Blockchain Trilemma - S5W2 - Homework Post for @nane15

In life, there are things that cause us some level of stress more than others. One such thing is trying to take a decision and pick and option from among very delicate choices. This situation is also present in the sphere of technology and the blockchain industry is not spared.
There some crucial things that need to be taken into consideration when building a blockchain project. In most cases, it is very difficult to achieve all the required outcome. Many developers have had to accept a particular limitation while enjoying other advancement.
The problem of trilemma highlights one difficulty that is plaguing blockchain projects. This class by Prof. @nane15 is very educating I will give more information on this in the following assignment questions.
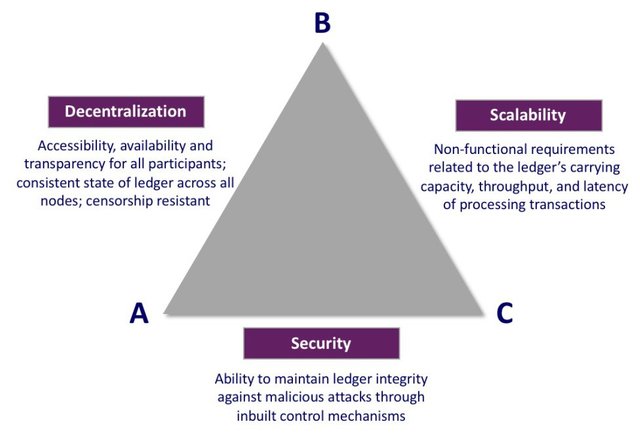
Explain in your own words what the Blockchain Trilemma is
The term trilemma as I have shade some light in the introduction is about making a choice among three vital options whereby it seems that all three cannot be mutually achieved, implying that a maximum of two could be possible while leaving out the third one. In blockchain terms, trilemma is a situation whereby a blockchain attempts to create high security, optimum scalability and high degree of decentralization into a project which usually seem like only two of these can be attainable.
It is the target of blockchain software developers to produce a blockchain that fosters strong decentralized system, formidable security and high scalability, but over time, most blockchains have been able to realize only twonof these three targets. These three targets appear to be impossible to be put together and as such a project can only settle for a possible two while sacrificing the third. This is what constitutes the theory of blockchain trilemma.
From projects developed on previous years, it is always that a project has high decentralization, high, security but low speed or processing transactions. Or it has high scalability, high security but low decentralization. The case is always that one of these three essentials is found to be missing.
This conceived problem and challenge is quite peculiar to blockchain platforms unlike the centralized ones. In the early years of the 1980s, the trilemma issue was conveyed in the tag of CAP theorem. In the early as the 1980s, computer scientists developers brought up this theorem to explain the challenges of computing infrastructure.
In the CAP theorem, decentralized data stores which birthed blockchains, can only provide two of three pivotal features of consistency, availability, and partition tolerance concurrently. This makes up the abbreviation CAP. This is pointer to the problem of trilemma in technology from historical times.
Vitalik Buterin, the astute software engineer and developer is credited with coining this term trilemma which signifies a set of three major hurdles that developers battle with when building blockchains. On hitting this stone wall, blockchain developers take the option of letting go one of the components as an opportunity cost to have the other two.
Different blockchain developers have had to make a choice between these three options to take out one. This is solely dependent on the aim of the project and the design. It is undecided which of these three is less important than the others. However, many blockchain researchers and authorities possits that, while trying to leave out a component, security should not be tampered with as every other thing will need to be built on a secure network.
Is the Blockchain Trilemma Really a Trilemma?
In all reality, there no stated facts or legislation that promotes or solidifies that there is the trilemma. The concept from inception was created to so as to be able to appropriately express the challenges and issues that blockchain developers have to grapple with in trying to build a blockchain. It is not as if it is a generally accepted law or an established fact.
At best, it is still a theory and there have been numerous propositions by many that these three options and essential components of high security, decentralization and scalability can be achieved and integrated into a blockchain.
CertiK, the reputable blockchain audit and security firm holds this view. Some blockchain networks like, Solana, Polkadot, Algorand and even the proposed Ethereum 2.0 all lay claims to having remedy for this problem.
So, as it is, it is not like that trilemma has been stamped as an inherent condition or concept. There are a number of protocols and solutions that have been proposed to remove this problem. Thus, it is not a certified condition.
Define the following concepts in your own words: A. Decentralization B. Scalability C. Blockchain Security
- DECENTRALIZATION
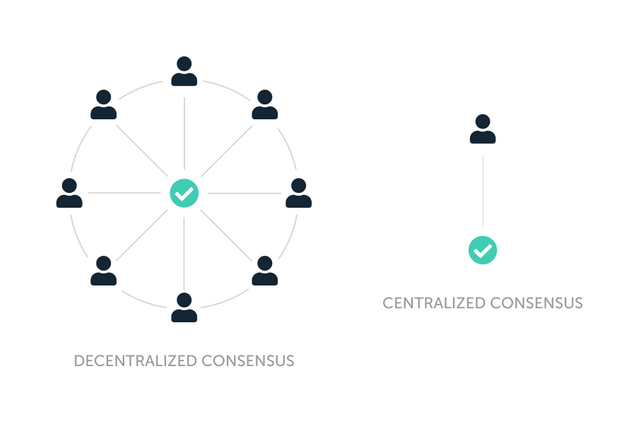
Decentralization literally refers to spread or distribution across different points. It means that there is no concentration of power or resources in a particular place. This means that no one individual or location is in control but that control is spread across a number of locations.
In blockchain sphere, decentralization can be defined as a situation whereby no one body, organization or individual owns exclusive rights and powers to run the affairs of a blockchain or make regulations concerning the details and operations or a cryptocurrency asset.
It means that multiple computing nodes are responsible for validation and verifying transactions taking place on a blockchain before certifying it and adding it to the blocks. It refer to shared power and participation of multiple users of a blockchain in taking decisions concerning the blockchain and running it.
This has been a central theme about cryptocurrencies and blockchain from the very beginning. Satoshi Nakamoto aimed to take power from the banks and other financial institutions and give it to the people who were the owners of the funds this way bypassing all the protocols and unnecessary restrictions enacted by these organizations.
In this case, each miner or validation node enjoys equal rewards and privileges. No singular user or miner can influence any process on the blockchain network without approval from the rest. This is what decentralization entails. The placement of power and rights in the hands of users without there being a central control unit.
- SCALABILITY
This can be defined as the tendency of something being adjustable in capacity and being resizable. In reference to a blockchain, scalability addresses the condition of the network being adaptable to accommodate the changing volume od users and transactions. It is concerned with the rate at which transactions can be handled and processed.
It is the ability of a blockcain to be able to facilitate and support increasing amount of transactions, executing conveniently, at considerable speed and at minimal cost. It rates how a blockchain is able to support high transactional throughput and future growth.
It is the level of scalability that will determine how a blockchain network will be able to host additionally users and processes taking place on the blockchain. The main issue about scalability is about how much a blockchain system can sustain, and whether the system can operate smoothly as demand increases both in work load and in data and user volume.
- BLOCKCHAIN SECURITY
Not many people will not understand what the work security means. It is simply a condition of something valuable not being exposed to danger, risks, damage, alteration, infiltration or theft. Security in blockchains is defined as the situation where the data stored in the blocks are protected and cannot be tampered with by any fraudulent means or experience malicious attacks.
Blockchain security is therefore about the installing of a formidable firewall and protection such that the blockchain becomes impenetrable and resistant to attacks making it not vulnerable. Security here means the level of threat a blockchain can repel and how exposed and prone it is to suffering attacks.
Many blockchains in recent time have had some attacks which the hackers mostly exploit flash loans which are loans that demand no collateral. These have been mostly through the smart contracts built on some blockchains.
A notable case of security breach is that which occured in August 2020 on the Ethereum Classic (ETC) blockchain. The blockchain suffered three 51% attacks which modified over 4,000 blocks, manipulated the stored data and was able to double spend ETC currency.
Based on your knowledge, explain at least two viable solutions to the challenges posed in the Blockchain Trilemma.
At the moment, several studies and experimentaion has be conducted to profer solutions to this challenge and these options are been assessed and explored by some projects. The solutions are grouped as:
First Layer Solutions
This refers to dealing with the challenge by developing blockchain networks that employ protocols that are use compatible language which can incorporate these three components into the workings of the blockchain. These kinds of solution attempt to engineer the blockchain from the foundation programing. These methods aim to improve a component of a blockchain directly by adjusting some things like upgrading or changing them.
The major areas of change include:
- Consensus Protocol
Here, the network proposes a different mining method and means of validating transactions. Different consensus protocols have their unique limitations and advantages as regarding the aspect of security, scalability and decentralization. Proof of Work (PoW) has the advantage of high, outstanding security and decentralization, but has low transaction throughput.
Proof of Stake (PoS) offers high scalability but less decentralization. Some advanced consensus protocols have also been developed like the decentralized proof of Stake (DPoS), bazanthine protocols and others which have been propsed to make achieving the three targets possible.
- Sharding
This involves breaking transactions into smaller data-sets which are called "shards." The sets of data can then be simultaneously processed side by side. Which makes it possible for sequential work on numerous transactions at the same time.
In this method, each network node do not hold a copy of every block from genesis to present, but data is shared and held by different processing nodes. The "shards" provide proofs to the main chain and transmit information among them like sharing addresses, balances, and general state. This is done through cross-shard communication protocols and techniques.
Second Layer Solutions
These options if dealing with the trilemma are concerned with creating alternative means or projects through which activities involving the assets of a particular blockchain having a trilemma issue could be carried out.
This is like creating a plug-in or an attachment program next to the blockchain. This is usually done on blockchains which support the creation of smart contracts. Through these smart contracts, activities concerning the deficient aspect of the trilemma are concentrated here thus, giving blockchain additional tools in optimizing its operations.
The areas of focus of this second layer solutions are:
- State Channels
This second layer method creates a two-way communication between a blockchain and off-chain transactional channels. The off-chain transactional channels are created adjacent to the mainchain and they are protected by multi-signature or smart contract mechanism.
When transactions completely executed on the state channel, the result of processing the transactions are transmitted to ans recorded on the underlying blockchain. This is found in systems like Celer, Ethereum's Raiden Network, Bitcoin Lightning, and Liquid Network.
- Nested Blockchains
As the name implies, this involves building multiple level blockchains while having the main or parent chain. The main chain delegates network functions to these sub level chains which process the transactions and send back the result to the mainchain.
Here, a combination of various chains are used. It is like having many linking paths to the main road. There is an interconnection of secondary chains in a web-like pattern and transactions are distributed across these various channels which take them back to the base blockchain. An example of this is the OMG Plasma project.
- Side Chains
To improve the services of a blockchain, a sidechain which is a blockchain-adjacent to the transactional or mainchain. These chains are programed on independent consensus mechanism from the original chain. In this sidechain, the weaknesses of the mainchain are improved upon, while the mainchain maintains overall security. The sidechain can be focused on scalability.
There will always be things that give us tough time in any endeavor that is worth while. There will be problems to solve. As one problem is solved, others will emanate. Building functional and sustainable blockchain projects demands that certain features and components be put in place. A blockchain project cannot really do well in the absense is tight security, decentralization and adequate scalability.
However, achieving these three has not been very easy with many projects only boasting of sufficiency in two out of the three. This is where the problem of trilemma comes in. However, it is not as if this cannot be handled. To tackle this, thee have been proposed methods and techniques which are currently underway in some blockchain projects.
It is plausible to say that there is a solution to any problem. Accordingly, it is hoped that very soon, most blockchains will be able to deal with this problem and position themselves in the most optimal state to operate properly.
I am glad to take part in your first class @nane15 as Steemit Crypto Academy Beginners Professor. Nice job.