Acute Pancreatitis, causes, diagnosis & Treatment
Acute Pancreatitis, causes, diagnosis & Treatment
Acute pancreatitis (AP) is inflammation of the pancreas. It occurs suddenly and causes pain in the upper abdominal (or epigastric) region. The pain often radiates to your back.
AP can also involve other organs. It can also develop into chronic pancreatitis if you have continued episodes.
What causes acute pancreatitis?
Acute pancreatitis is caused directly or indirectly. Direct causes affect the pancreas itself, its tissues, or its ducts. Indirect causes result from diseases or conditions that originate somewhere else in your body.
Gallstones are one of the major causes of acute pancreatitis. Gallstones can lodge in the common bile duct and block the pancreatic duct. This impairs fluid from flowing to and from the pancreas and causes damage.
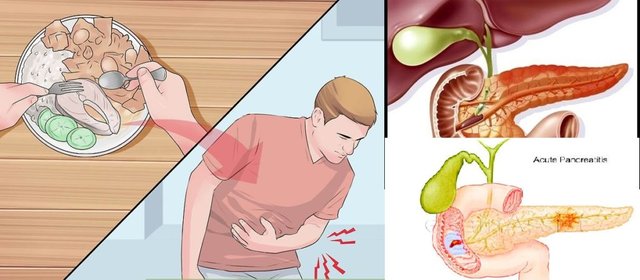
Direct causes
Other direct causes of acute pancreatitis include:
sudden immune system attacks on the pancreas, or autoimmune pancreatitis
pancreatic or gallbladder damage from surgery or injury
excessive fats called triglyceridesin your blood
Indirect causes
Indirect causes of acute pancreatitis include:
alcohol abuse
cystic fibrosis, a serious condition that affects your lungs, liver, and pancreas
Kawasaki disease, a disease that occurs in children younger than 5 years old
viral infections like mumpsand bacterial infections like mycoplasma
Reye’s syndrome, a complication from certain viruses that can also affect the liver
certain medications containing estrogen, corticosteroids, or certain antibiotics
Who is at risk for acute pancreatitis?
Drinking too much alcohol can put you at risk for pancreatic inflammation. The National Institutes of Health (NIH) defines “too much” as more than one drink a day for women and a maximum of two drinks a day for men. Men are more at risk than women for developing alcohol-related pancreatitis.
Smoking tobacco also increases your chance of AP. Smoking and drinking rates are similar in black and white Americans, but black Americans are more than two times as likely to develop AP. A family history of cancer, inflammation, or another pancreatic condition also puts you at risk
Recognizing the symptoms of acute pancreatitis
The predominant symptom of acute pancreatitis is abdominal pain.
Pain may vary depending on certain factors. These include:
pain within minutes of drinking or eating food
pain spreading from your abdomen to your back or left shoulder blade area
pain that lasts for several days at a time
pain when you lie on your back, more so than when sitting up
Other symptoms can also increase the pain and discomfort. These include:
fever
nausea
vomiting
sweating
jaundice(yellowing of the skin)
diarrhea
bloating
When any of these symptoms are accompanied by abdominal pain, you should seek immediate medical care.
Diagnosing acute pancreatitis
Your doctor can diagnose AP by using blood tests and scans. The blood test looks for enzymes (amylase and lipase) leaking from the pancreas. An ultrasound, CT, or MRI scan allows your doctor to see any abnormalities in or around your pancreas. Your doctor will also ask about your medical history and ask you to describe your discomfort.
Treating acute pancreatitis
Often you will be admitted to the hospital for more testing and to make sure you get enough fluids, usually intravenously. Your doctor may order medications to reduce pain and treat any possible infections. If these treatments don’t work, you may need surgery to remove damaged tissue, drain fluid, or correct blocked ducts. If gallstones caused the problem, you may need surgery to remove the gallbladder.
If your doctor concludes that a medication is causing your acute pancreatitis, stop using that medication right away. If a traumatic injury caused your pancreatitis, avoid the activity until you’re fully recovered from treatment. Check with your doctor before increasing your activity.
You may experience a lot of pain after acute pancreatitis, surgery, or other treatments. If prescribed pain medication, be sure to follow your doctor’s plan to reduce your discomfort once you get home. Avoid smoking completely, and drink a lot of fluids to make sure you don’t get dehydrated.
If pain or discomfort is still unbearable, it is important to check back with your doctor for a follow-up evaluation.
Acute pancreatitis is sometimes linked with type 2 diabetes, which affects your insulin production. Eating foods like lean protein, leafy vegetables, and whole grains can help your pancreas produce insulin more regularly and gently.
Lifestyle and diet
Stay hydrated at all times. Keep a water bottle or an electrolyte-infused drink like Gatorade.
Help prevent AP by limiting the amount of alcohol you drink. If you’ve already had pancreatitis and haven’t made lifestyle changes, it’s possible to develop it again. Children, and teens under the age of 19, should not take aspirin unless their doctor prescribes it. Aspirin can cause Reye’s syndrome, which is a known trigger for acute pancreatitis.
Complications of acute pancreatitis
Acute pancreatitis can cause pseudocysts in your pancreas. These fluid-filled sacks can lead to infections and even internal bleeding. Acute pancreatitis can also disrupt the balance of your body chemistry. This can lead to more complications.
You might also face the possibility of diabetes or kidney issues that lead to dialysis. Or malnutrition, if your acute pancreatitis is severe, or if you develop chronic pancreatitis over time.
In some people, acute pancreatitis can be the first sign of pancreatic cancer. Talk to your doctor about treatment as soon as you’re diagnosed with acute pancreatitis to avoid complications. Quick and effective treatment reduces your risk of complications significantly.
welcome to my world