Basic electricity / Electicity Generators
Electricity is an energy, and all we do is transform mechanical energy (pedalling on a bicycle / waterfall from a waterfall) by means of a device (dynamo / turbine-generator) into electrical energy, or transform chemical energy (chemical compounds in a battery that react by transferring electrons from one pole to another) into electrical energy. There are also other electrical power generation systems such as: solar energy through photovoltaic panels, wind energy through wind turbines among other forms. In this section we are going to see some electric power generation processes. In this way we are making progress in learning about basic electricity.

The intention is to "expel" the electrons from the orbits around the nucleus of an atom. To expel these electrons requires some energy, and 6 kinds of energy can be used:
a) Rubbing: Electricity obtained by rubbing two materials together.
b) Pressure: Electricity obtained by applying pressure to a crystal (e.g. quartz).
c) Heat: Electricity produced by heating materials.
d) Light: Electricity produced by light that falls on photosensitive materials.
e) Magnetism: Electricity produced by the movement of a magnet and a conductor.
f) Chemical: Electricity produced by the chemical reaction of certain materials.
In practice only two of them are used: chemistry (battery) and magnetism (alternator). The other forms of electricity production are used but in specific cases.
There are three common methods of generating electricity
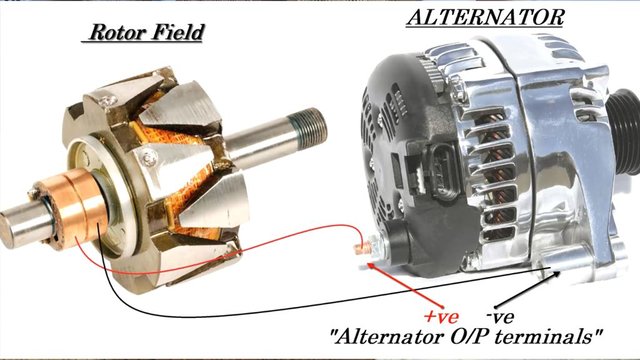
- Dynamo and alternator
These machines are composed of a rotating moving part, called a rotor and a fixed or static part called a stator. The rotor consists of copper wire coils that rotate with the shaft. The stator is a fixed magnet or electromagnet that surrounds the rotor.
By turning the machine shaft, the magnet creates a variable magnetic field on these coils by inducing a voltage at the coil terminals. This tension is removed from the machine by means of brushes or slip rings.
An inverse construction can also be found, i.e. the magnet on the shaft or rotor and the coil on the stator. This voltage generated in the machine can be direct or alternating, depending on the construction or assembly of the slip rings.
A dynamo is an electric generator formed by a coil of varnished copper wire coiled in a sweet iron core (not steel) that rotates within a magnetic field produced by a magnet placed around it and that when it rotates transforms the kinetic energy it receives into continuous electric energy.
An alternator is an electric generator similar to a dynamo but with better advantages, because it is more robust and durable. It produces alternating electric current by changing the polarity every half turn, so it must be rectified to convert it to DC, if it is to be used for certain applications that require it (for example, the alternator in the car takes advantage of the rotating movement of the engine to recharge the battery, but it must be rectified before it goes to the battery, which is DC). In hydroelectric power plants, giant alternators are also used to generate three-phase alternating current.
- Batteries
A battery is essentially a can full of chemicals that produce electrons. Chemical reactions are capable of producing electrons and this phenomenon is called electrochemical reaction, and the speed of electron production made by this reaction controls how many electrons can pass through the terminals.
Modern batteries use a variety of chemicals to perform their reactions. The chemistry of common batteries includes:
- Zinc batteries, also known as standard carbon batteries. Zinc-carbon chemistry is used in any AA, or related battery. The electrodes are made of zinc and carbon, with an acidic bond between them as an electrolyte.
- Alkaline batteries. The electrodes are zinc and manganese oxide with an alkaline electrolyte.
- Nickel-cadmium battery. It uses nickel hydroxide and cadmium electrodes with potassium hydroxide as the electrolyte. It's rechargeable.
- Nickel-metal hydride. Rechargeable. It quickly replaced nickel-cadmium because it does not suffer from the memory effect problems of the previous one.
- Lithium-ion. Rechargeable. Very good performance, used in the latest laptops and mobile phones.
- Silver-zinc. Used in aeronautical applications because the performance is good.
Normally batteries are grouped in series to obtain high voltages or in parallel for high currents.
Batteries have the ability to store electrical energy in the form of chemical energy, once stored the energy are electricity generators, this quality is used in the development of UPS uninterruptible power systems, are also used in combination with solar panels to obtain energy in those places where the power grid does not reach, among many other applications that I hope we can share in the future.

- Power plants, turbines and generators.
The electricity we consume is transported by a network of cables, which is produced basically by transforming kinetic energy into electrical energy. To do this, they use turbines and generators. Turbines are huge wheels with blades and gears that rotate over themselves again and again, driven by external energy. Generators are devices that transform the kinetic - motion - energy of a turbine into electrical energy (similar to a very large alternator).
There are two main types of electricity generating plants: hydroelectric and thermoelectric (steam-heated, gas-heated and combined-cycle).
Hydroelectric power plants: they use the force and speed of water to turn the turbines. There are two types: passing (which make use of the natural kinetic energy of river water) and reservoir (water is accumulated by dams, and then released under greater pressure to the power plant).
Thermoelectric plants: use heat to produce electricity. They heat a substance, which can be water or gas, which when heated comes out under pressure and move turbines and then the movement is transformed. As we have already seen, many energy sources can be used to power a thermoelectric plant: coal, oil, natural gas, solar, geothermal or nuclear energy, biomass, etc. These are the main ones used:
Steam-fired power stations. In this case, water is used in a closed cycle (it is always the same water). The water is heated in large boilers, using coal, gas, biomass, etc. as fuel. The turbine moves due to the pressure of the water vapour, and its kinetic energy is converted into electricity by a generator.
Gas-fired power stations. Instead of water, these plants use gas, which is heated using various fuels (gas, oil or diesel). The result of this combustion is that gases at high temperatures mobilize the turbine, and its kinetic energy is transformed into electricity. (There is one in Huelva, and it uses natural gas)
Combined cycle power plants. They use two turbines, one gas turbine and the other steam turbine. The heated gas mobilizes a turbine and then heats water, which is transformed into steam and mobilizes a second turbine.
Note: There are many types of power plants that have not been named and are currently in use. Ex.:
Wind power plant with wind turbines (the blades of the wind turbines act as a turbine)
Solar power plant with solar and photovoltaic panels (solar panels only heat water or other liquid, and photovoltaic panels collect the sun's radiation in the form of photons creating a potential difference in silicon or other plates, accumulating the electricity generated in batteries.
Nuclear power plant (which, from the fission ("rupture") of one isotope atom of Uranium or another, creates energy in the form of heat and "radiation", which heats water until it evaporates to move the turbine blades and this movement is used by the generator to generate electricity).
Others: Tidal power, Biomass, Geothermal.

link
In the next issue I will be describing a little bit the components used in the electrical circuits, these are the ones that allow us to control the eclectic energy for our own benefit.
REFERENCES
A. E. Fitzgerald, Electric Machinery Sixth Edition
Dr G.W. McLean, Generac Corporation

upvote for me please? https://steemit.com/news/@bible.com/2sysip