Science: What is the science behind sudden ZAP(Static Electricity)⚡⚡⚡
~Sharing will enrich everyone with more knowledge
-Ana Monnar
It's been a long time since my last post dear friends, We had a lot of projects to be done this semester but then we still manage to finish all the tasked before this semester ends. And now that I'm back, let's get back into action steemit friends
What is the science behind STATIC ELECTRICITY⚡

I know most of us here experience this when we are walking especially on a soft carpet and once you are about to reach your doorknob a sudden ZAPPPPPP! happens🤣
But then what causes this sudden jolt of static electricity, but before we dig in to that let me explain to you first the so called "nature of matter"
The Nature of Matter🌲....

To understand the science behind static electricity, we first need to know a bit about the nature of matter. All matter is made up of atoms that consist of three types of smaller particles and these particles are negatively charged electrons, positively charged protons, and neutral neutrons. Normally, the electrons and protons in an atom balance out, which is why most matter you come across is electrically neutral. But then these tiny electrons are tiny and almost insignificant in mass, and rubbing or even a friction can give loosely bound electrons causing enough energy to leave their atoms and attach to others, migrating between different surfaces

when this happens, the first object is left with more protons than electrons and becomes positively charged, while the one with more electrons accumulates a negative charge. This situation is called a charge imbalance or also called as net charge separation, But nature tends towards balance, so when one of these newly charged bodies comes into contact with another material, the mobile electrons will take the first chance they get to go where they are most needed, either jumping off the negatively charged object, or jumping onto the positively charged one in an attempt to restore the neutral charge equilibrium or what we call as charge equilibrium.
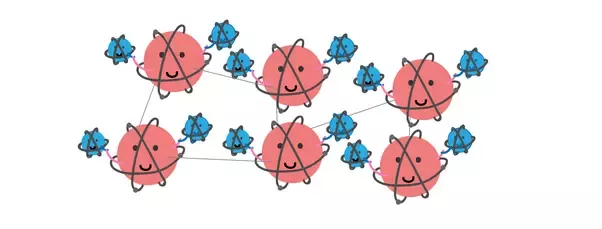
And this quick movement of electrons, called static discharge, is what we recognize as that sudden spark. This process doesn't happen with just any objects. Otherwise, you'd be getting zapped all the time. Conductors like metal and salt water tend to have loosely bound outer electrons which can easily flow between molecules
On the other hand, Insulators like plastics, rubber and glass have tightly bound electrons that won't easily jump to other atoms. Static build up is most likely to occur when one of the materials involved is an insulator. When you walk across a rug or carpet, electrons from your body will rub off onto it, while the rugs or carpet's insulating wool will resist losing its own electrons. Although our body and the rug or carpet together are still electrically neutral, there is now a charge polarization between the two. And once we reach to touch the door knob, ZAAAAAP happens! ⚡⚡⚡ 🤣🤣
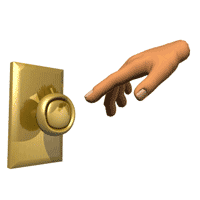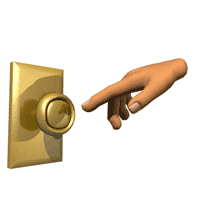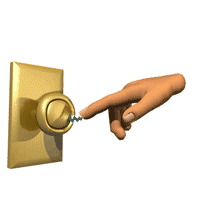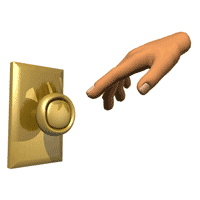
The metal door knob's loosely bound electrons hop to your hand to replace the electrons your body has lost. When it happens in your bedroom, it's a minor nuissance.
But in the great outdoors, static electricity can be terrifying destructive force of nature. In certain conditions, charge separation will occur in clouds. Though, we don't know the exact reason why this happens

But it may have to do with the circulation of water droplets and ice particles within them. Regardless, the charge imbalance is neutralized by being released towards another object or body, such as a building, the Earth, or another cloud in a giant spark that we all know as LIGHTNING
And just as your fingers can be ZAPPED! over and over in the same spot, you better believe that lightning can strike the same place more than once!

How to avoid STATIC ZAP⚡....

Since all of us witness the effects of static electricity everywhere. And this effects occur when an insulating material such as plastic, rubber, or even a wool that is in our carpet or rug is involved. And these materials lose electrons depending on its inner structure of materials and the electrons that are bound to it. And these materials are ranked in which they lose or gain electrons, This ranking is called the triboelectric series

Generally, The human body is composed of 60% or more water resulting the human body is a good conductor of electricity! But dry human skin is a different story.
Static Electricity can occur when you rub your feet or even when you rub your cats fur like what you see in the gif, It is important to remember that static charges, get accumulated even insulating material, but only lasts for a short while. If these charges are not zapped off, then they leak off
The best practice to avoid a static zap is simply to touch the Earth's or the ground, a wall, or a wooden door, before you touch anything that is conductive metal or material

1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8
Thanks for hanging in my fellow Steemians I hope you learn something from my blog, feel free to comment on the comment section below😊
⛅⛅ Have a nice day everyone ⛅⛅
》》SPREAD THE VIBES《《


 ApexZachMarie
ApexZachMarie 