primary reformer 61-101-B PID(proprtional Integral Derivative
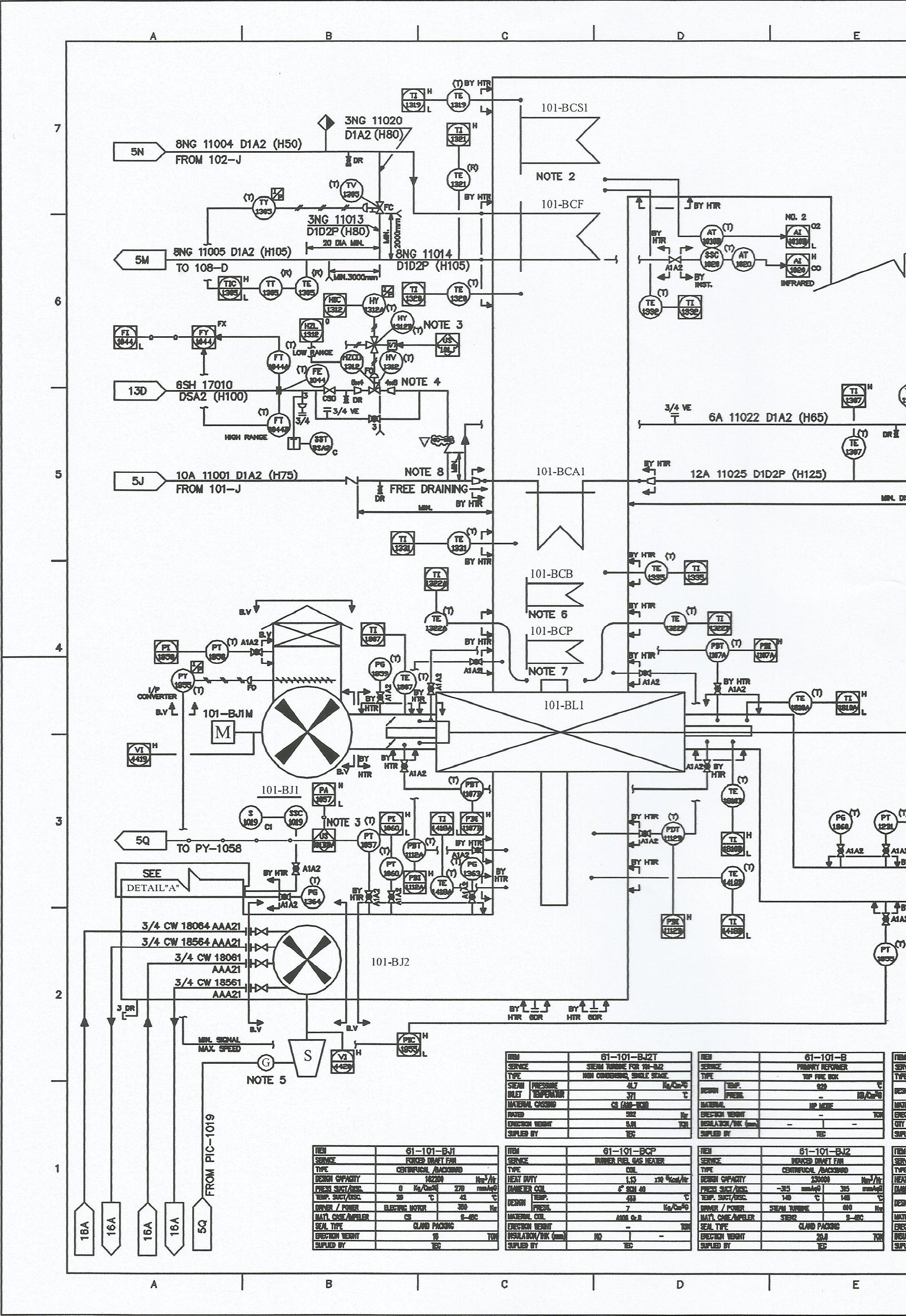
The Proportional Integral Derivative (PID) controller is one of the most widely used types of controllers in the industry today. PID controller consists of three components, namely component Proportional (P), Integral component (I) and Derivative components (D). These three components are complementary to each other, so that the weaknesses in one component can be covered by other components. Components I and D can not stand alone and are always combined with the P component, being a PI or PID controller. The PID controller will issue a control action by comparing errors or errors that are the difference between process variables and setpoints, which will be used as controller inputs to issue control signals (u (t)).
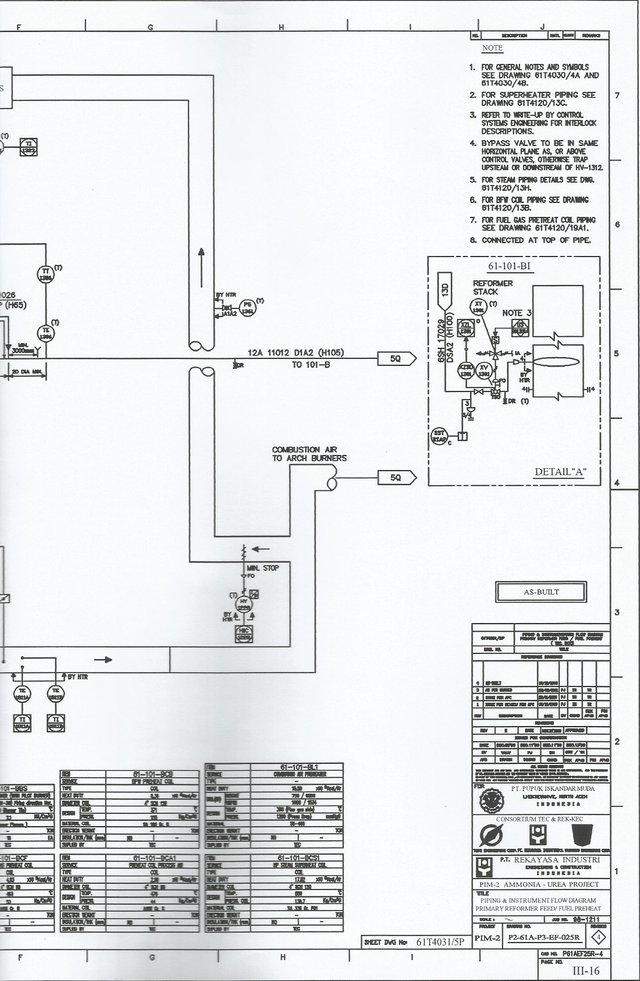
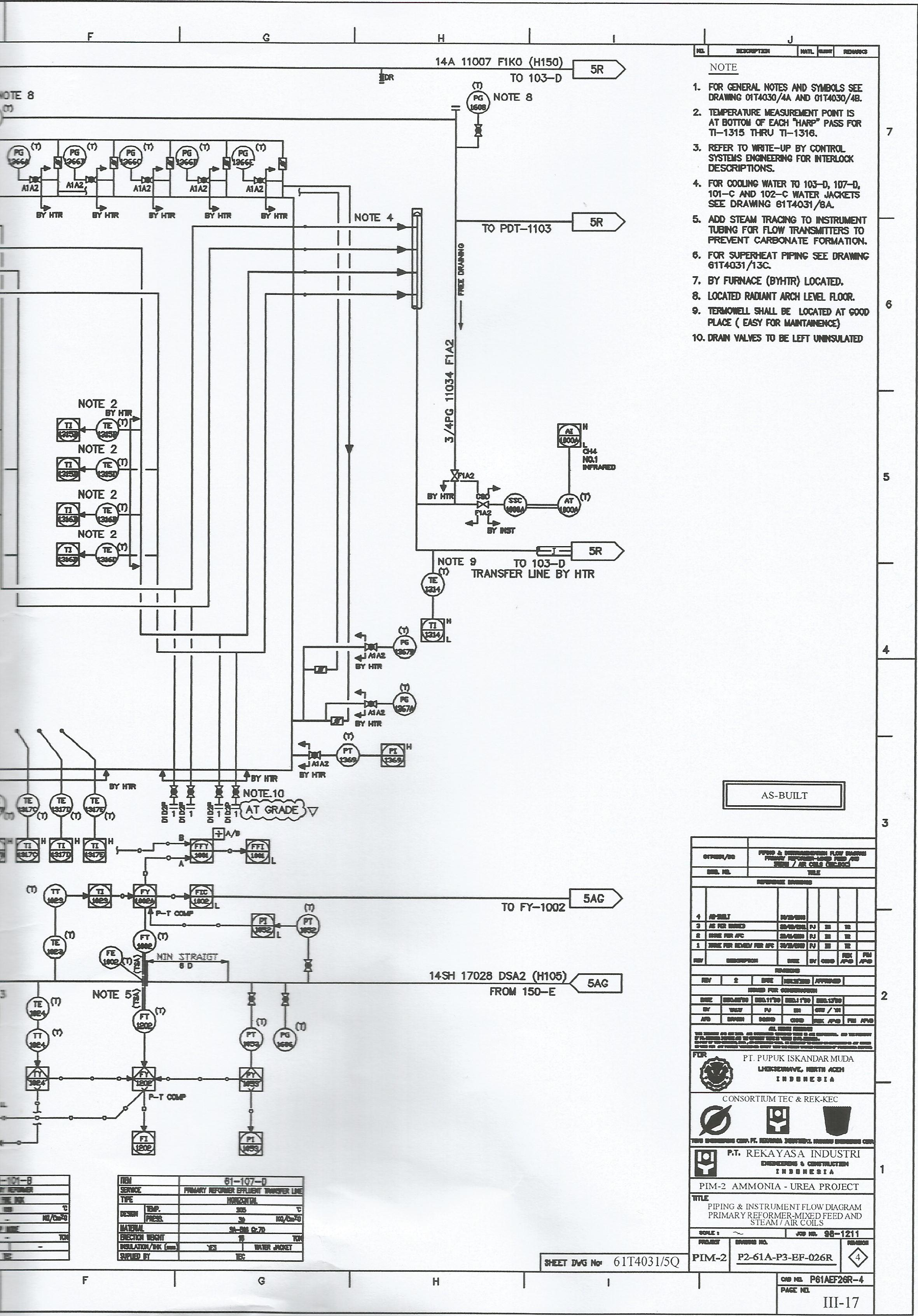
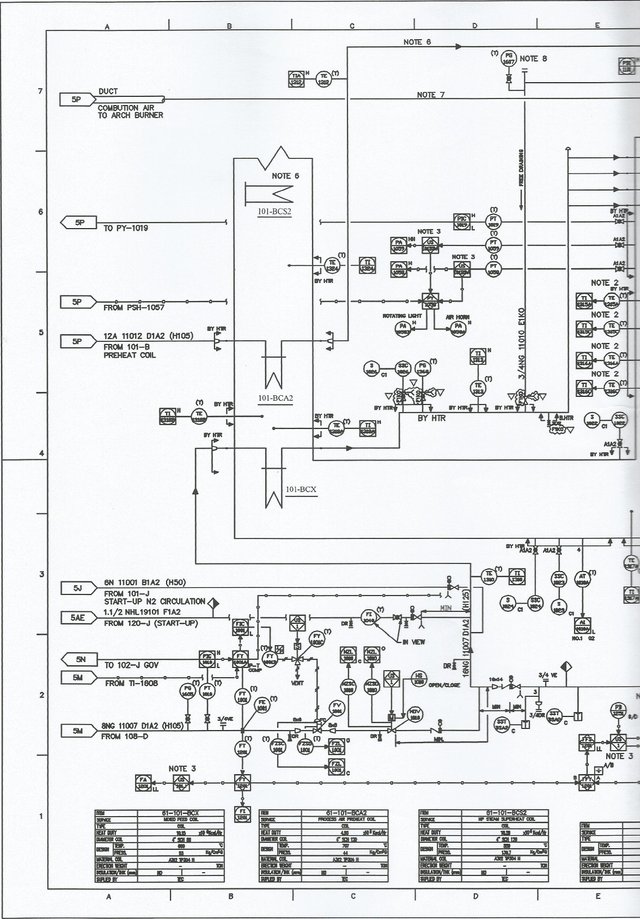
Influence on the system:
Increase or decrease stability.
Can improve transient response especially: rise time, settling time
Reduce (not eliminate) Steady state error
Nb: to get rid of Ess, it takes big KP, which will make the system more unstable
Proportional Controller gives a direct (comparable) effect on error. The bigger the error, the greater the control signal the controller generates. For more details then see the following picture.
Influence on the system:
Eliminates Steady State Error
Slower response (compared to P)
Can Increase Instability (because it adds order to the system)
The change of control signal is proportional to the error change. The bigger the error, the faster the control signal increases / changes. More details then see the following picture
Influence on the system:
Eliminates Steady State Error
Slower response (compared to P)
Can Increase Instability (because it adds order to the system)
The change of control signal is proportional to the error change. The bigger the error, the faster the control signal increases / changes. More details then see the following picture
congratulations to watch this video may be useful for the needy
Hopefully this post is useful for all users of steemit.
thanks steemit