Java Graphical User Interface: ExceptionHandling With Eclipse
What Will I Learn?
- The user will learn the concept of ExceptionHandling in Java programming.
- The user will learn how to implement the concept of ExceptionHandling in a java program.
Requirements
- A fully functional computer system is required for this tutorial
- On the computer system, Java Development Kit (JDK) must be installed.
- Also the computer system must have Java IDE installed. Probably Eclipse.
Get JDK here
Get Eclipse IDE here
Difficulty
- Intermediate.
Tutorial Contents
Welcome to this tutorial guys. As we all know, this wouldn't be our first time meeting here as we discuss the concept of FlowLayout in the previous tutorial. Today, we are going to loo into another fresh topic which is ExceptionHandling in Java Programming.
ExceptionHandling
Exceptionhandling is one of the most powerful concepts in Java programming. This concept is the mechanism that handles runtime errors that disrupts the normal flow of Java program. Sometimes when running a program, wrong input or actions by the user (which weren't included or programmed in the application) may of course interrupts the normal flow of the program. To counter this, Java programming language ensures some robust and object oriented way to handle such error that may arise and this leads us to what we call ExceptionHandling in Java programming.
In this tutorial, we will be creating a Java application program that implements the concept of Exception handling in Java. As we progress in creating this program, I will be explaining each line of code so we all understand this concept pretty well and quick. Let's get on it.
We are going to create a class and name it teeking.java. We can name the class anything we link. Be it what the program is all about which is ExceptionHandling or any other preferred name. I enjoy using my name for classes and sometimes variables, kindly pardon me.
teeking.java Class
This class all our codes such as the components needed in this program, the main method and all other stuffs that we are going to use in creating this program. Take a look at this class below.
You see how simple that looks? That it is!
It is time we start writing the code and like I mentioned earlier, we are going to be doing this line after line for a perfect understanding of this concept.
The first thing we need to do as we start creating this program is to use the import statement to call in some classes from the Java Foundation Classes (JFC) which help us in using some components. In this program, we will be making use of the messageDialog and inputDialog boxes and in order to be able to use that, we need to import the JOptionPane from the swing class. To do that, we use the code below:
import javax.swing.JOptionPane;
The JOptionPane class pretty much allow us to use the Dialog boxes and with it, user can input from keyboard while using the program.
Secondly, we need to create the main method inside which our components and all other codes are going to be implemented. Let's do that below:
public static void main(String[] args) {
The main method is a very vital line of code that is responsible for the execution of Java program.
It's time to declare our primitive variables or better still the components needed in this program. Variable takes a value and a datatype.
int firstNum, secondNum;
double answer;
int x=1;
String input;
From what we can see, we have three variables of int datatype; firstNum, secondNum and x, a variable of double type and input of String type. We set an initial value of 1 to x, this I will explain later as the program progresses. These components will be used in the program.
Now we are going to add something to this program and that pretty much handles the concept of ExceptionHandling. This will counter the problem that is meant to arise when a user inputs something different from what is expected of him in the input prompt box that shows up. Imagine a scenario where we need to divide some certain numbers for example; firstNumand secondNum and a user inputs 10 and 0 for firstNumand secondNum respectively. Surely the program will shut down bringing some errors that the program can't handle such computation. You know how frustrating that could be if we actually build a very big program and within it such small stuff spoils the whole thing. we don't want that to be the case and so the concept of ExceptionHandling will counter that and help us fix such problem.
Now in order to handle exceptions, you need to use something called try and catch which are pretty much keywords in Java programming. try and catch means we are telling the program to try a set of codes and if you it encounters an error while running it, instead of shutting down the program, it is going to do some other stuff.
Let's go ahead and implement what we have just discussed in our program. It's pretty simple. We just need to type the following.
try{
What we did above has paved way for our main components as the try statement up there is awaiting some lines of codes that it needs to try just like the English meaning.
The next thing to do now is to add some codes that will prompt the user to enter a number (of his choice) and these codes will be withing the try statement. This will be used to implement this concept in the program. See how we do that below.
input = JOptionPane.showInputDialog(null, "enter a number");
firstNum = Integer.parseInt(input);
The input = JOptionPane.showInputDialog(null, "enter a number"); line prompt the user to number with the String texts "enter a number". The number that's entered by the user is then stored as the value for the variable firstNum which implies the second integer number and hence could be used anytime within the program.
This is repeated again and whatever the user entered the next time is stored as the secondNum which means second integer number.
input = JOptionPane.showInputDialog(null, "enter another number");
secondNum = Integer.parseInt(input);
Like I mentioned above, whatever the user input this time is stored as the second number.
Now that we have acquired our variables, the next thing we need to do is to computerise our answer variable. This variable is linked to the other two variables; firstNum and secondNum and its value is dependent of what the user entered when he was prompt to. The following lines of code will help you in understanding this.
answer = firstNum/secondNum;
That's pretty easy, right? the variable answer is declared to be firstNum divided by the secondNum. I believe that's just an easy stuff we can all understand easily.
The next thing for us to do is to display our program's computation result through a window. To do this, we make use of the JOptionPane statement. See how we do that below.
JOptionPane.showMessageDialog(null, "Your anser is " + answer);
All those components are placed withing our try statement and now we need to add the next keyword, catch (Exception) which pretty much handles what happens when the user do a wrong thing (ie input the wrong variable) while running our program. Let's do that now.
catch(Exception e){
JOptionPane.showMessageDialog(null, "You aren't permitted to do that");
}
You see that? That pretty much tells the user; "Hey buddy, you aren't permitted to do that" or something like that depending on your String you want to be displayed.
Okay, let me tell you something new. How about if we want to keep prompting the user to input the correct variable or number? Like I mean, he can't go anywhere without ensuring that he input the correct numbers in the input prompt boxes? Then we can just make use of the while statement to get this done.
This is how we do that, right from we will go back to where we typed the try statement up above and just a line before it, we will type the while statement. I don't want us to get confused with this, so I will paste the entire codes within the do while and let's see how that looks.
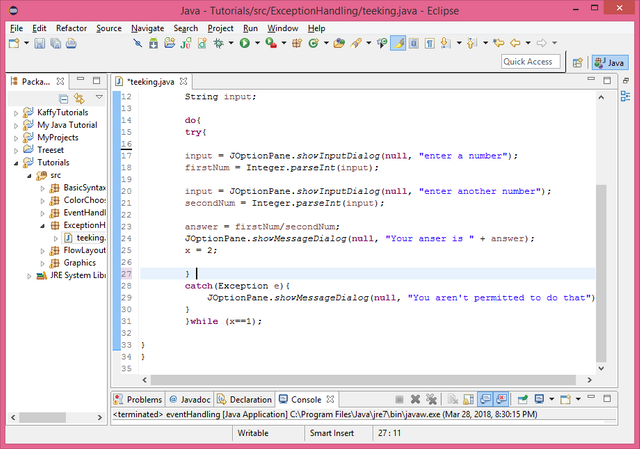
do{
try{
input = JOptionPane.showInputDialog(null, "enter a number");
firstNum = Integer.parseInt(input);
input = JOptionPane.showInputDialog(null, "enter another number");
secondNum = Integer.parseInt(input);
answer = firstNum/secondNum;
JOptionPane.showMessageDialog(null, "Your anser is " + answer);
x = 2;
}
catch(Exception e){
JOptionPane.showMessageDialog(null, "You aren't permitted to do that");
}
}while (x==1);
You see those lines of code above, those pretty much ensure that the user inputs the correct or better still expected stuffs when the input dialog boxes show up while running the program.
Check below the full code for teeking.java class.
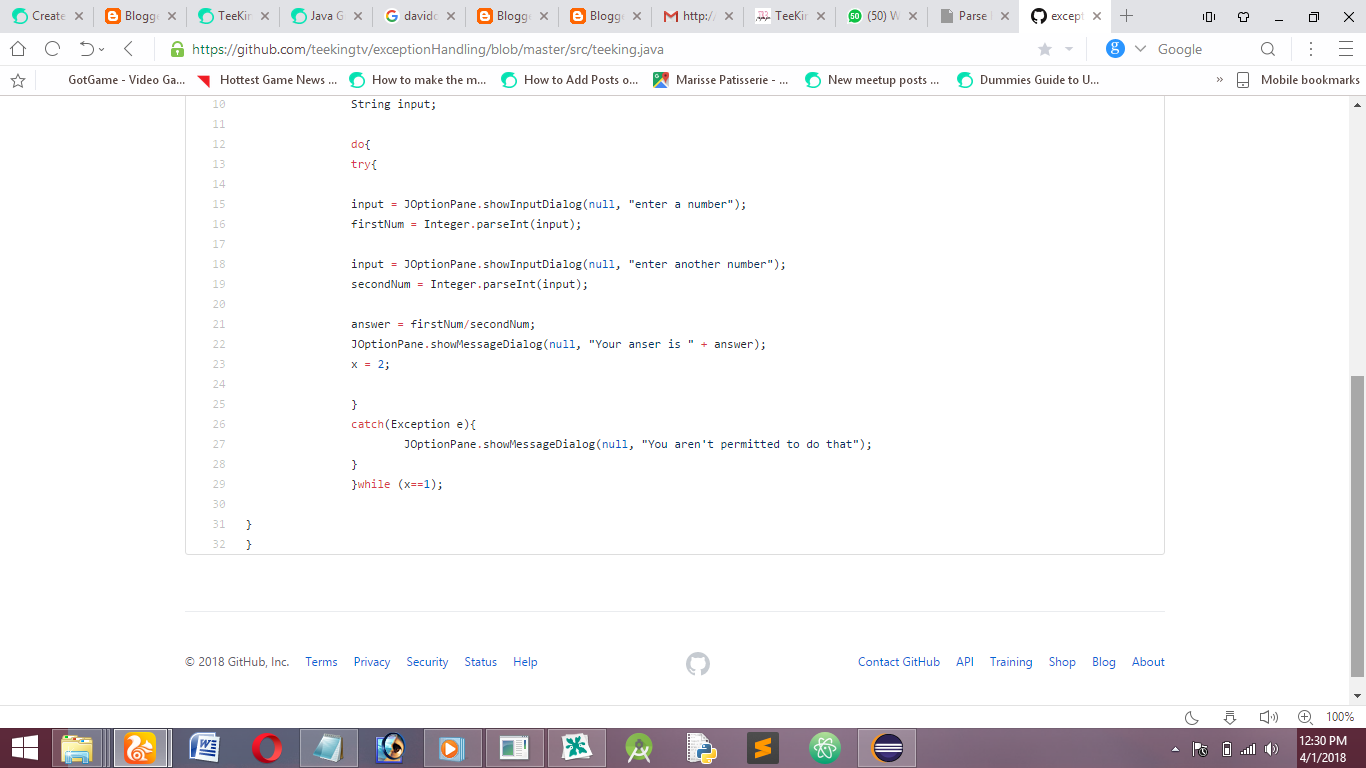
teeking.java Full Code
import javax.swing.JOptionPane;
public class teeking {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int firstNum, secondNum;
double answer;
int x=1;
String input;
do{
try{
input = JOptionPane.showInputDialog(null, "enter a number");
firstNum = Integer.parseInt(input);
input = JOptionPane.showInputDialog(null, "enter another number");
secondNum = Integer.parseInt(input);
answer = firstNum/secondNum;
JOptionPane.showMessageDialog(null, "Your anser is " + answer);
x = 2;
}
catch(Exception e){
JOptionPane.showMessageDialog(null, "You aren't permitted to do that");
}
}while (x==1);
}
}
That is that about our program.
This is not a complex program but as it looks, it treats and teach us the concept of ExceptionHandling which is a very important concept in Java programming.
Output
Now, it's time we run our program and see how it implements the concept of exceptionHandlingin Java programming.
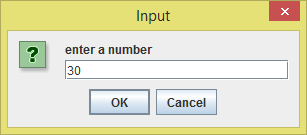
When the program is run, the first thing we see is a dialog box that prompts the user to input the first integer number. As the user inputs the first number, then he's required to click on
Okay.
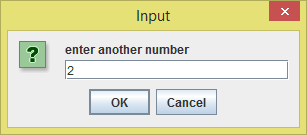
The second dialog box then shows up waiting for the user to input another number. You can I entered
2 here.
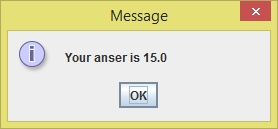
Since what we input are considered valid, things worked pretty cool. Now let's how it turns out when unexpected stuffs are inputted into our dialog boxed.
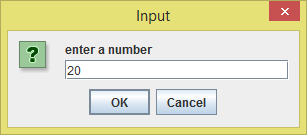
I just entered 20 as the first number
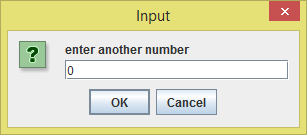
And I entered 0 as the second number. Let's see what happens.
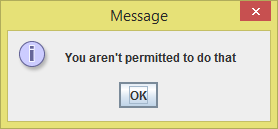
You can see what it brings. It's telling us that we aren't permitted to do that.
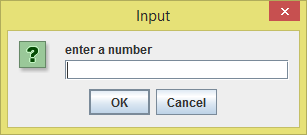
And hence the input dialog comes up again and of course it will continue to show until the user input the right stuffs in there.
This concept, as simple as it looks is a very vital concept in Java programming. This is used in big programs as it ensure free flow of programs.
Source Code On GitHub
The source code for this program is available on my GitHub. You can check it out.
Curriculum
- Java Graphical User Interface With JFrame: FlowLayout With Eclipse
- Java Graphical User Interface With JFrame: JColorChooser With Eclipse
- Java Graphical User Interface With JFrame: Drawing Graphics With Eclipse
- Java Graphical User Interface With JFrame: Event Handling And Action Listening
Posted on Utopian.io - Rewarding Open Source Contributors
Thank you for your contribution, yet it cannot be approved because it does not follow the Utopian Rules.
While I liked the flow of your tutorial and its simplicity, yet there are many key aspects of exception handling you did not cover and few reasons why it cannot be accepted:
For one, your error message to the user is very basic, you did not rely at all at the response from the exception handling error to propagate the message.
Your input prompt does not tell the user what will happen with the numbers he is sending, so he can easily get stuck in an infinite loop.
You did not mention anything about the different classes available for exception handling (IOException, FileNotFoundException,...)
You should have at least mentioned something about the "finally" block too.
There are many online tutorials that tackle this in a much better way, so unfortunately your tutorial does not have an added value. You can check the first few results on google (some examples: https://stackify.com/specify-handle-exceptions-java/ and https://www.tutorialspoint.com/java/java_exceptions.htm)
You can contact us on Discord.
[utopian-moderator]
Hey @mcfarhat, I just gave you a tip for your hard work on moderation. Upvote this comment to support the utopian moderators and increase your future rewards!
I have read and understood your points and I believe they will help me do better in my next tutorials.
However, if I am allowed to explain some stuffs...
The error message to the user may not be well written reason being that this tutorial is in intermediary level. I believe the point of this tutorial to be about the key aspect or concept it tackles and not how the program looks. The reader already know how he can direct his error messages and can choose any method to pass the error message to the user. The point isn't how the program looks but to introduce this concept to the Java programming learner who is reading this.
Same with the input prompt. Of course the reader could use any form of input. Like I emphasized in the tutorial, this regardless of how basic it looks is the basis to
exceptionHandling.*I might not have mentioned the different classes of
exceptionHandlingavailable in Java specifically, but this program pretty much tells the reader what this is all about.I ensure my tutorials seem so basic for quick understanding of each concept I tutor. This is a very clear difference between my tutorials and any other form one might have found on the internet.
I try to make learning Java programming look as simple as it can ever be.
Hoping to hear from you soon, @mcfarhat
Hello! I find your post valuable for the wafrica community! Thanks for the great post! @wafrica is now following you! ALWAYs follow @wafrica and use the wafrica tag!