Beginning of astronomy
The first astronomers are still from the ice age. Already 30,000 years ago, our ancestors began to look at the sky. Why? Probably out of curiosity, because then in every place in the world you could admire the naturally clean and dark night sky.
Stonehenge in July 2007
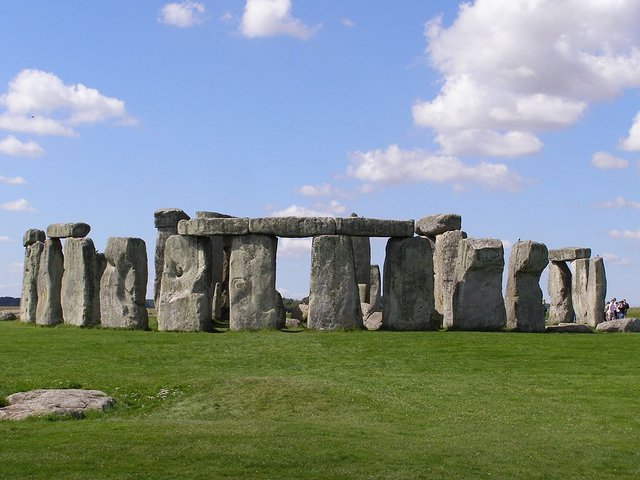

In France, a fragment of bone was found, covered with cuts corresponding to successive phases of the moon. Archaeologists estimate that it is over 30,000 years old, in other words from the ice age. In more recent times, buildings such as Stonehenge (photo above) began to emerge, which was created over 4,000 years ago. His task was to determine the direction of the sunrise during the equinoxes (the first day of spring or autumn). People living close to nature watched the sun go through the sky every day. They also observed changes related to the seasons. The movements of the Sun, moon and stars were then clock and calendar for mankind. Maybe it wasn't accurate information, but enough for the needs of hunters and gatherers. In addition to setting time, the sky has always been considered by people as the home of the gods. Often, the phenomena in the sky had their religious references.
Cuneiform inscriptions, Stela of Iddi-Sin, king of Simurrum

Astronomy has taken a step forward 10,000 years ago in Mesopotamia (current Iraqi area), where the first farmers' settlements appeared. They used signs in the sky to designate individual stages of plant cultivation. Figures of Star Lion, Bull and Scorpio appeared on the bas-reliefs in Mesopotamia about 3,000 BC. Above fragment of the plate with their notes. The first astronomers also noticed that the Sun and the Moon are moving among the sky belt, in which later the 12 zodiac constellations were named. The lane of the planet was also moving along the belt, considered deities, and there were eclipses, which aroused great fear and were considered the wrath of the gods.
The air god Shu, assisted by other gods, holds up Nut, the sky, as Geb, the earth, lies beneath
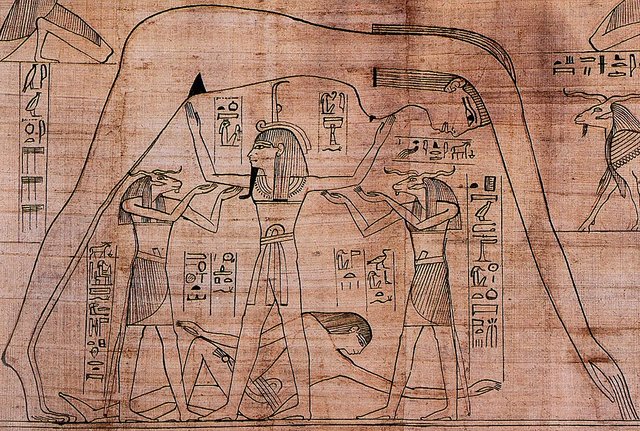
Other ancient civilizations have created their views and beliefs. In Egypt, people's lives followed the floods of the Nile that irrigated farmland. The priests there, observing the sky, came to the conclusion that these floods of the Nile preceded the east of the star Sirius just before the Sun. The sky was filled with Egyptian gods. Orion's constellation was Osiris, and the Milky Way became the goddess Nut. The sun of course also had its god - Ra. He was the creator of the world and the master of order in the universe.
A star map with a cylindrical projection. Su Song's star maps represent the oldest existent ones in printed form
Chinese astronomers carefully observed stars, planets, supernovae and comets. They created their stellar calendar about 1,300 BC. As in Mesopotamia and Egypt, there were also strong links between astronomy and astrology in China. The Chinese emperor was for the people link connecting the heavens with Earth. It was even required to predict the future from the astronomers there. At the time, they really showed great intelligence.In the photo above, the Chinese sky map from antiquity.
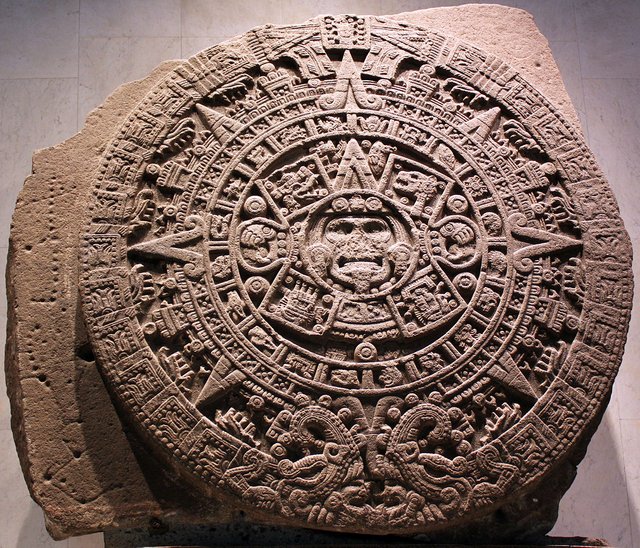
Sun Stone, at National Anthropology Museum in Mexico City, Mexico
In the New World the priests of the Aztecs and the Maya were also looking at the sky. Maya, inhabited southern Mexico from the third century BC to the ninth century AD. They followed the cycles of stars and planets, focusing on the planet Venus, who was a god of rain for them. The Aztecs also recognized Venus as their god Quetzalcoatl. They personified him with the figure of a serpent. When Venus disappeared and appeared for five of his cycles in 8 years, the Aztecs performed rituals and offered blood sacrifices to appease the deity. They also created the so-called Sun Stone visible in the photo above. This is an Aztec calendar.
Hawaiian navigators sailing multi-hulled canoe, c. 1781
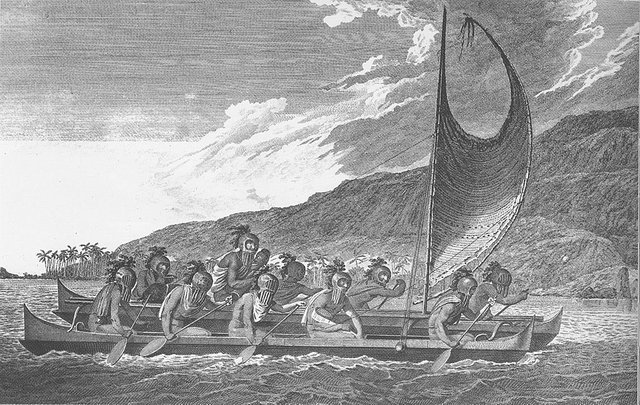

In the Pacific island cultures, the observation of the sky had a practical dimension. Knowledge of the sky was needed by navigators to orient themselves at sea. In equatorial areas, stars and planets rise and set at a large angle to the horizon. The bright facility was thus a safe reference point for maintaining the course at sea during the next few hours. Navigators used maps of the sky made of twigs or shells. As you can see, a lot happened before the telescope was discovered. I will bring you closer to the future of astronomy.
Greetings to lovers of Astronomy!
References:


This post has been voted on by the steemstem curation team and voting trail.
There is more to SteemSTEM than just writing posts, check here for some more tips on being a community member. You can also join our discord here to get to know the rest of the community!
What an uterly fascinating trip through the history of astronomy. Well done @astromaniac we often think that our ancestors were 'primitive'. Far from it they in fact had to be very ingenious to work out where they were without our modern conveniences. GPS etc.
Thank you! I will continue the history of astronomy in the next posts. I encourage you to follow my profile. Greetings!
Done. I'm always happy to follow good content creators. ;-)