The New Deal: solving economic issues in the 1930’s
The New Deal: solving economic issues in the 1930’s

America's economy fundamentally is built upon a capitalistic form of commerce. Capitalistic societies particularly America, experience periods of booms and busts that led to periods of great economic growth, and periods of sharp economic decline. With the growth and development of capitalistic economics in America, there needed to be an implementation of a regulation system to maintain economic stability.
With the implementation of the Federal Reserve System in 1912, America underwent a new economic form of monetizing and printing money. In 1930, this economic system faced a sharp decline that leading Americans to unemployment and starvation. It was up to Pres. Roosevelt to implement a new economic regulation system, along with an infusion of emergency funding for welfare programs which were the first of its kind in America. All of this was done to alleviate the economic suffering Americans across the country were enduring, and inject new life into the American economy.


With the American economy booming after economic woes of the late 1800s, Americans thought their economic woes were behind them. After World War I Ameri-can farmers found themselves with an abundance of wheat without an expansion to other markets to sell products led to farmers starting to lose out on profits. The banking system, on the other hand, was allowed to spiral out of control with little to no government oversight. This lack management and oversite of American economics led to the Great Depression. During this era of economic instability, Americans were stricken with property and hunger.
The government was needed to step in to alleviate the pressure on American citizens from a financial standpoint.

In 1931 Pres. Herbert Hoover was a staunch proponent of bigger government. Hoover felt that the federal government should not step in and take on the role of "centralizing" mandates and rule over the American people. Hoover felt that state and local governments should have a more prominent role in assuming responsibilities of handling issues that concern the general public regardless of the standpoint. If individuals are partaking in local and state governments, then there is no limitation to their involvement in policy making and their liberty. Hovers opinion was that America is a government for the people by the people, and federal action would suppress the people from taking on these issues.

Businessman Henry Ford echoed the sentiments of Pres. Hoover by saying Americans need to be self-reliant, and they should have an innate instinctual ability to be active and create employment for on their own if the need arises.

Since unemployment was a glaring issue for most Americans during the Great Depression, Ford insisted that if there were no job openings to acquire, Americans must not assume that they are unable to work. If they think this way, it will create a mindset of waiting for something to be given instead of a proactive approach of providing what you need for yourself. Henry Ford had an issue with the perception of charity stating it was a "barbarous thing in our system" for Americans to have an expectation of a handout from the government. He felt that there was a difference between giving out of the kindness of your heart which he stated was "a much more costly effort", because it implies an individual must give from his own pocket to help others in an act of altruism.

Ford thinks the implementation of a welfare system giving money to those who are unemployed sets a precedent against the American ideology of entrepreneurship and self-reliance which are staples of a capitalistic society. Ford felt that if Americans would reapply themselves to agricultural means of productivity, they could alleviate their economic woes. Ford insists that Americans must have a foothold in business as well as agriculture, because as he stated the American landscape has not "shrank in either extent or productivity", so it should be exploited for personal gain. Since cash has become a scarce commodity Americans must reapply themselves to agricultural means of self-sufficiency to produce food and wages for themselves to supplement income lost from industrial employment.
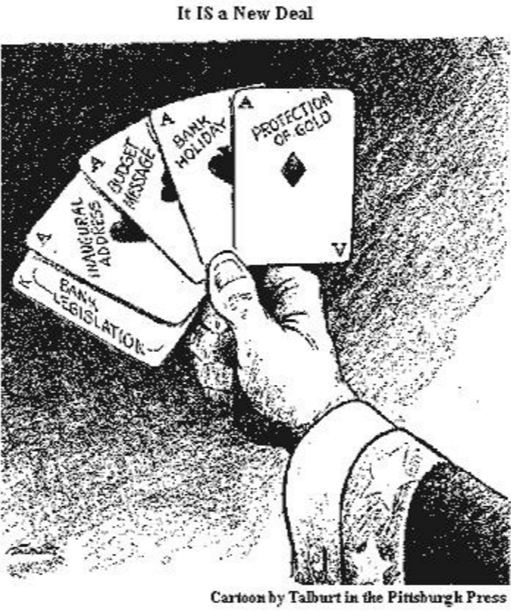

In 1933 Pres. Roosevelt implemented the new deal act which alleviated some of the pressure on Americans which entail reinvigorated the economy and introduced the welfare system. The new deal brought much-needed bank regulations to restrict insider-trading and regulations such as the Glass-Steagall act which ended up being repealed in 1998. Roosevelt put the blame of economic woes on individuals he called the money changers, which were the primary group to have control of the Federal Reserve System can manipulate the economy. Roosevelt felt that the new deal had to be implemented for the greater good of the American people, and reconstruction of the economy which is geared towards bringing relief to all in the present, and future Americans as well. He felt that the new deal should help everyone involved because his sentiment was "progress of our simulation will be retarded if any large body of citizens falls behind".

An example of Roosevelt's idea to look out for everyone is seen in his implementation of the Social Security system. Roosevelt made sure that everyone from the day they were born until they perished was able to pay benefits into the Social Security system and receive benefits either at their retirement, or during a period of physical disability, or during a period of unemployment. The promise of FDR's new deal was implemented to help every segment of American society in an effort to alleviate any economic woes for every individual in need.

Opponents of FDR's new deal said he introduced big government and the corporatization of the American economy. Aside from the perception of America becoming corporate ties and adapting the government policy, opponents of the new deal policy were able to point out in 1939 17.2 Americans were unemployed which was an increase of almost 1% from the amount of people that was unemployed in 1931 at the beginning of the depression. The stock market also tanked in the middle of the decade with half of the market dropping from 1937 to 39.
Proponents of the new deal feel that was just a temporary solution for an economic problem that is perpetual due to the implementation of the Federal Reserve System and its form of economy bureaucracy. Many historians looking back at the new deal have said that "Roosevelt was constrained in what he could accomplish", signifying that he could only do so much to stop the negative effects of the Great Depression. Past presidents and historians feel that the time period in which Roosevelt implemented the new deal was a trying time where they move to push such legislation was a very daunting task, but Roosevelt was able to build a foundation of a welfare system that could help all Americans despite their demographic or ethnicity.

Pres. Roosevelt legislation of the new deal took America out of the doldrums of the Great Depression and implemented a welfare system to alleviate individual’s problems. The implementation of the new deal wiped the slate clean for Americans and help those who work in industrial means and those who work and make their wages from agriculture. The new deal also had provisions to help those in the future who are participating in the Social Security system which was for all Americans and future Americans. Roosevelt's vision for the new deal was not only to help Americans in the 1930s but it had the foresight to implement things such as Social Security to help Americans in the future giving them a safety net in retirement, or in the event of disability, or unemployment. With welfare programs implemented and banking regulations installed, Roosevelt's new deal gave new life to the American economy and brought rise to a system that is in place even to this day.
Source: Hoffman, Elizabeth Cobbs, Edward J. Blum, and Jon Gjerde. "Chapter 8 Prejudice The Depression, the New Deal, and F.D.R." Major Problems in American History: Documents and Essays / Edited by Elizabeth Cobbs Hoffman, Edward J. Blum, Jon Gjerde. Boston, MA: Wadsworth Cengage Learning, 2012.

If you enjoyed my work
All proceeds from upvotes on this post are going to more Steem Power.
Also, if you're looking for a long term investment try out cloud mining with Genesis-Mining.com and their Sha-256 bitcoin mining LIFETIME contract.
Use the promo code "1jibey" for 3% off your order. It's a great opportunity, check it out!
Fascinating!
you are factually right but analytically (what causes what sequentially and what could have been done to prevent that) a little bit weaker. there are many concept out there to explain 1929 from Milton Friedman to FA Hayek to John Maynard Keynes.