About to explode in a supernova
About to explode in a supernova

Image created by me in playgroundai View of Betterheus if it were our sun
Betelgeuse is barely 8 million years old or so, in cosmic terms it's the blink of an eye, hominids were already walking on two feet when Betelgeuse began to glow in the sky.
Souce
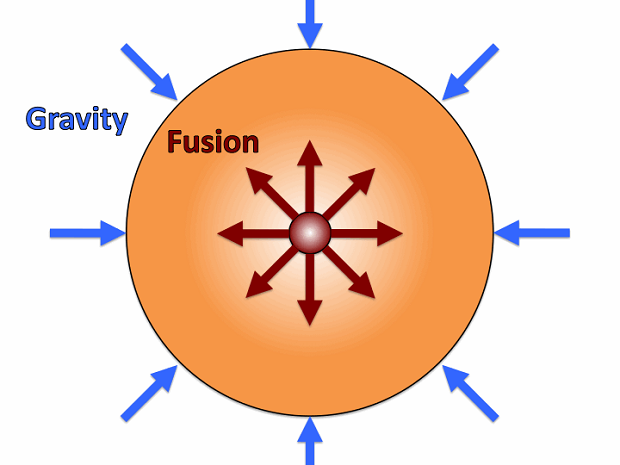
The gravity of a star is immense and it is a force that pulls all its material towards the core, but the heat and energy released by the powerful fusion reactions inside it pushes outwards, this is called hydrostatic equilibrium, gravity it wants the star to collapse, but the outward-pushing nuclear fusion reactions prevent it from doing so.
Souce
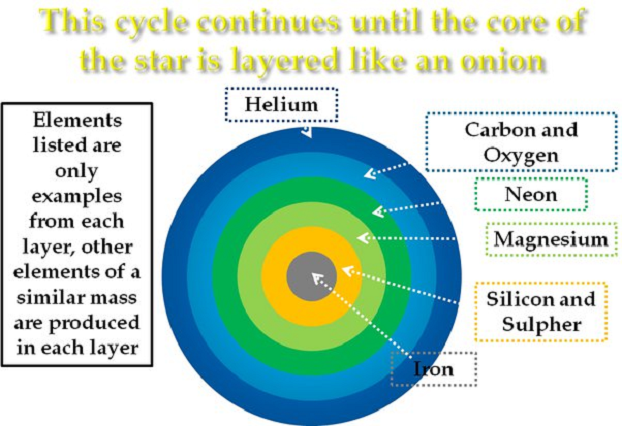
The fusion reactions are creating increasingly heavier elements that are accommodating like the layers of an onion, carbon, oxygen, silicon and iron iron can no longer be fused into a heavier element, so the energy of the reactions of fusion that was pushing outward decreases the hydrostatic balance is broken and the core collapses under the weight of the outer layers, gravity wins over fusion, in half a second, this is surprising in half a second the iron core that is the size of our moon is compressed to a volume 30 times smaller in half a second.
Souce
The star in the sky would look exactly the same but our neutrino detectors, which are very isolated places, will suddenly detect a wave of neutrinos coming in the direction of the star warning us that it is about to explode, the outer layers of the star accelerate its fall towards the core to a speed of one tenth the speed of light, when they collide core now made up of super packed neutrons the sudden deceleration creates an outward shock wave but is stopped by the weight of the rest of the material

Can you imagine seeing this in the sky. Imagen creada por mi en playgroundai
Gravitational waves propagate at the speed of light, like neutrinos, so that would be the second signal we would detect hours or minutes before the explosion, the wobble begins to spin the neutron nucleus accelerating it until it rotates 10 times per second and this is the moment in which the star makes cabum.
Thank you for visiting my blog. If you like posts about #science, #planet, #politics, #rights #crypto, #traveling and discovering secrets and beauties of the #universe, feel free to Follow me as these are the topics I write about the most. Have a wonderful day and stay on this great platform :) :)
Interesting. According to the article you linked, What is Betelgeuse? Inside the Strange, Volatile Star,
But I also found A Stunning Revelation Could Mean Betelgeuse Is Set to Blow, which says:
Either way, it seems like the YouTube livestream might be a little premature. ;-)
It would be weird to see Orion without his shoulder.
That is correct, there is a lot of uncertainty; but it is possible that we will run with the luck that happens in our time and be able to see something so spectacular.