Crypto Academy Beginners' course - Homework Post for Task 3 : The Genesis Block by @cryptogecko

I have planned to complete my first few assignments from the Introductory assignment lot, and would also be posting assignments from the Beginners' and Intermediate sections. I am not eligible to post advanced level courses as my reputation has yet not reached the 65th level. I hope that my assignments help me reach that level so that I can complete advanced level assignments in the next week.
This assignment focuses on the Genesis block of a blockchain. Professor @awesononso has beautifully explained the features and information of the Genesis block in his assignment course post.
So, let us start with the questions we were given in the assignment post by our professor.


Since its conception, blockchain technology has been dubbed as the "most significant technological innovation of the 21st century". There is a widespread belief that the words "blockchain and cryptocurrency" came into existence after the inception of Bitcoin, and when blockchain technology and Bitcoin became extremely popular throughout the world for their ability to send funds anonymously anywhere in the world.
Contrary to popular belief, what many people today refer to as blockchain was conceptualized by two scholars and mathematicians Stuart Haber and W. Scott Stornetta in 1991. In their first paper, the two authors devised a cryptographically secure way to encrypt documents' timestamps so that they could not be tampered with.
The Bitcoin blockchain has now been around for around 12 years and the technology used by Bitcoin has been incorporated into various industries, including finance, entertainment, and education. As blockchain technology continues to gain popularity, a number of new applications have emerged, making it clear that it will become increasingly important as digital economies flourish.
My aim with this assignment is to explore the history and evolution of cryptocurrencies and to demonstrate their advantages over traditional fiat currencies by illustrating how more secure cryptocurrencies are compared to fiat currencies.
First of all, the question we must answer is what led to the development of blockchain?
After writing their first paper defining the earliest form of blockchain technology, Stuart Haber and W. Scott Stornetta wanted to store more than one document on the blockchain's single block. Their system was upgraded in 1992 to integrate Merkle trees to improve efficiency and allow them to collect more documents on a single block. But the history of blockchain was only made famous in 2008, courtesy of someone or some group of people named Satoshi Nakamoto.
It has been widely assumed that Satoshi Nakamoto is the genius behind blockchain technology. In spite of all the questions surrounding the identity of Nakamoto today, it is very hard to identify him since there are so many possible candidates as to who developed Bitcoin, the invention that put digital ledger technology on the world map.
In the last few years, it has been proven that blockchain technology can be applied to different fields in addition to cryptocurrencies as well. This blockchain technology was described in a whitepaper published in 2009 by Satoshi Nakamoto. Among other things, Satoshi Nakamoto explains that the decentralization part of blockchain technology and the lack of centralized control it offers makes it an ideal method of improving trust in digital real-time economies.
Due to the fact that Satoshi Nakamoto left the Bitcoin scene and handed over the Bitcoin technology to other core developers, blockchain technology has evolved and with it, new applications have arisen.

To answer this question, we will discuss and show the process to explore the Bitcoin blockchain. To explore the Bitcoin blockchain, we will be using blockchain.com block explorer website.
You can probably get a considerable amount of information from a block explorer since it allows you to inspect a large number of details, as well as verify that every single transaction in each block is completely transparent and open.
It is worth noting that coinbase in this context refers to the transaction that is automatically integrated into every Bitcoin block to reward the block miner. The coinbase exchange website you know and trade your cryptocurrency on, is not being discussed here.

Image: Block 0 of the Bitcoin Blockchain (Genesis Block)
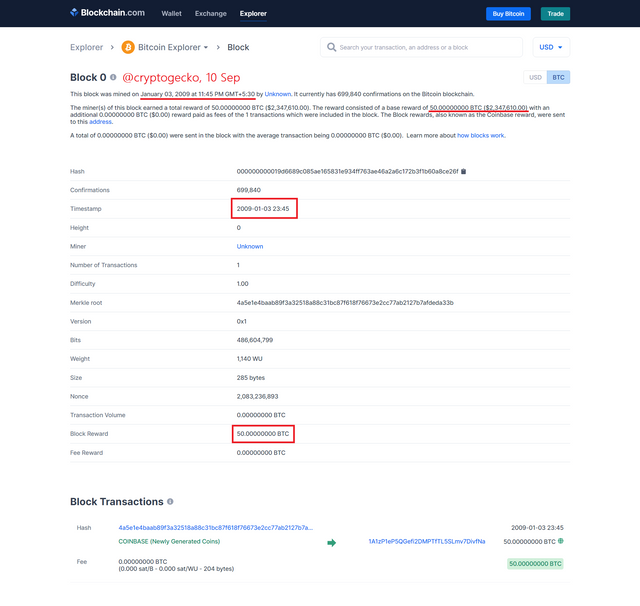
The image above shows that the Genesis Block, or the first block ever generated on the Bitcoin blockchain, was mined on the 3rd of January 2009. In the image, the time is in Indian Standard Time, which is GMT +05.30.
The table below shows the different attributes from the block details and also provides the value of these attributes. These can be used to uniquely identify a block in the blockchain.
| Attribute | Value |
|---|---|
| Block Hash | 000000000019d6689c085ae165831e93 |
| 4ff763ae46a2a6c172b3f1b60a8ce26f | |
| Merkle Root | 4a5e1e4baab89f3a32518a88c31bc87f |
| 618f76673e2cc77ab2127b7afdeda33b | |
| Nonce | 2083236893 |
A reward of 50 bitcoins was provided to Satoshi for mining the block. However, the reward for mining each block on the Bitcoin blockchain has now been reduced to 6.25 bitcoins as the rewards are halved after every 210K blocks. The reward for generating the block was transferred to address 1A1zP1eP5QGefi2DMPTfTL5SLmv7DivfNa.
We will now explore the second block on the Bitcoin blockchain, although it is assigned the number 1, it is the second block because the first block was assigned the number 0.

Image: Block 1 of the Bitcoin Blockchain
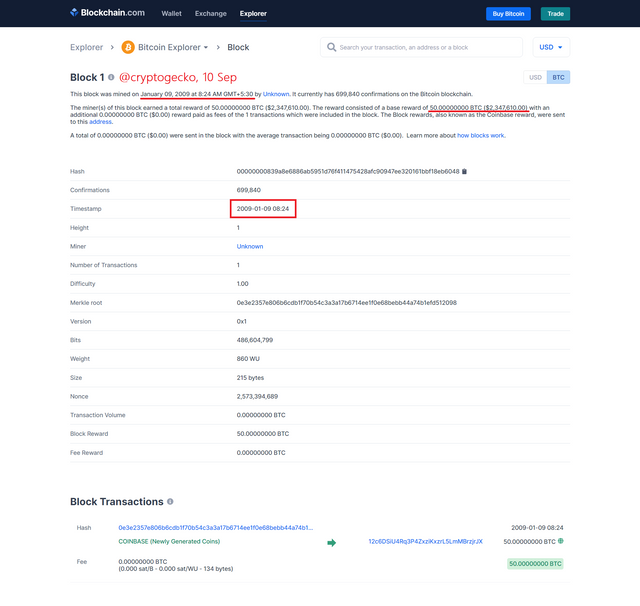
Block number 1 or the second block on the Bitcoin blockchain was mined on the 9th of January 2009. This second block took close to 6 days to be mined.
The table below shows the different attributes of the second block and also provides the value of these attributes.
| Attribute | Value |
|---|---|
| Block Hash | 00000000839a8e6886ab5951d76f4114 |
| 75428afc90947ee320161bbf18eb6048 | |
| Merkle Root | 0e3e2357e806b6cdb1f70b54c3a3a17b |
| 6714ee1f0e68bebb44a74b1efd512098 | |
| Nonce | 2573394689 |

Image: Satoshi Nakamoto's Address (1A1zP1eP5QGefi2DMPTfTL5SLmv7DivfNa)
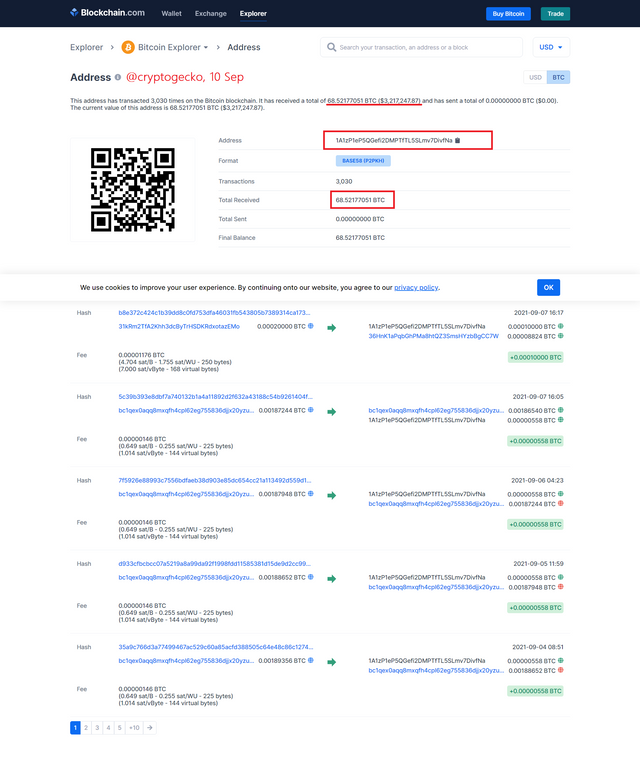
Satoshi Nakamoto's address was the first miner for the Bitcoin blockchain and also the first address to receive mining rewards. Although no new rewards were collected by the address after the first reward, people have been sending small amounts of Bitcoins to this address to this day to show their gratitude towards the developer for innovating and establishing such technology that has changed and touched the lives of millions around the world.
To this date, around 3031 transactions have been made to this address and all the transactions are incoming transactions and not one is used to send money to another address. The address currently holds around 68.52177609 BTC and is valued at 3,196,114 US Dollars at the current price.

While exploring the block description and details, you will find that the transaction hash of the Genesis block will lead you to a page where you can find the inputs and outputs generated by the block.
The input section of the block has a secret message by the famous Satoshi Nakamoto. The hex value can be used to get the secret message encrypted behind the hex code.
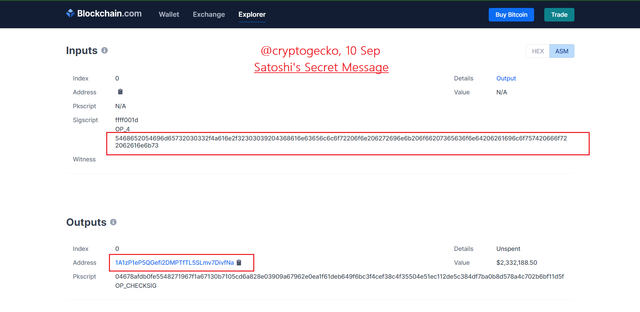
Upon converting the Hex code to the Normal Text message we can see below in the image that the secret message refers to the newspaper heading of The Times printed on the 3rd Jan of the year 2009.
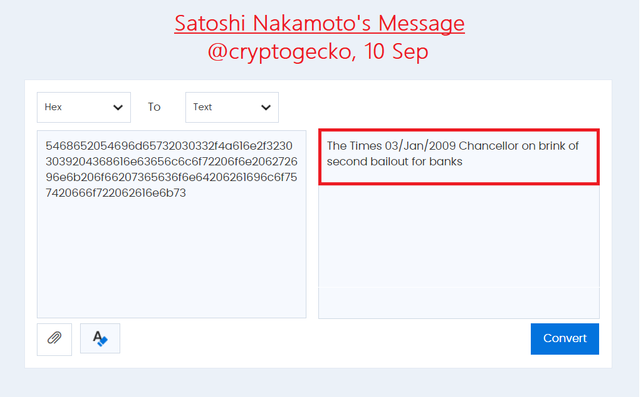
The headline on the newspaper read: "Chancellor on brink of second bailout for banks."
According to me and what I have read, I conclude that Satoshi's message was trying to attract the attention of the users to the bailout of the banks after the financial crisis of 2008. He was trying to show the negative effects of too much power given to the banks in the financial ecosystem and how it badly affects society.
Not only did Satoshi pointed out the negative side of the financial industry, but he also provided the world with a solution that we as a society have included in our daily lives and are using to advance the humanities approach towards every aspect of our life and use cases are being developed to help us in every major field.
References:
Blockchain.com Explorer | BTC | ETH | BCH. (n.d.). Blockchain.Com. Retrieved September 10, 2021, from https://www.blockchain.com/btc/tx/4a5e1e4baab89f3a32518a88c31bc87f618f76673e2cc77ab2127b7afdeda33b
Centieiro, H. (2021, September 1). Decoding Bitcoin’s First Block Coinbase Transaction. Medium. https://medium.com/geekculture/decoding-bitcoins-first-block-coinbase-transaction-aeefe87ceec0
Iredale, G. (2020, December 21). History of Blockchain Technology: A Detailed Guide. 101 Blockchains. https://101blockchains.com/history-of-blockchain-timeline/

Thank you very much for reading my assignment
