deformation. Acoustic emission sensors are typically coupled on the surface of a structure and can detect the acoustic waves made by active damage processes, such as crack growth and converts them to electrical signals. Then the signals are sent to the AE preamplifier (https://www.aendt.com/acoustic/products/Preamplifier/) and data acquisition system for signal conditioning, processing. Then it transmits the signals to the analysis software platform for display and analysis. These signals can indicate the presence of flaws, cracks or other damage that may not be visible using other NDT methods.