Steemit Cryptoacademy Week 16 Homework Task Submitted To Professor @pelon53| The Hedera Hashgraph| By @bukkyi4u
Explain in detail the Gossip protocol, used in Hashgraph.
WHAT IS THE GOSSIP PROTOCOL USED IN HASHGRAPH?
created with Canva
A gossip protocol is a system of proceeding which uses the idea of how epidemics spread to disseminate or pass information on a peer-to-peer system or basis over a computer network. Normally, this process would work on a distributed system meaning that the same form of a ledger is stored by different computers at the same time. The most important use of this peer-to-peer system is to ensure that any data or information is passed across to every single node or user. Actually, the gossip protocol does not depend on a central server or system for this. Instead, the system depends on each member node to disseminate the information to every other node.
Severally, the gossip protocol has also been called an epidemic protocol. This is due to the fact that information is spread among members in the manner in which viruses are spread across biological ecosystems. It can, again, be conceptualized as a situation whereby office workers would sit idle and then spread rumours of events across. Gossip protocol constitutes an interesting area of study due to the fact that it forms a vital link in the system by which the Hashgraph described by professor @pelon53 achieves consensus.

HOW THE GOSSIP PROTOCOL WORKS
In practice, this gossip protocol consensus of the hashgraph simply means that a member node, like Jennifer, can choose another member node, like Francis at random and reveal every information she has at that moment to the selected node. After doing this with Francis, Jennifer would then select any other member node of choice and repeat the same process of revealing the information to it. Equally, Francis on his own randomly chooses any other node of his choice and reveals the same information to such a node. In turn, all the other nodes that have received the information repeat the same random process with any other node they may decide to choose. With this gossip system in place it means that once a member of the community becomes aware of an information, the same information spreads to every other member in a very fast and exponential manner. This will be done until every member node in the community becomes aware of the same information.
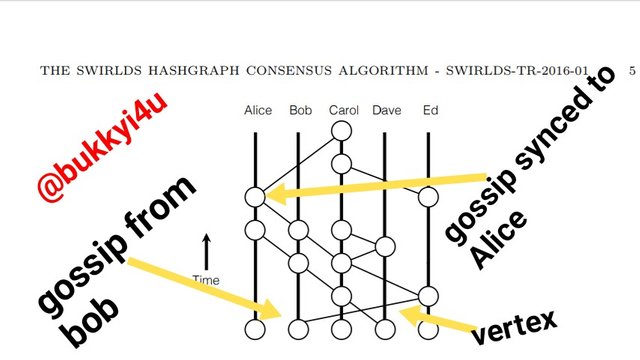
Screen from hedera whitepaper
The timeline of events of any single gossip protocol that occurs can always be represented in the manner of a directed graph as shown above. In the Alice column, every single vertex represents a gossip event that occurs. An example is as can be seen with the top event in the Alice column in which case Bob performs what is known as a gossip sync to Alice by revealing all the information that was privy to him to Alice. In that same vertex there are two edges which are downwards in nature. These two edges represent the immediately preceding gossip syncs that had been sent to Bob and Alice. It should be noted that the lower vertices represent gossip events that had occurred earlier. This is because in the graph time flows upwards.
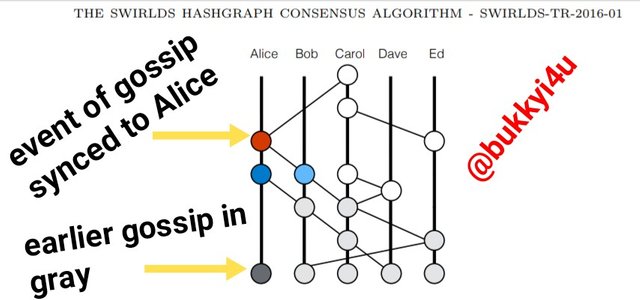
screen from hedera whitepaper
Actually, in the consensus of the Hashgraph this graph does not really exist in any stored in memory. However, it is understood as a data structure. The figure above gives an illustration for this data structure. A sequence of bytes, which represents a vertex (or event), is stored in the memory of the data structure. This sequence of bytes is usually signed by its originator. An example is the case in which a single event linked to Alice (represented in red) is used to connote the fact that Bob performed a gossip sync and revealed all the information he had to Alice. Actually, this gossip sync will be initiated and signed by Alice. It will be made to carry two other event hashes, namely:
- The last event linked to Alice
- The last event linked to Bob before the gossip sync was performed
With this red event a payload of any transaction that Alice may have claimed to perform could be represented. Also, it could carry the date and time or timestamp which Alice would claim for the transaction created at that moment and represented in the red event. The ancestors preceding that event (represented in gray) would normally not be contained within that event, instead they are usually determined by a set of hashes that are cryptographic in nature. This particular hashgraph serves the purpose of keeping the record of how members had communicated with one another.
Actually, this gossip protocol of the Hashgraph can be used to transmit just about any type of information. It can be used to reveal identities of other users or member nodes. It can be used to gossip about blocks in blockchain or any transaction. Generally, it can be used to gossip just about any information that is meant to be distributed. But then there is a special case. How about a situation where the protocol is meant to gossip about gossip? I mean how about if a hashgraph itself was to be gossip? Usually, this would occur in a situation whereby Bob performs a gossip to Alice and, in this case, decides to reveal the information of events he knew about which Alice did not know about.
The gossiping of the hashgraph itself has the power of putting so much information at the hands of members. Usually, information on a transaction which occurs on a payload could be quickly disseminated to Alice and would get to every other member who will also know the exact time it occurred. Interestingly, Alice would also know the exact time that Bob got to know about that information. Alice would also know the exact time that Carol got to know of the fact that even Bob himself equally knows about the transaction! Gossip about gossip! This sort of deep chain reasoning is activated when every member is given a copy of the particular hashgraph.

THE ORIGIN AND INTRODUCTION OF THE GOSSIP PROTOCOL
Actually, this protocol finds its origin from a sort of algorithm describing how epidemics replicate which were earlier explained by Swinehart Danm, Demers Alan, Hauser Carl,Greene Dan, Irish Wes, Shenker Scott, Larson John,Terry Doug and Sturgis Howard in their 1987 work titled "Epidemic Algorithms for Replicated Database Maintenance".
The publication of this study steered so much interest in the world of computing technology. This is due to the fact that the operating system it describes is very good for extremely large networks that are highly decentralized. Evidently, the routing systems that had preceded the internet system we are now using are known to have run this kind of gossip-type technology protocol. In the middle of 2010, an American computer scientist known as Leemon Baird had introduced this concept into his brainchild called Hashgraph whereby transactions were completed as time-sequences and not as the usual blocks associated with blockchain.

Explain Tolerance to Byzantine Faults in Hashgraph.

Tolerance to Byzantine Faults is a property that can be possessed by a system whereby such a system, which is technically referred to as being Byzantine fault tolerance, could continue its operations even a member or a participant in the operation chain has opted out or has begun to work contrary to an established methodology in the operation. The use of this in the Hashgraph means that the Hashgraph can still converge or that it can still reach consensus even if a node or some nodes have opted out of the network or have begun to go against the rules.
Byzantine Faults Tolerance is an attribute of a consensus algorithm and not one itself. The particular type of it used in the Hashgraph is the Asynchronous Byzantine Fault Tolerance (ABFT). The ABFT refers to a property, in a consensus algorithm that is Byzantine fault tolerant, that makes it possible for the nodes that are honest to give a guarantee of being able to agree on the order and timing of transactions that are made over the network in a secure and fair manner. They 'asynchronous' type in the Byzantine fault tolerance has the advantage of overcoming a major challenge in the Byzantine fault tolerance.
This challenge has to do with timing in fault tolerance. In coming to a consensus many Byzantine Fault Tolerant systems simply assume that message latency would have a maximum threshold. The ABFT simply removes this assumption and makes room for some messages that could be delayed or lost. Hence, this particular system will still reach consensus even with such delayed or lost messages. This is based on the fact that this particular protocol would anticipate that the message of an honest node will eventually go through and, therefore, serve for the purpose of reaching consensus. This situation actually reflects the fact that a node can determine whether another node's message would be delayed indefinitely or not go through.
Generally, in a system that is Byzantine Fault Tolerant, even if as much as one-third of all the nodes have become malicious and delaying the verification and implementation of transactions on time or have begun to send out corrupting signals, a system can still reach consensus with the number of honest nodes that are trusted to eventually agree on the order and timing of transactions.

Make a comparison between Hashgraph Vs Blockchain, for a voting process in your country. Which technology would you choose? Why?

Blockchain technology is continually evolving. Interestingly, there are still some other types of the Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT) that are ready to even overtake blockchain technology. One very good example of such a technology that is set to deliver more quality is the Hashgraph. This particular one has an entirely different approach to the issue of distributed ledger. Claims are that it is much faster, secure and fair in its approach. Consequently, it is important to consider the two technologies of Hashgraph and blockchain side-by-side to draw out their similarities and differences.
HASHGRAPH VS BLOCKCHAIN
First of all, we should understand the real meaning of distributed ledger technology. A distributed ledger technology is a system or networking of different peers or member nodes for the purpose of sharing common information to reach consensus or an agreement on order and time. There are quite a good number of them in the technology world today. However, we are looking at the two of just Hashgraph and blockchain for today. Generally, DLTs claim to offer more integrity, security, transparency, decentralization and speed. Unfortunately, not all DLTs can claim to offer all these. Without further ado let us understand Hashgraph and blockchain in more detail.
What Is Hashgraph?
Hashgraph is a network for reaching consensus that offers distributed ledger technology in a way that is quite different. From the white paper it is described as a consensus algorithm or a data structure and not entirely a system. Again, it is described as specifically being a distributed ledger technology. Its patent belongs to the Swirlds and as such cannot be used except by its licensed creators. This technology uses virtual voting and gossip about gossip as ways of reaching consensus and maintaining its connectivity.
Hashgraph comes with a technology that enables it to offer a fast, secure and fair network. The technology is coded with the Lisp programming language together with JavaScript. Consequently, it means that Solidity is offered and supported by it. Actually, the most significant and important aspect of the Hashgraph is the speed it offers.
What Is Blockchain?
Actually, the blockchain is among the most popular systems of distributed ledger technology. It is the technology that is used by a lot of cryptocurrencies, including Bitcoin, the very first of them all. It enables a peer-to-peer network by which information is distributed and disseminated. The Bitcoin utilises the most basic type of it which is not very efficient. Other types of the blockchain have emanated with some other cryptocurrencies and come with more efficiency. Ethereum is known as a second generation type of blockchain which enables smart contracts and DApps. In the most technical form of it, blockchain is seen as a series of blocks which represent a record of peer-to-peer nodes connected for the purpose of sharing and disseminating information.
The technology comes with an append-structure and a database that cannot be corrected (that is, immutable). Storing data on previous blocks means that they cannot be changed again. This makes it good for such processes as voting, finance and supply chain management in the present world. You can learn more about blockchains here. Alright, I would like to give some sort of comparison between Hashgraph and blockchain.
| Variable | Blockchain | Hashgraph |
|---|---|---|
| Consensus | Actually, no single approach is adopted for reaching consensus; proof-of-work, proof-of-stake, delegated proof-of-stake are all different approaches | the form of consensus utilised is the virtual voting with the Hashgraph itself being a consensus mechanism |
| Programming language | different languages are utilised for the purpose of writing codes and programs | the writing of codes and programs are entirely done with Lisp and JavaScript |
| Speed | Actually speed here depends on the platform cryptocurrency order particular blockchain in question but they are technically not as fast as the Hashgraph usually possessing between 100 and 10,000 TPS | utilizes the gossip protocol which is very fast and capable of processing over 500,000 TPS |
| ABFT | does not utilise this mechanism and would have to rely on a minimum node compliance to reach consensus | utilizes the asynchronous Byzantine fault tolerance which makes for high credibility even in the presence of malfunctioning nodes |
| Accessibility | it could be public, private or hybrid; it has been utilised by so many networks like Bitcoin, Ethereum and others | public as in Hedera Hashgraph, could be also private and is currently being used by about 300 known companies |
| Fair | less fairer | more fairer |
| Security mechanism | uses cryptographic hashing which gives it a good level of security | uses asynchronous Byzantine fault tolerance which equally gives it a high level of security |
| Efficiency | less than 100% efficiency is achieved due to the block approach used and in the case where two blocks are produced at a time one has to be discarded | up to 100% efficient since it doesn't rely on the creation of blocks but only makes use of events that can be gossiped |
| Approach | data is stored in the form of blocks | data is stored and accessed with the use of directed acyclic graph for time-sequencing |
| Development and Adoption | has passed its development stage and has been widely adopted and used by the numerous number of cryptocurrencies in the market today | is somewhat still in its development stage and is patented to the Swirlds, though it is being used by some companies and a variant of it is being utilized by the Hedera Hashgraph |

For an electronic voting process three factors are very important, namely authenticity, integrity, confidentiality and speed. Actually, for a voting process in my country I would prefer the Hashgraph technology to the blockchain.
source:pixabay
I do have my reasons for preferring the Hashgraph to the blockchain and I'm going to give a few points to buttress my assertion. To start with, the blockchain has a lot of issues with scalability. Inasmuch as votes cast can not be changed as a result of immutability and inflexibility, it should be understood that the blockchain is quite incapable of handling the large volume of votes to be cast at a time. The blockchain can be quite slow in handling the large number of millions of voters that usually participate during elections in my country Nigeria. Another issue is with the high cost and intensive method of computing power that is required to power a blockchain. Assuming we even intend to build a computing system that can power this, it would require so much resources, time and energy that may not have been necessary at the end of the day. Attacks on server connections on voters' devices can even lead to system penetrations that will undermine the credibility of the whole process with blockchain.
Some of the major reasons why I prefer the Hashgraph is because, first, it handles the issue of time very efficiently. Again, the Hashgraph is asynchronous and will not have to wait for any other transaction before votes cast are transmitted. The gossip method used in the Hashgraph is quite fast in disseminating information. Also the use of excellent fault tolerance can go a long way in helping secure the system from possible cyber-attacks and manipulations that would undermine the credibility and authenticity of votes cast. Again, with the Hashgraph, every single node is aware of the presence of every other node which means that the total number of voters can be known and not manipulated in any way. So, I prefer the Hashgraph for the voting process in my country Nigeria to the blockchain technology.

Explore Hedera Hashgraph(https://hedera.com/) (show screenshots).

HEDERA HASHGRAPH IMPORTANT STATISTICS
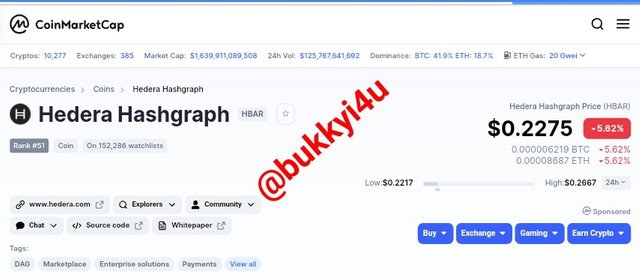
screen from coinmarketcap
Before I continue I would like to give a brief analysis of the Hedera Hashgraph. Hedera Hashgraph is a network that is public and on which users can build powerful and strong decentralized applications. Usually, it is referred to as the internet trust layer and is built to correct some inefficiencies observed with earlier blockchains like instability and poor scalability. It comes with a more efficient and fairer approach.
| Metric | Statistics |
|---|---|
| Hedera Hashgraph Price | $0.2265 |
| Price Change (24h) | $-0.01584 |
| 24h Low / 24h High | $0.2217 / $0.2667 |
| Trading Volume (24h) | $293,495,060.09 (47.07%) |
| Volume / Market Cap | 0.1518 |
| Market Dominance | 0.12% |
| Market Rank | #51 |
| Market Cap | $1,933,607,676.07 |
| Fully Diluted Market Cap | $11,271,135,363.64 |
| Circulating Supply | 8.58B HBAR (17%) |

On the Hedera Hashgraph website that can be accessed from https://hedera.com, you will find a lot of interesting features. I am going to talk about a few of them.

The features I am going to talk about can be accessed by clicking on the three horizontal lines that are located to the top right corner of the landing page or homepage as displayed in the screenshot above.
NETWORK

screen from hedera.com
This feature lets you in on a lot of opportunities. You can mint and develop your own fungible and non fungible tokens. Here, you can even develop timestamps that can be verified and used for the ordering of applications. Generally, you will find all the important and interesting things that can be obtained from the underlying network from this feature.
DEVS

screen from hedera.com
This feature lets you in on a few important developmental resources available on the network. With this feature you can learn how to select preferred languages when using the API, also you get to learn how to contribute to important proposals being made. Again, you can learn more on how to estimate fees and there is a Learning Center where you can get more knowledge on distributed ledger technology.
USE CASES

screen from hedera.com
This feature of the website describes the important areas and aspects where the Hedera Hashgraph can be useful. It enumerates such functions as online payment, permissioned blockchain, tokenized assets, credentials management and a few other important use cases.
HBAR

screen from hedera.com
This section gives important information related to the Hedera Hashgraph cryptocurrency. Here you would learn things like buying guides for the HBAR. It describes the cryptocurrency as being very fast and low in fees. Again, it gives a guide on its mainnet account quick creation. You will also get valuable information on its supported wallets and exchanges.
Governance
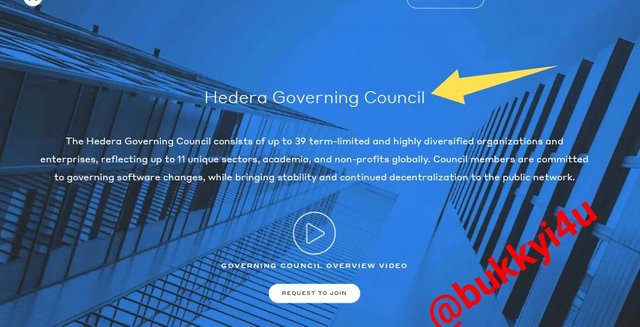
screen from hedera.com
This is one of the other interesting features on the website. Under this governance section you would click through to get first-hand information on how the network is governed. Here you would even see a button to 'REQUEST TO JOIN' the governing council. You would get the information that the network is governed by over 39 large-scale operations that represent over 11 global sectors. Also, it would be noted that the council members will work to maintain decentralization and bring about changes to softwares when necessary. There is a video overview that presents the governing council and below is displayed a list of many of the leading corporations globally that are behind the governing council.

ABOUT
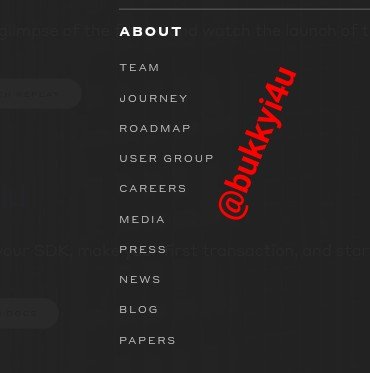
The about feature let's you in to the developmental stages and a lot of the important information like the team behind the project, the journey so far, papers that have been presented on the project, the roadmap of the project, media briefings and press releases, as well as a few other information like user groups that have been created and blogs, also.
Team


The team featured on the about section reveals the wonderful team behind the project and the network. Also, it unveils the investors who have keyed into the network.
Journey
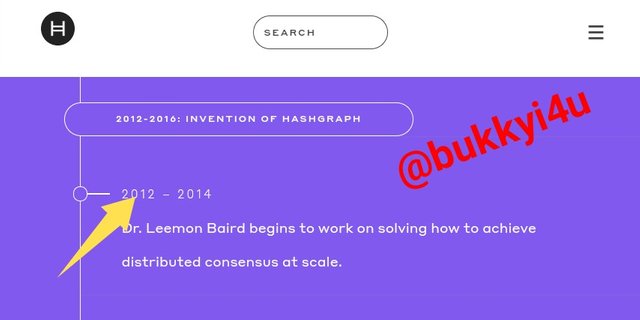
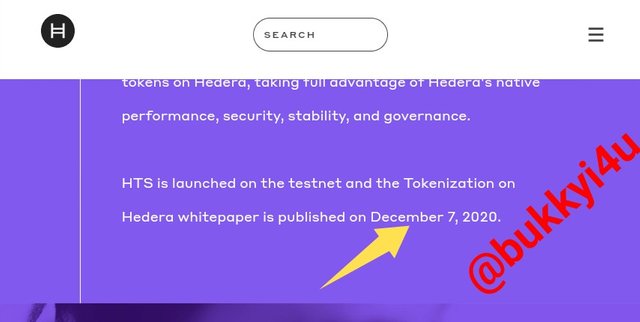
The journey section reveals the important steps that have gone into the developmental stages of the network. It shows how Dr. Leemon Baird started the project in 2012 and how it was eventually launched and the white paper finally published on the 7th of December 2020.
Roadmap

This feature represents the vision embodied by the network's governing council and is described as being audacious. It presents the stages in the presentation of the network to the world and starts from the first quarter 2021 to the second half of 2021.
User group

The Hedera user group is a group created to foster close relationships between the governing council of the network and the ever growing and increasing community behind the network.
Careers

This feature of the about section reveals some of the important careers that are still open or that may have been filled in the network.
Media

Through this feature the founders of the network are able to keep in touch with the ever-growing community by hosting live webinars in their monthly Town Hall where Dr. Leemon Baird and Mance Harmon, who are the co-founders field questions from viewers. Also, passed podcasts and webinars can be streamed.
Press

Through the press feature some important and featured press briefings of the Hedera Hashgraph are released for public consumption. Also, important and landmark events are posted on the blog here.
News

Through the news feature of the about section Hedera Hashgraph publishes important and relevant updates that are related or that affect their network on a regular basis.
Blog

This is another important feature that appears in the ABOUT section. Through this feature important and relevant articles are published on the Hedera Hashgraph blog for anybody to read. These articles also appear on the internet search engines.
Papers

On this feature important papers that have been presented in the history of the Hedera Hashgraph, including the white papers, are published. Clicking here will take you back to the hedera hashgraph homepage.

CONCLUSION
The Hashgraph is a quite interesting distributed ledger technology that has been tested to be much faster, secure and efficient than the blockchain. It uses the Byzantine Fault Tolerant method to ensure credibility and for reaching consensus. However, for now, it is patented and can only be used by the Swirlds. So far it has only been tested on the Hedera hashgraph.
The blockchain may have been around for quite a longer period and may have received much greater adoption and usage, still, the hashgraph does have a lot of better potentials than the blockchain. It is my earnest desire to see that the Hashgraph becomes adopted and utilised in a very large scale. However, I do hope that subsequent projects that would be developed on newer versions of the blockchain would find a way of borrowing from the Hashgraph or develop entirely new features to at least meet up with it to some extent on the areas where it has comparative advantages.


Gracias por participar en Steemit Crypto Academy:
Muy bueno tu trabajo. Felicitaciones.
Espero seguir leyendo tus publicaciones.
Calificación: 10
This particular post under which I am commenting which was mentioned by professor @pelon53 among the top pick for week 16 has not been upvoted by @steemcurator02
Hello professor @pelon53, this post pays out in 2 days time but has not been upvoted by @steemcurator02. Please, do call the attention of @steemcurator02 to this post.
Buenas, ten paciencia amigo