The Modular Blockchain Trilemma and Its Solution
Assalamu Alaikum
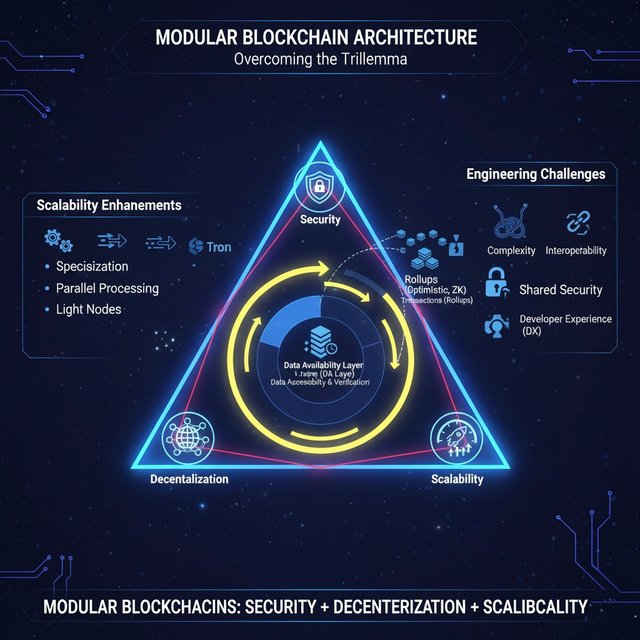
The modular blockchain trilemma is a fundamental challenge in blockchain technology that states that a traditional (monolithic) blockchain cannot achieve the highest levels of security, scalability, and decentralization at the same time. Typically, any blockchain design prioritizes two of these three and compromises the third.
Security : Keeping transactions and data on the blockchain secure and immutable.
Decentralization : Control of the network is not in the hands of a single entity or small group.
Scalability : Increasing the transaction processing capacity of the network, especially as the number of users increases. The modular blockchain concept is a new approach to overcoming this trilemma.
A modular blockchain differs from a traditional monolithic blockchain. In monolithic blockchains (e.g. Bitcoin), all core functions—transaction processing, data storage, and consensus—are performed in a single layer. In contrast, modular blockchains divide these functions into different, specialized layers or modules.
Function : This layer is where transactions are actually processed and smart contracts are executed. It updates the state of the blockchain.
Role in scalability : This layer is separated from the main chain and executed off-chain. Rollups (e.g. Optimistic Rollups and ZK-Rollups) are the main execution layer solutions, which can process thousands of transactions in batches and post their proofs to the main chain (base layer). This reduces the pressure on the main chain and increases scalability many times over.
Function : This layer ensures that all transaction data is easily accessible and available for verification by all participants in the network.
Role in Scalability : When rollups submit their transaction data to the base layer, the DA layer ensures that that data is available to everyone so that if someone wants to provide fraud proof or reconstruct the state of the network, they can do so. Using innovative techniques like Data Availability Sampling (DAS), light nodes can ensure data availability with high confidence without having to download the entire block, which helps increase block size and throughput. Projects like Celestia are working on this layer.
Function : This layer manages the process of reaching agreements within the network, ensuring that the order of transactions and the state of the blockchain are valid for everyone. It ensures the core security of the network.
Role in scalability : In modular architectures, the consensus layer combines with the data availability layer to ensure data order and security. By separating execution (e.g., rollup) and data availability functions, the consensus layer can focus more on its primary task—maintaining security and decentralization—and thus minimize the tradeoffs required for scalability.
Modular blockchains provide the following benefits to increase scalability by solving the trilemma :
Specialization : Each layer is optimized for a specific task. The execution layer focuses on increasing transaction speed, while the consensus layer focuses on data availability and security.
Parallel Processing : Different execution layers (multiple rollups) can process transactions simultaneously, which significantly increases the total throughput of the network.
Light Nodes : New methods in the data availability layer allow light nodes to verify the authenticity of transactions without having to download the entire block. This makes it easier to participate in the network, which helps increase decentralization.
Modular blockchains have some significant engineering challenges :
Complexity : Modular architectures are much more complex than monolithic chains. Managing the movement of data and proof between different layers and creating a cohesive ecosystem is a major challenge.
Interoperability and Composability : Ensuring smooth communication and composability (i.e., the ability of dApps to easily interact with each other) between different modules or chains can be difficult.
Shared Security Implementation : Advanced proof mechanisms (e.g., ZK-Proofs, Fraud Proofs) and bridge designs are needed to ensure that security is properly "shared" from the consensus layer to the execution layer.
Developer Experience (DX) : Understanding and using new modular stacks and tools is a steep learning curve for developers.
In essence, modular blockchain architecture effectively addresses the blockchain trilemma, as it preserves security and decentralization at the base layer and uses specialized off-chain layers for scalability. Today's discussion concludes here. I hope you've found it interesting. Please share your thoughts on today's topic. Prayers for everyone. May everyone be well. Amen.
Twitter
https://x.com/BokhtiarMr90788/status/1981006210259427708?t=WkUc7i-4HnUKONx1YkkjTQ&s=19
https://x.com/pussmemecoin/status/1980572506479292696?t=EcqFsODmJWhFnMl1IccQ3Q&s=19
https://x.com/BokhtiarMr90788/status/1981006573960155420?t=HGsA5h_lFvqIP4ofd_wvAA&s=19
https://coinmarketcap.com/community/post/369907358
It is a great article of The Modular Blockchain Trilemma and Its Solution.
This was a profound and highly organized post on the Modular Blockchain Trilemma, Wow @bokhtiar1444. I also enjoyed the way you divided the concept into well-defined parts execution, data availability, and consensus because it made it easy to follow even with the non-technical reader.
The section, in which you described how modular blockchains get layers apart to scale them without losing security and decentralization, impressed me. You made such an intricate topic so realistic.
I also like the fact that you have mentioned about the engineering problems, the fact that you are honest makes your post even more valuable to learners and blockchain fans.
This is an excellent work by @bokhtiar1444. It makes me remember that the true innovation is to find a solution to difficult problems using intelligent design and collaboration.