The Human Eye--- Refraction and Refractive Errors with Eye Health Safety Tips Included.
Hey people, its your favorite steem blogger @hrhmikelength, its been a while though, without further ado, let's go into today's business THE HUMAN EYE taking into prospect REFRACTION as it entails the basic unit operation the human eyes operate on.
Introduction
The human eye is a very delicate organ which reacts to light and pressure. It is also important to note that the human eye provides a 3-dimensional, moving object which are normally coloured in daylight. It is also of great interest to know that the human eye can differentiate between about 10 million colours and is possibly capable of detecting a single photon.
In as much as the eye play a vital role in humanity thereby placing in us a greater quest to understanding the eye and keeping it in perfect condition.
Let's talk REFRACTION as this showcase a basic principle on how the eye operates
What is Refraction?
Refraction is the bending of light as it passes through one object to another, here I will be considering the phenomenon natural application in the vital organ the eye, for more knowledge of the refraction phenomena visit here. Vision occurs when light rays are bent(refracted) as they pass through the cornea and the lens. The light is then focused on the retina, the retina converts the light rays into electric signals which serves as message that are sent to the brain through the optic nerves. The brain interpreted these messages into the images we see.
As light travels through different medium, the refractive phenomenon tends to occur simultaneously for example when light travels through water or lens its path is bent or refracted. In similar cases the human eye is composed of structures that possesses refractive properties similar to water and lenses.
Refraction in the eye thus occurs when light rays passes through the curved, clear front surface of the eye(cornea), lens, and also the internal fluids in the eye as they all posses refractive powers to varying degree.Sight Schematics
In a bid to understand how we see, the process of vision begins when light rays that are reflected off objects travel through the eyes optical system which are refracted and focused into a point of sharp focus(retina)
The retina is a specially evolved tissue which is lined at the back of the eye, where light sensitive cells(photoreceptor) capture the reflected images when exposed to light. These images are then transmitted to the brain for interpretation via the optic nerves.
- What are refractive errors?
Refractive errors simply stated means that the light is not bending properly when it passes through the lens of your eyes.
NOTE: Refractive errors are imperfections in the human eye optics that causes a dysfunction in the proper focusing of light, thereby causing blurred vision.
Refractive errors occurs primarily when the shape of the eye prevents light from focusing on the retina, The length of the eyeball(longer or shorter), changes in the shape of the cornea, or ageing of the lens.
Causes of refractive errors
The basic causes of refractive errors is highlighted thus:Eye length; If the eye is too long, light is focused before it reaches the retina, causing nearsightedness. If the eye is too short, light is not focused by the time it reaches the retina. This causes farsightedness or hyperopia.
Curvature of the cornea; If the cornea is not perfectly spherical, then the image is refracted or focused irregularly to create a condition called astigmatism. A person can be nearsighted or farsighted with or without astigmatism.
Curvature of the lens; If the lens is too steeply curved in relation to the length of the eye and the curvature of the cornea, this causes nearsightedness. If the lens is too flat, the result is farsightedness.
Types of refractive errors
The most common types of refractive errors are myopia, hyperopia, presbyopia, and astigmatism.
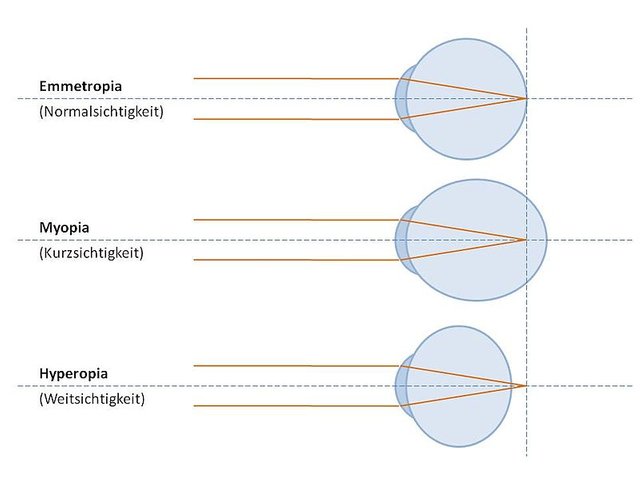 )
)- Myopia(nearsightedness) is the most common refractive error of the eye, its a condition where objects up close appear clearly, while objects far away appear blurry with myopia, light comes to focus in front of the retina instead of on the retina.
Hyperopia(farsightedness) is a common type of refractive error where distant objects may be seen more clearly than objects that are near. However, people experience Hyperopia differently. Some people may not notice any problem with their vision, especially when they are young. For people with significant Hyperopia, vision can be blurry for objects at any distance, near or far.
Prespyobia is an age-related condition in which the ability to focus up close becomes more difficult. As you age the crystalline lens within the eye becomes increasingly rigid causing loss of focus at near range. Presbyopia occurs in all people regardless of refractive error.
Astigmatism If you have Astigmatism your cornea is oval in shape rather than spherical causing visual distortion. This can occur in combination with long or short sightedness. In the case of astigmatism the eye does not focus light evenly onto the retina, the light sensitive tissue at the back of the eye and as such causes images to appear blurry and stretched out.
- Signs and symptoms of refractive errors
Blurred vision appears to be the most common symptoms of refractive errors. Other symptomsay include: - Blurred vision
- Double vision
- Haziness
- Glare or halos around bright lights.
- Squinting
- Headaches
- Eye strain.
- Diagnosis and treatment of refractive errors
In the possible occurrence of any of the signs and symptoms above the individual is advised to visit a medical centre or a certified opthalmologist who will perform a comprehensive dilated eye examination.
Also your eye care professional performs a test called refraction and this can be done with a computerized instrument (automated refraction) or with a mechanical instrument called a phoropter that allows your eye doctor to show you one lens at a time (manual refraction).
Often, an automated refraction will be performed by a member of the doctor's staff, and then the eye care practitioner will refine and verify the results with a manual refraction.
Your refraction may reveal that you have more than one type of refractive error. For example, your blurred vision may be due to both nearsighted and astigmatism.
Treatment
In the event that one is diagnosed with refractive errors of any sort, it can be corrected with contact lenses, surgery or eye glasses depending on the specificity of his refractive errors.
Eyeglasses are the easiest and safest method of correction. Contact lenses can provide a wider field of vision, howerever they are associated with a risk of infection.
Eyeglass lenses and contact lenses are fabricated with precise curves to refract light to the degree necessary to compensate for refractive errors and bring light to a sharp focus on the retina.
Refractive surgery permanently changes the shape of the cornea. Vision correction surgeries such as LASIK aim to correct refractive errors by changing the shape of the cornea, so that light rays are bent into a more accurate point of focus.Eye health and safety tips
- Eat healthy
- Using computers and smart phones for so long time continually may lead to dry eye, eye strain and blurred vision.
Apply 20/20/20 rule
Use anti-reflective spectacle lenses while using computers. - Use protective lens for sports, and protective googles when necessary.
- Avoid over exposure to UV rays as this could lead to cataract, macular degeneration and pterygia.
- Get your eyes examined by a professional routinely.
- Ocular infections could be viral, bacterial, chlamydial or fungal, see a specialist for diagnosis. Don't settle for over the counter medications.
- Quick medical intervention may save the eye after traumatic events. In cases of present of floaters and flashes may indicate underlying conditions.
- Avoid rubbing or pulling the objects out in the case of penetrating injuries. Go straight to the clinic.
- For chemical accidents, irrigate with extravagant amount of distilled water immediately, see eye specialist afterwards.
- Be safety conscious.
Remember with proper sight comes the proper appreciation of the cosmos we live in. Treat your eyes with all the care and attention it deserves.
References:
allaboutvision.com--- refractive errors and refractions
wikipedia.com--- the human eye
wikipedia.com---refraction
Refractive error facts

)