Ramesses

Around 1279 BC, Ramesses II, also known as Ramesses the Great, ascended the throne, and went on to build more temples, erect more statues and obelisks, and sire more children than any other pharaoh in history.[51] A bold military leader, Ramesses II led his army against the Hittites in the Battle of Kadesh (in modern Syria) and, after fighting to a stalemate, finally agreed to the first recorded peace treaty, around 1258 BC.[52] With both the Egyptians and Hittite Empire proving unable to gain the upper hand over one another, and both powers also fearful of the expanding Middle Assyrian Empire, Egypt withdrew from much of the Near East. The Hittites were thus left to compete unsuccessfully with the powerful Assyrians and the newly arrived Phrygians.
Egypt's wealth, however, made it a tempting target for invasion, particularly by the Libyan Berbers to the west, and the Sea Peoples, a conjectured[53][54] confederation of seafarers from the Aegean Sea. Initially, the military was able to repel these invasions, but Egypt eventually lost control of its remaining territories in southern Canaan, much of it falling to the Assyrians. The effects of external threats were exacerbated by internal problems such as corruption, tomb robbery, and civil unrest. After regaining their power, the high priests at the temple of Amun in Thebes accumulated vast tracts of land and wealth, and their expanded power splintered the country during the Third Intermediate Period.[55]
Third Intermediate Period (1069–653 BC)
Main article: Third Intermediate Period of Egypt
Following the death of Ramesses XI in 1078 BC, Smendes assumed authority over the northern part of Egypt, ruling from the city of Tanis. The south was effectively controlled by the High Priests of Amun at Thebes, who recognized Smendes in name only.[56] During this time, Berber tribes from what was later to be called Libya had been settling in the western delta, and the chieftains of these settlers began increasing their autonomy. Libyan princes took control of the delta under Shoshenq I in 945 BC, founding the Libyan Berber, or Bubastite, dynasty that ruled for some 200 years. Shoshenq also gained control of southern Egypt by placing his family members in important priestly positions.
In the mid-ninth century BC, Egypt made a failed attempt to once more gain a foothold in Western Asia. Osorkon II of Egypt, along with a large alliance of nations and peoples, including Persia, Israel, Hamath, Phoenicia/Canaan, the Arabs, Arameans, and neo Hittites among others, engaged in the Battle of Karkar against the powerful Assyrian king Shalmaneser III in 853 BC. However, this coalition of powers failed and the Neo Assyrian Empire continued to dominate Western Asia.
Libyan Berber control began to erode as a rival native dynasty in the delta arose under Leontopolis. Also, the Nubians of the Kushites threatened Egypt from the lands to the south.
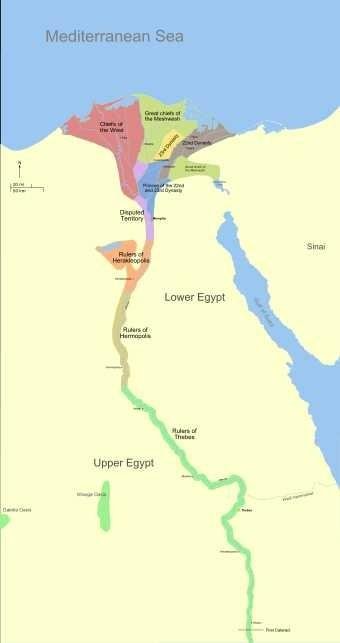
Around 730 BC Libyans from the west fractured the political unity of the country
Drawing on millennia of interaction (trade, acculturation, occupation, assimilation, and war[58]) with Egypt,[59] the Kushite king Piye left his Nubian capital of Napata and invaded Egypt around 727 BC. Piye easily seized control of Thebes and eventually the Nile Delta.[60] He recorded the episode on his stela of victory. Piye set the stage for subsequent Twenty-fifth dynasty pharaohs,[61] such as Taharqa, to reunite the "Two lands" of Northern and Southern Egypt. The Nile valley empire was as large as it had been since the New Kingdom.
The Twenty-fifth dynasty ushered in a renaissance period for ancient Egypt.[62] Religion, the arts, and architecture were restored to their glorious Old, Middle, and New Kingdom forms. Pharaohs, such as Taharqa, built or restored temples and monuments throughout the Nile valley, including at Memphis, Karnak, Kawa, Jebel Barkal, etc.[63] It was during the Twenty-fifth dynasty that there was the first widespread construction of pyramids (many in modern Sudan) in the Nile Valley since the Middle Kingdom.[64][65][66]
Piye made various unsuccessful attempts to extend Egyptian influence in the Near East, then controlled by Assyria. In 720 BC, he sent an army in support of a rebellion against Assyria, which was taking place in Philistia and Gaza. However, Piye was defeated by Sargon II and the rebellion failed. In 711 BC, Piye again supported a revolt against Assyria by the Israelites of Ashdod and was once again defeated by the Assyrian king Sargon II. Subsequently, Piye was forced from the Near East.[67]
From the 10th century BC onwards, Assyria fought for control of the southern Levant. Frequently, cities and kingdoms of the southern Levant appealed to Egypt for aid in their struggles against the powerful Assyrian army. Taharqa enjoyed some initial success in his attempts to regain a foothold in the Near East. Taharqa aided the Judean King Hezekiah when Hezekiah and Jerusalem was besieged by the Assyrian king, Sennacherib. Scholars disagree on the primary reason for Assyria's abandonment of their siege on Jerusalem. Reasons for the Assyrian withdrawal range from conflict with the Egyptian/Kushite army to divine intervention to surrender to disease.[68] Henry Aubin argues that the Kushite/Egyptian army saved Jerusalem from the Assyrians and prevented the Assyrians from returning to capture Jerusalem for the remainder of Sennacherib's life (20 years).[69] Some argue that disease was the primary reason for failing to actually take the city; however, Senacherib's annals claim Judah was forced into tribute regardless.[70]
Sennacherib had been murdered by his own sons for destroying the rebellious city of Babylon, a city sacred to all Mesopotamians, the Assyrians included. In 674 BC Esarhaddon launched a preliminary incursion into Egypt; however, this attempt was repelled by Taharqa.[71] However, in 671 BC, Esarhaddon launched a full-scale invasion. Part of his army stayed behind to deal with rebellions in Phoenicia, and Israel. The remainder went south to Rapihu, then crossed the Sinai, and entered Egypt. Esarhaddon decisively defeated Taharqa, took Memphis, Thebes and all the major cities of Egypt, and Taharqa was chased back to his Nubian homeland. Esarhaddon now called himself "king of Egypt, Patros, and Kush", and returned with rich booty from the cities of the delta; he erected a victory stele at this time, and paraded the captive Prince Ushankhuru, the son of Taharqa in Nineveh. Esarhaddon stationed a small army in northern Egypt and describes how "All Ethiopians (read Nubians/Kushites) I deported from Egypt, leaving not one left to do homage to me".[72] He installed native Egyptian princes throughout the land to rule on his behalf.[73] The conquest by Esarhaddon effectively marked the end of the short lived Kushite Empire.
However, the native Egyptian rulers installed by Esarhaddon were unable to retain full control of the whole country for long. Two years later, Taharqa returned from Nubia and seized control of a section of southern Egypt as far north as Memphis. Esarhaddon prepared to return to Egypt and once more eject Taharqa; however, he fell ill and died in his capital, Nineveh, before he left Assyria. His successor, Ashurbanipal, sent an Assyrian general named Sha-Nabu-shu with a small, but well trained army, which conclusively defeated Taharqa at Memphis and once more drove him from Egypt. Taharqa died in Nubia two years later.

Twenty-fifth Dynasty
His successor, Tanutamun, also made a failed attempt to regain Egypt for Nubia. He successfully defeated Necho, the native Egyptian puppet ruler installed by Ashurbanipal, taking Thebes in the process. The Assyrians then sent a large army southwards. Tantamani (Tanutamun) was heavily routed and fled back to Nubia. The Assyrian army sacked Thebes to such an extent it never truly recovered. A native ruler, Psammetichus I was placed on the throne, as a vassal of Ashurbanipal, and the Nubians were never again to pose a threat to either Assyria or Egypt.