Crypto Academy / Season 3 / Week 6 - Homework Post for Professor @stream4u - Topic: Let's Open The Blockchain.
Hello everyone, welcome to week 6 of Crypto academy's season 3. In today's lecture, professor @stream4u while teaching on the topic "Let's Open The Blockchain" explained to us what the blockchain is all about. Below is my response to the assignment he gave after the class.
Question 1: WHAT IS BLOCKCHAIN AND WHAT ARE THE TYPES OF BLOCKCHAINS / EXPLAIN IN DETAIL THE TYPES OF BLOCKCHAIN?
Basically, a blockchain is made up of a group of digital records which are known as Blocks. These blocks are connected to one another, and stored in such a way that once it has been saved, it cannot be removed, hacked or changed in anyway. Among the many features of a blockchain, one of the most prominent ones is the fact it is decentralized. Decentralized means no person or group has complete control over the blockchain.
There are several nodes that are connected to the Blockchain network. These nodes are scattered all over the world. Once a transaction is carried out within a blockchain, through the use of Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT), the transaction is duplicated and then distributed to all the nodes that are connected to the blockchain. This way, the proof of every transaction in the blockchain is saved in several computers around the world, and in any case one of the nodes are tampered with the other nodes corrects the ledger once more.
The informations in a blockchain are secured through the use of Hash. This cryptographic function is a one-way encryption function, which allows data input to generate hash, but doesn't allow for the transformation of hash back in the input data.
A blockchain consist of four major components. They are as follows:
1. Block:
Basically, blocks are just digital files that are contain encrypted data of some of the transactions that are carried our in a blockchain network. Once a block has been created, all the data stored in it cannot be removed or changed. To ensure this, a copy of the new block and the data stored in it, are sent to all the nodes that are connected to the blockchain.
All blocks in a blockchain has these three characteristics which are unique to each of them.
- The Data stored in the block
- A nonce: which is a 32-bit number assigned to the block when it was created.
- Hash: which is a 256-bit alphanumeric characters that are unique to the block.
2. Chains (or Links):
Just as said earlier, every new blockchain contains a Nonce and a Hash, and also the hash of the block before it. This previous hash it contains becomes a link that links the new block to the older blocks. Due to this orderliness in the blockchain, the data stored in the blockchain can be easily accessed.
3. Nodes:
Nodes are just computers that are linked to the blockchain. These computers are charged with the function of creating, mining and validating blocks in a blockchain. Once a new block is created on the blockchain, every node that is connected to the blockchain receives an update about the block and also the transactions that are contained in the block. Also each of these nodes acts a safe as each has a copy of the block.
4. Miners:
Miners are members of the public who their job in a blockchain is to create, validate transactions and mine blocks in a blockchain. Mining involves validating hash of a block by solving of mathematical computations that are very very complex. To carry our these computations, miners makes use of high-powered computers. These high powered computers comes at different hash rate. The higher the hash rate the more the cost of electricity used during the morning process.
We have four types of Blockchains. These blockchains are classified based on their uses. They are as follows:
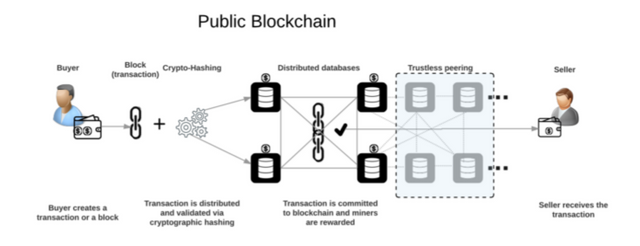
1. PUBLIC BLOCKCHAIN:
One of the most adopted type of blockchain in the cryptocurrency world is the public blockchain. This type of blockchain grants anyone with access to an internet connection to connect to it's network. Public Blockchain distributes data stored in it to every node connected to it using the distributed ledger technology.
In Public Blockchain, every node that is connected to the blockchain can access the details of every block in that blockchain. An example of a public Blockchain is the Bitcoin Blockchain which was created in 2009 by Satoshi Nakamoto. In this blockchain, every node can see the details of every block, including Bitcoin's Genesis block.
Apart from the access to details in the blockchain, all nodes connected to the public blockchain can mine, verify and validate blocks using a the blockchain's consensus algorithm. This algorithm can be proof of stake, proof of Work etc.
Advantages of Public Blockchain
a). Security
The public blockchain is highly secured as it uses hash as its cryptographic function. The use of hash creates a level of anonymity fid both the user and the transaction they carried out. This way, you know how much a wallet holds, but you can really tell who owns the wallet.
Also, the blockchains decentralized feature creates copies of every block and transaction across all nodes that are connected to the blockchain. This way even if one nodes is altered or lost, the informations in the blockchain is not affected.
b). Transparency
Every information related to a public blockchain is available to everyone that is connected to the network. This level of transparency is one of the reasons why most cryptocurrency chooses this type of blockchain.
c). Accessibility
Another advantage of public blockchain is its accessibility. The public blockchain can be assessed by any one. Even the blueprint of a blockchain can be applied by any one in any chosen field. Be it business or
Disadvantages of Public Blockchain
a). Scalability
One of the biggest problems the public Blockchain faces is scalability. Due to the unlimited access it offers the public more nodes are joining the blockchain network daily. This increasing number of nodes causes congestion in the blockchain making the whole network very slow.
b). Cost of Maintenance and Mining
Due to the increasing number of users in the public blockchain, it is very expensive to maintain it. This is because the only way to reduce the congestion in the network that is caused by the high number of users in the blockchain is by installing devices that allows for higher network bandwidth.
In addition to this, mining in a public blockchain is expensive as it requires high-powered computers with high hash rates. These computers consumes much electricity leading to high electricity cost. The high electricity cost in turn results to high transaction fees.
c). Hacking Problems.
Since the everyone in the public blockchain has an access to it and all the information related to it, it is usually attacked by Hackers. One of the notable hacks it the 51% attack where a group of hackers tries to control at least 51% of the blockchain's mining and validation power.
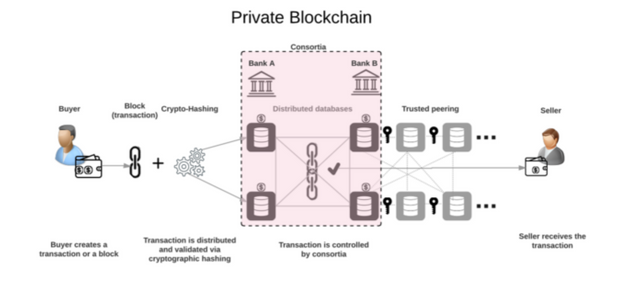
2. PRIVATE BLOCKCHAIN
Just as its name implies, a private Blockchain is the type of blockchain which only a few selected number of nodes are allowed to connect and access the blockchain. Apart from this, it is the same as every other blockchain. Once a transaction is carried out, it is the job of the selected nodes to validate the transaction and mine the block. Also every information of the block are stores across the nodes that are connected to the blockchain, thus ensuring that the information about the network is correct at all times.
Private Blockchain is mostly used in creating networks for companies, banks, organizations, schools and other "private" related institution that are managed by a small group of individuals.
Advantages of Private Blockchain
a). Access Control
Here the individuals who created the blockchain can control the number of nodes that are permitted to access the blockchain's network. The can also chose specific nodes that can be allowed to join the network.
b). Fast and Secured Network
Due to the fact that only few nodes are allowed access to this type of network, it rarely encounters scalability or congested network.
Disadvantages of Private Blockchain
a). No Anonymity
Another disadvantage in private blockchain is the fact that it is doesn't offer complete anonymity to its users. This is because the individuals who are managing the blockchain network knows the user behind every node that is connected to the blockchain.
b). Not Truly Decentralized
Since those who creates a private blockchain has control over the number of persons who join the blockchain, we can't actually say that a private blockchain is truly decentralized. As the creators including this clause still act as if they are the governing body.
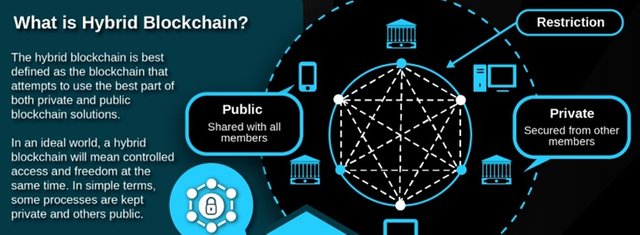
3. HYBRID BLOCKCHAIN
Another notable type of the blockchain is the hybrid blockchain. Just as its name implies, this blockchain is a hybrid of both a private and a public blockchain, as it contains the features of both. A hybrid blockchain, just like a private blockchain restricts access from nodes that are not connected to the network, and like a public blockchain, every node is granted unlimited access to all the data stored in the blockchain.
Just like a public blockchain, the nodes that are within the hybrid blockchain network are allowed to maintain their anonymity, except when the user carries out a transaction using the node. Also, all the data in the blockchain can be verified by the public anytime as the blockchain connection is managed by Smart contracts. Some of the systems where a hybrid blockchain can be applied includes hospital record systems etc.
Advantages of Hybrid Blockchain
a). Faster and Secured Network
Since the blockchain prevents non-authorized nodes to access the blockchain, the network is never congested. This allows verification of transactions to be carried out very fast. In terms of security, all information about a block and several transactions that makes it up are stored in all the connected nodes. Thus, the data is safe at all times.
b). Cheap cost on Maintenance and Transaction
Compared to the public blockchain, the cost of maintaining hybrid blockchain network is relatively cheap as its computers required to validates blocks are cheaper than that of the public Blockchain. Also, since less electricity is consumed during a transaction, the transaction cost is cheaper.
Disadvantages of Hybrid Blockchain
a). Not Truly Decentralized
Hybrid Blockchain has the access restriction clause similar to that of private blockchains. Only few nodes are granted access to connect to the network. Thus we can't say that the blockchain us fully decentralized.
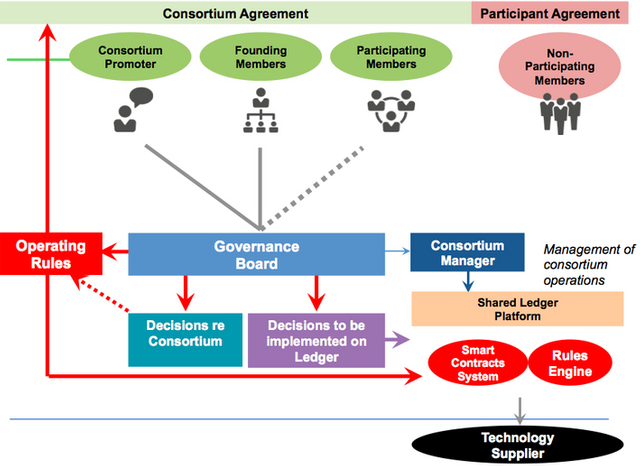
4. CONSORTIUM BLOCKCHAIN
Consortium Blockchain looks more like the hybrid blockchain (although they are not the same), in the sense that it contains the feature of private and public blockchain. The major difference between the two is that the verification of transactions and validation of blocks in a specific consortium blockchain are done by nodes from a different consortium blockchain.
In this type of blockchain, the nodes that are connected to the blockchain can only initiate a transaction and also receive from other nodes, but for a block or a transaction to be verified, the help of nodes from a different consortium blockchain (or consortium promoter) is required.
Advantages of Consortium Blockchain
a). Fast and Secured Network
Just like the hybrid blockchain, the consortium blockchain is fast and secured. Since the blockchain prevents non-authorized nodes to access the blockchain, the network is never congested. This allows verification of transactions to be carried out very fast. In terms of security, all information about a block and several transactions that makes it up are stored in all the connected nodes. Thus, the data is safe at all times.
b). Connectivity to Multiple Blockchains
The consortium blockchain allows certain nodes that are connected to another blockchain to access and validate blocks in its blockchain.
Disadvantages of Consortium Blockchain
a). Not Truly Decentralized
Consortium Blockchain has the access restriction clause similar to that of private and hybrid blockchains. Only few nodes are granted access to connect to the network. Thus we can't say that the blockchain us fully decentralized
Question 2: WHAT ARE THE BENEFITS OF BLOCKCHAIN?
Below are some of the benefits of the blockchain technology.
1. Data Decentralization
In blockchain technology, transaction and block details are distributed and stored in all nodes that are connected to the blockchain. Every one who is connected to the blockchain can access the blockchain's Data. Data decentralization in blockchain is one of the most notable benefits of decentralized blockchain as it provides the blockchain with a level of security and transparency.
2. Reduced Cost of transaction
The cost of transacting internationally across borders is cheaper when done using cryptocurrencies than using fiats. This is because the cryptocurrency world is international and not limited to specific region. Thus, the same amount of BTC can be sent to different nations across continents at the same rate without the extra charges common with transferring money through bank.
3. Trustworthy
Blockchain is a trustworthy system. Although the users who interact in the network are anonymous and none really knows the other, the system is design in such a way that every user is assures of a safe transfer and validation of blocks.
4. Security
The blockchain technology is a highly secured system, thus, it is not surprising that several sectors are adopting it. The security of the blockchain technology can be attributed to its decentralized nature and it's immutability. Also, its use of cryptographic functions and encryption to generate hash for data makes the system more secured.
5. Immutability
Another benefit of the blockchain is its immutability. Once a data stored in the Blockchain, it cannot be removed or changed. This is because both dates and time stamps are added to the data, and every attempt to change it creates a new block altogether. This is one of the reasons why the blockchain is considered to be very secured.
Question 3: EXPLAIN BLOCKCHAIN DISTRIBUTED LEDGER
Blockchain Distributed Ledger
The Blockchain Distributed Ledger is the system by which all the data and transactions within blocks are distributed across to all the authorized nodes that are connected to the blockchain. The major difference between the centralized system and the decentralized is that a decentralized system uses a distributed ledger while a centralized system stores all information in a database.
Unlike the centralized system where all information are stored in a storage
/database, the blockchain distributed ledger makes sure that a copy of all transaction and block detail are distributed across connecting nodes.
Properties of Blockchain Distributed Ledger
Below are some of the properties of a blockchain:
a). Distribution
The distributed ledger makes sure that every node has a copy of its ledger. Also, once a new block is validated, a copy of the block is sent immediately to all nodes connected to the blockchain. This way the block chain is transparent and secured at all times.
b). Security using cryptographic function.
All data in the distributed ledger are secured using the hash function. Since the original Data cannot be regenerated back from the hash value, all data in the ledger are safe at all times.
c). Immutability
Once a data is stored in a distributed Ledger, it cannot be removed nor changed, as each time a block or data is saved in a distributed Ledger, a time and date stamp is added to it for easy referencing.
d). Unanimous and Anonymity
The unanimous nature of the blockchain distributed ledger makes it possible for all nodes the accept a validated block regardless of which of the nodes validates it.
Also, the anonymous nature of the blockchain distributed ledger provides security to the users by keeping their nodes and Identity hidden from other users.
Question 4: WHAT IS BLOCKCHAIN DOUBLE SPENDING AND HOW BITCOIN HANDLES THIS PROBLEM?
Blockchain Double Spending is said to have occurred if the same specific crypto amount from a user is used to perform several transactions in the blockchain. To better explain this, assuming a user wants to send 20 ADA to another usee, a double spending occurs when he sends 20 ADA to the receiver, and the receiver receives it, yet him (the sender) wasn't debited 20 ADA from his wallet. Then using the same 20 ADA he can Still carry out another successful transaction in the blockchain.
Whenever this occurs in a blockchain, it means that the blockchain has been attacked. Most times the culprits are both the sender and the receiver. This happens when the details of a certain transaction is rebrocasted in a blockchain, and due to the fact the culprits hold more than 51% validation power, they validate the transaction although they know filly well the transaction is false.
We have various types of blockchain double-spending, Some are:
a). Race Attack:
Race Attack double-spending occurs in a blockchain when a con-man carries out several transactions using the same amount of crypto with the hope of spending it before the transaction is confirmed. This type of double spending can only be successful if the recipient mistakenly accepts the transaction without it being confirmed.
b).Finney Attack:
Finney Attack double-spending occurs in a blockchain when a miner creates a fake transaction using the details obtained from a different block. This type of double spending can only be successful if the recipient mistakenly accepts the transaction without it being confirmed.
c). Vector 76 Attack:
Vector 76 Attack double spending is a type of double-spending which occurs in a blockchain when a group of hacker generate and send fake crypto assets as payment to other users in the blockchain using a software. Since the blockchain corrects itself, when the blockchain verifies the cryptocurrency sent to the receiver and the maths doesn't add up, the payment is automatically disappears from the recievers wallet. It more or less like collecting counterfeit money as payment for service delivered.
The Bitcoin Blockchain handles the problems of double spending through the use of confirmation of transactions by miners and distributed ledger technology. Any transaction that has not been confirmed by validators are not included into the block. Thus, a receiver will only receive the payment sent by the sender after the transaction has been verified, confirmed and added to the blockchains distributed ledger.
If a hacker launches any of the three double spending attack on the Bitcoin Blockchain, what the blockchain does is to removed the unconfirmed transaction from the blockchain while the confirmed one is sent to the receiver, and then added to the distributed ledger. Once a transaction is added to the distributed ledger, it cannot be reversed.
Question 5: PRACTICAL + THEORY, VISIT BLOCKCHAIN DEMO AND CHECK SECTION BLOCKCHAIN, THEN EXPLAIN IN DETAIL HOW BLOCKS HASHES WORK IN BLOCKCHAIN, WHAT WILL HAPPEN WHEN ANY MIDDLE OF THE BLOCK GETS CHANGED, TRY TO GIVE SCREENSHOT FOR EACH POSSIBLE DETAILS.
The blockchain uses hashing Function to encrypt details of the data and transactions stored in a block. I will be using Block Demo to explain how hash works.
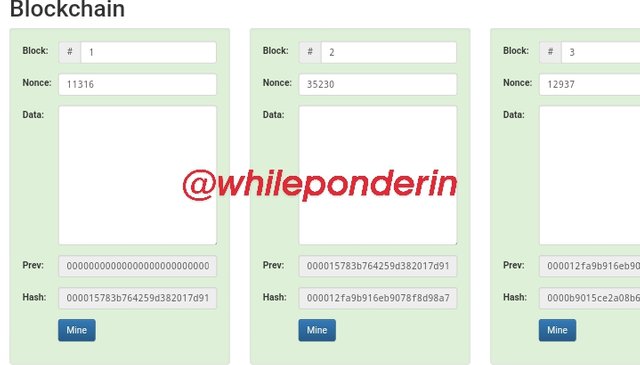
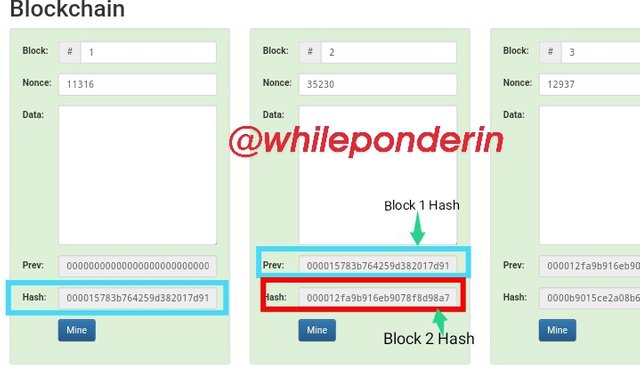
The screenshots above shows a blockchain structure which consists of only five (5) blocks. In each of these blocks, you will notice that they have a block number, a hash and a nonce. Each succeeding block is linked to the previous one (and the blockchain) by the addition of the hash of the previous block into the succeeding block.
From screenshot above, you can see the details of two blocks.The hash of block one (1) is: 000015783b764259d382017d91a36d206d0600e2cbb3567748f46a33fe9297cf.
Since it's the first block (or the Genesis Block) it doesn't have a previous block. Thus under previous we have: 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Block 2
Block 2 has a previous block (i.e block 1). In other to link block two to block one, the hash of block 1 is added as block 2's previous hash:
000015783b764259d382017d91a36d206d0600e2cbb3567748f46a33fe9297cf.
The hash of block 2 is given as:
000012fa9b916eb9078f8d98a7864e697ae83ed54f5146bd84452cdafd043c19.
The previous hash and the hash signifies that in the blockchain, block 2 is linked directly to block 1.
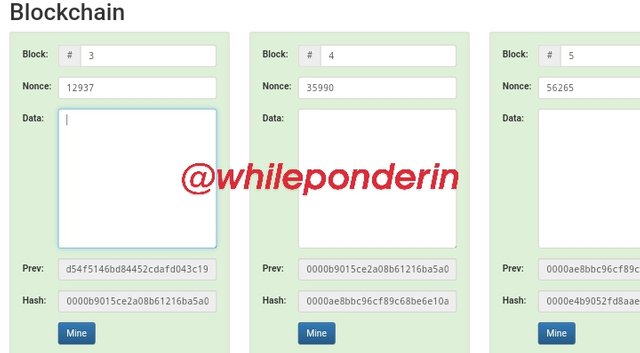
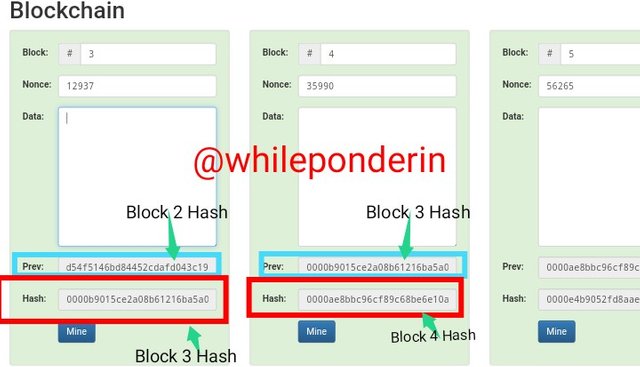
Block 3
In the same manner, Block 3 has a previous block (i.e block 2). In other to link block 3 to block 2, the hash of block 2 is added as block 3's previous hash:000012fa9b916eb9078f8d98a7864e697ae83ed54f5146bd84452cdafd043c19
The hash of block 3 is given as:0000b9015ce2a08b61216ba5a0778545bf4ddd7ceb7bbd85dd8062b29a9140bf
The previous hash and the hash signifies that in the blockchain, block 3 is linked directly to block 2.
The same logic applies for Block 4 and 5, where the previous hash for Block 4 is the hash of Block 3 and the previous hash of Block 5 is the hash of block 4.
Looking at the Blockchain used in the example above, you will notice its blocks has no data stored in them. When a data is inserted into any of the Block, the Block automatically generates a new hash. Since this hash is totally different from the formal one, the system will request that the whole blockchain be re-mined.
Assuming we input the data "steemit crypto academy season 3 week 6" into Block 1 and "stream4u" into block 2 of the demo Blockchain we will notice that the values of the nonce and hash of the entire blockchain changes.
Mining involves the validation of blocks in a blockchain with the aid of high-powered computers. Validation of block consist of calculating the nonce value of the block. Once the correct nonce has been obtained, the block is considered to be validated and therefore added to the blockchain. All valid blocks in a blockchain usually have the same laters in the beginning. For instance, in the Blockchain Demo, all valid block hash begins with 0000, then followed by other values.
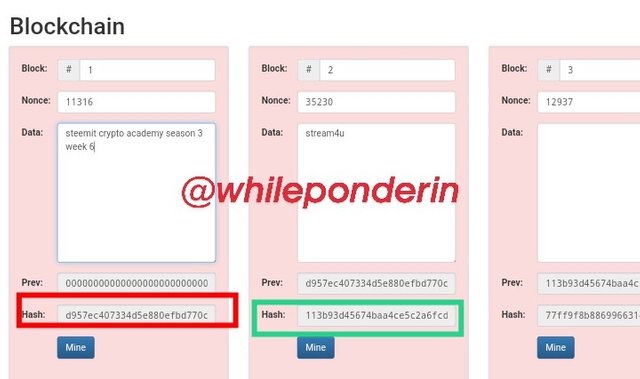
When I input the data "steemit crypto academy season 3 week 6" into Block 1 and "stream4u" into block 2 of the demo Blockchain, I noticed that although there was a change in the value of their hashes, the color of the blocks changed to red. The reason is that the hashes didn't start with "0000" implying that the block wasn't valid.
For instance, block 1 has a nonce of 11316 and hash:
d957ec407334d5e880efbd770c5a8c418d96665da385cc090055df83b0dba916
Block 2 has a nonce of 35230 and hash: 113b93d45674baa4ce5c2a6fcd8731914fb2c3120acf8677c3fe9015942dc311
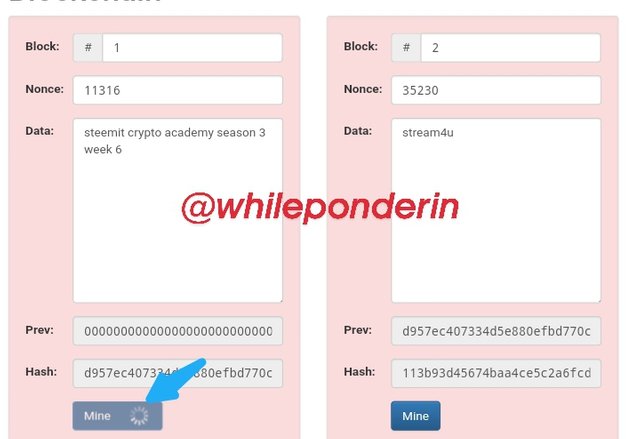
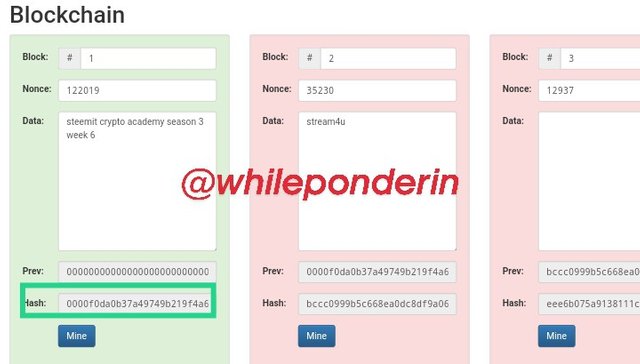
When I tried to mine block 1 by clicking on "Mine", its nonce value changed to 122019 and it's hash to:
0000f0da0b37a49749b219f4a690fe642a7796f4c53bd9c2012f1c32e9d4d5c3
Since it started with 0000, the color of the block changed to green as it was accepted. So I tried to mine block 2.
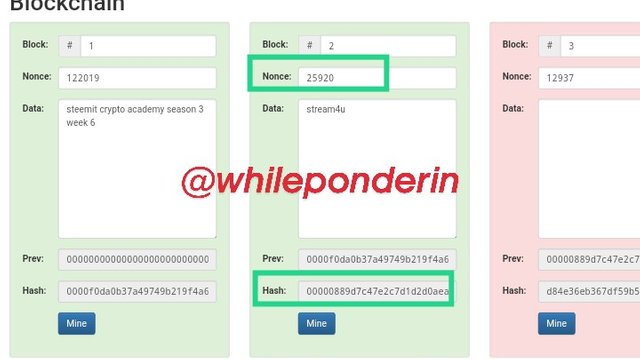
When I tried to mine block 2, it's nonce value changed to 25920 and it's hash to:
00000889d7c47e2c7d1d2d0aeabbabbaa4685237527e98c5d38d874532af3d75
Since it started with 0000, the color of the block changed to green as it was accepted
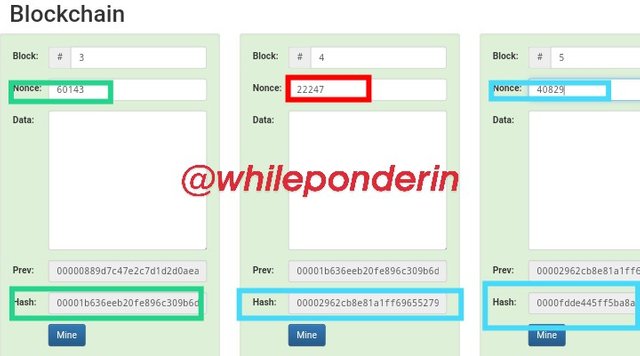
I did the same for Block 3,4 and 5 respectively and obtained;
Block 3:
noice= 60143 00001b636eeb20fe896c309b6d9ec90c67e6a100b5123c3a97f4f14f61754636
Block 4:
noice= 22247
00002962cb8e81a1ff69655279ed250c0110c9ffbb93d74a3d34b37ecad12708
Block 5:
noice= 40829
0000fdde445ff5ba8a44f2e5877f30b19e43536701fdc6a2cd6300cedb844995
Each time a valid Hash for a block is created, the color of the block changes from Red to Green, as noticed above.
Question 6: What Is Race Attack in blockchain? OR What Is Finney Attack in blockchain? OR What Is Vector76 Attack in blockchain?
Race Attack double-spending occurs in a blockchain when a con-man carries out several transactions using the same amount of crypto with the hope of spending it before the transaction is confirmed. Normally, for this to work, the con-man sends the same crypto using different nodes (or devices) to several users in the same blockchain. This is done so fast (thus the name, Race Attack) with the aim of using that same token to buy a lot of asset before the ledger corrects itself.
This type of double spending can only be successful if the recipient mistakenly accepts the transaction without it being confirmed. As the blockchain before confirming a transaction will first cross check its ledger, it will validate only one of the transaction, while the rest will be invalidated. Thus, it's advisable to wait for the transaction to be confirmed first before accepting it.
Example, if a con-man who has only 0.3 BTC in his wallet sends the 0.3 BTC to 5 individuals in the blockchain (using different nodes) as payment for an item (goods or services). If any of the sellers releases the item when the transaction has not been confirmed yet by the miners, he will lose his item without getting any payment in return, as the miners will only validate one of the five 0.3 BTC transaction while the remaining 4 will be canceled, and if the seller is unlikely it mightly likely not be his that will be confirmed.
Question 7: LIMITATIONS/DISADVANTAGES OF BLOCKCHAIN
Although the blockchain has several advantages, it has some disadvantages too. Some of them are:
1. Scalability:
One of the biggest problems the Blockchain faces is scalability. Due to the unlimited access it offers the public more nodes are joining the blockchain network daily. This increasing number of nodes causes congestion in the blockchain making the whole network very slow.
2. Cost of Maintenance and Mining
Due to the increasing number of users in the blockchain, it is very expensive to maintain it. This is because the only way to reduce the congestion in the network that is caused by the high number of users in the blockchain is by installing devices that allows for higher network bandwidth.
In addition to this, mining in a blockchain is expensive as it requires high-powered computers with high hash rates. These computers consumes much electricity leading to high electricity cost. The high electricity cost in turn results to high transaction fees.
3. Hacking Problems.
Since the everyone in the blockchain has an access to it and all the information related to it, it is usually attacked by Hackers.
4. Irreversibility
Any transaction confirmed can never be reversed back. If a user mistakenly sends his cryptocurrency to the wrong wallet address, the asset is gone forever.
The Blockchain is the foundation of cryptocurrency. The success that we see Cryptocurrency experience today is due to how efficient the Blockchain is. It's decentralized nature, it's immutability, and data storing using distributed ledger makes it so secured that a user can sleep comfortably without worrying about losing his asset due to a market crash or loss of data.
As day say, nothing in this world is completely perfect. Blockchain system has some loop holes and some hackers are devicing new techniques to exploit them. Therefore it's advisable to make sure that you wait for miners to confirm a transaction, and it's block added to the blockchain before accepting the transaction.
Thank you professor @stream4u for this amazing lesson.

Hi @whileponderin
Thank you for joining The Steemit Crypto Academy Courses and participated in the Homework Task.
Total | 10/10
Your Homework Task verification has been done by @Stream4u, hope you have enjoyed and learned something new.
Thank You.

@stream4u
Crypto Professors : Steemit Crypto Academy
#affable
Thank you so much professor @stream4u. I learnt a lot from your lesson