An Introduction To Blockchain Application Development — Part 1; Build Your Own Blockchain Application with ARK Logic

In this post we will get familiar with the architectural approaches that make
blockchain application development almost like a walk in the park. We will
address five simple, yet efficient software development approaches for
blockchain applications. Each of them being supported with code samples and
tutorials.
This is an introductory post, that will be followed by separate tutorials and
workshops where we will build a fully working blockchain application.
Bootstrapping The Development Environment Setup
Before we jump into blockchain application development, we always need to have:
- Our own chain running.
- The knowledge to launch a local node.
- Connect to some kind of public test blockchain network that is run and
maintained by someone else and out of our control.
We all know the sysadmin magic that had to be done in order to get a blockchain
node running in the past. As a consequence a lot of developers got turned away
by the sheer complexity of the development environment setup or missing
cryptographic libraries and implementations. Luckily for all of us, our HERO —**
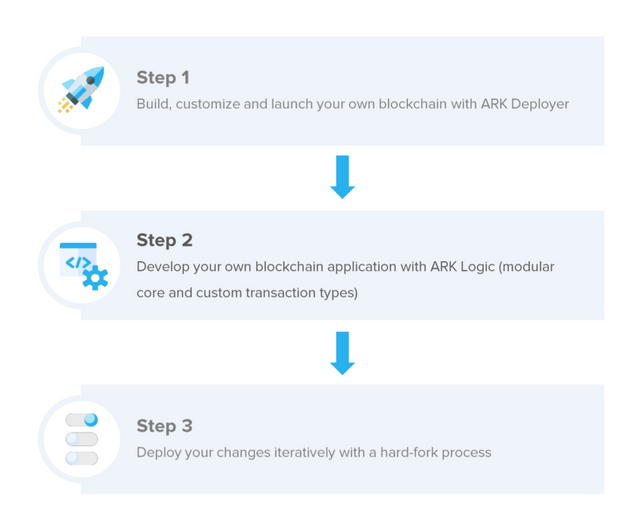
**The ARK Deployer came along. Delivering the
promise of seamless and easily customizable blockchain deployment in three
simple steps.
Everything we learned in the field (meetings with organizations, PoC projects
implementations, hackathons and workshops) combined with our expert knowledge
has guided us towards building a product to enable easy and simple deployment
of your very own custom chain in a only a few
minutes.
All ARK based bridgechains are accompanied with free and open-source SDK’s, that
enable you to jump right into application development and leave the blockchain
protocol and sysadmin details to be taken care of by our automation tools and
SDK implementations in more than 12 programming
languages. Feel free to join our friendly chat at
https://ark.io/slack and ask for help and guidance in
our #help channel.
With ARK’s **modular core **our distributed-servers/nodes running in the
background translate into **containers **— where you can deploy your own
blockchain based applications and you don’t need to worry about consensus
protocol or peer-to-peer network mechanics — it’s a protocol thing, just like
TCP/IP, well a lot more complex; but it’s there running in the background,
delivering security, trust and immutability — delivering the promise of
blockchain.
Distributed Blockchain Applications in General
From the start of my journey in the blockchain space, I always wanted to build
complex applications on top on this excellent technology. One of ARKs’ promises
was/is to deliver tools and best practices that will close this gap and make
blockchain application development a breeze. One of our first team
accomplishments towards this goal is ARK Logic
working hand in hand with the ARK Deployer.
This gives us the power to create agnostic blockchain applications, that can
be run within any blockchain based on ARK Core technology. By developing
applications on our plug-able core technology developers can
build blockchain agnostic applications, target bigger audiences and provide
cross-chain compatible solutions.
This introduces and further strengthens the role of the ARK Ecosystem, by
bringing in new interchain monetization services allowing businesses to fully
exploit and research new crypto driven business models. Our blockchain
application development approach is closing the gap between traditional
development practices by bridging the concept of software libraries and
blockchain development.

This is how we see the distributed blockchain applications development and
deployment on our core-technology stack:
- Blockchain application is an abbreviated form for decentralized
application-dapp, that can already be deployed as a blockchain module. - A dapp has its backend code running on a decentralized peer-to-peer network
(ARK). Contrast this with an app where the backend code is running on
centralized servers. - A dapp can have frontend code and user interfaces written in any language (just
like a normal application) that can make calls to its backend via simple API
calls, or by using any kind of protocol that was implemented as a communication
channel in the dApp module implementation (see point 1). - A dapp can also host its frontend on a decentralized network, in this case, the
language limitations must be compatible with ourcore-technologylanguage
landscape and our blockchain network servers as an application provider. - A dapp can implement only micro services, allowing modular design, easier
bug-fixing, and upgrading as a normal software application.
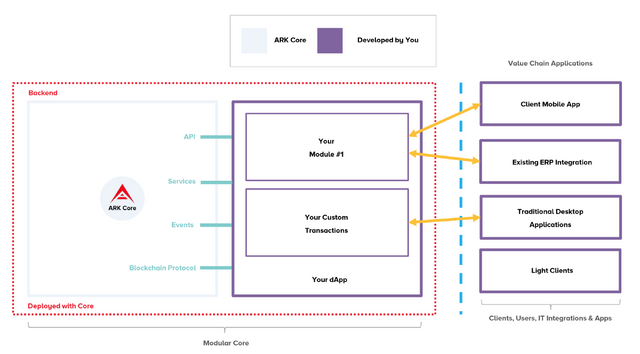
Ok, so what now? Now we can deploy a module, like in most web applications —
but where is “the blockchain/the ledger” and how do we use it?
Don’t worry, we got you covered with **ARK Logic — Enabling your application to
run in a modular fashion on the distributed network. **Your application life
cycle is maintained by our Core and is inherited by the overall life cycle of a
blockchain node. A strong benefit of plug-able applications/modules is having
access to the blockchain mechanics in a very simple and developer friendly way.
Blockchain interaction is something we take very seriously, and we deliver this
via the following approaches.
ARK Logic: Best Practices
In this section we will look into five core approaches that enable you to
seamlessly develop distributed blockchain applications on top of our platform.
As a developer you will learn:
- How to interact with the blockchain state.
- How to interact with the blockchain database.
- Learn to use events and react to state changes.
- Add new API endpoints via customizable HTTP server running within core nodes.
- Pack your blockchain application as a module and distribute it.
Interacting with the blockchain state
The core-blockchain package is the central entity around which everything
revolves. It provides a state-machine that controls the state of your node and
switches between states to sync, rollback or recover from a fork. It holds all
of the information that is important to know when you want to see what the
current state of your blockchain node is. Do not trust the database, trust the
in-memory data it exposes, as it’s updated in real-time.
Full Tutorial:
https://docs.ark.io/tutorials/core/plugins/how-to-interact-with-the-blockchain.html#getting-started
Interacting with the database
You can access blocks and transactions in a very simple and efficient way by
using the database plugin.
https://docs.ark.io/tutorials/core/plugins/how-to-interact-with-the-database.html#getting-started
Use events to listen and react to changes
Core provides a package called core-event-emitter which exposes an instance of
the Node.js EventEmitter. A common use-case is that your module will listen to
events that core emitted in order to process the data for monitoring. Your
module can also emit events that can be listened to by other plugins (or your
own for internal use).
https://docs.ark.io/tutorials/core/plugins/how-to-interact-with-events.html#listening-for-events
Add new API endpoints via customizable HTTP server running within core nodes
A common use-case for a plugin is that you process some data from within core
and want to make use of that data with an external application. The easiest way
to do this is through an HTTP server that exposes an API from which you request
the data.
https://docs.ark.io/tutorials/core/plugins/how-to-create-http-servers.html#getting-started
Pack and distribute your blockchain application as a module
The last piece of the puzzle is packing everything into a module and
distributing it to your blockchain network. Our plugins are modular by design,
meaning the concepts described above will all be already developed inside your
own module. Having your own module, enables you to publish it to the largest
package repository — npm, thus making it available to everyone.
Modules are very simple to write. At there core they are an object with a
register property, that is a function with the signature async function.
Additionally the plugin object has a required pkgproperty and several optional
properties including version.
Using the above mentioned concepts will make your blockchain application
development a breeze and it lowers the gap between enterprise application
developers and crypto developers. We encourage you to test these approaches
and start building your first blockchain application.
Next Steps: Part 2
Part two will cover introduction to developing custom transaction types with our
Generic Transaction Interface (GTI). The basic premise of GTI is to provide an
easy way to implement and include new transaction types in Core without the need
to modify more complex parts of the Core. It can be as simple as including
pre-defined templates depending on the use case of the blockchain or re-using
already present types and modify their parameters to introduce new ones.
Developing custom transaction types enables you to add your own custom logic and
data, validate it via existing consensus mechanisms and store it on-chain.
After that you will master all the skills needed to build blockchain
applications with ARK Logic. We will leverage that and build a blockchain
application together, from line 0 to the last readme instruction in the follow
up tutorials.
Follow us on social media ( Twitter | Facebook | Reddit | YouTube), join our community ( Slack | Discord ) and stay tuned to our blog on Medium. | Read the ARK Whitepaper Here