Basic structure of the Nervous System 4
you can find third part here https://steemit.com/body/@skytoin/basic-structure-of-the-nervous-system-3
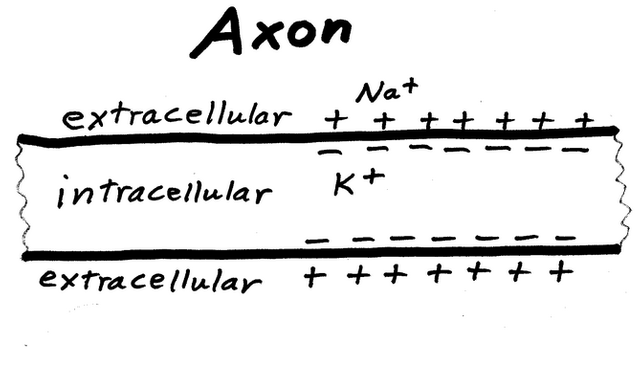
After a neuron was stimulated enough, it sends an electrical signal that travels down its axon to the next neuron. Speed of each signal stays approximately the same, but the frequency of signals can vary. The brain translates signals like computer reads binary code. The right question would how do we get that electricity in our bodies. Usually a body has equal amount of negative and positive charges, but some parts has more negative or positive charges. As we know from basic electricity opposite charges attract each other, to keep them separate (like in the battery) body has special barriers, before body needs to use the energy that their attraction creates. You can compare each neuron to a little battery in a body with its own separated charges. It needs special event to start the action that will brings charges together.
Basic electrical definitions would help I think. Voltage is electric potential difference, electric pressure or electric tension. In this example it’s a measure of potential energy generated by separate charges. Membrane potential is the terminology for difference in charge in a cell. Electrical potential difference can create a current in a body. Definition of a current is the flow of electricity (electric charge) from one point to another. Definition of resistance is a measure of the difficulty to pass an electric current through a material. Basically to relate this electrical terminology to nervous system, current means the flow of negative or positive ions (charged particles) through the resistance of cells’ membrane.
Resting neuron is like resting battery, all the positive and negative charges sit separately and it has no current. Neuron is more negative inside and extracellular space is more positive around a neuron in resting state. The value of resting membrane potential is -70 mV. Extracellular space is rich for positive sodium ions and inside neuron has plenty of positive potassium ions and negatively charged proteins. So in resting state negatively charged proteins is attracted to the walls by positive sodium ions from outside, while positive potassium ions are in the middle of the cell.