LIVER CANCER: HEPATOCELLULAR CARCINOMA THE CAUSES THAT PRODUCE, THE SYMPTOMS, TREATMENT AND PREVENTION
LIVER CANCER: HEPATOCELLULAR CARCINOMA
THE CAUSES THAT PRODUCE, THE SYMPTOMS, TREATMENT AND PREVENTION
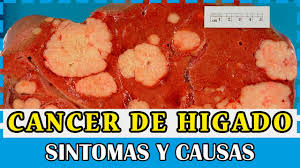
It is a cancer that starts in the liver.
CAUSES
Hepatocellular carcinoma is responsible for most liver cancers. This type of cancer is more common in men than in women. Generally, people 50 years of age or older are diagnosed.
Hepatocellular carcinoma is not the same as cancer with metastases to the liver, which begins in another organ (such as the breast or colon) and spreads to the liver.
In most cases, the cause of liver cancer is prolonged damage and scarring of the liver (cirrhosis). Cirrhosis can be caused by:
Excessive consumption of alcohol
Autoimmune diseases of the liver
Infection with hepatitis B or C virus
Prolonged (chronic) liver inflammation
Iron overload in the body (hemochromatosis)
People with hepatitis B or C are at risk for liver cancer, even if they do not have cirrhosis.
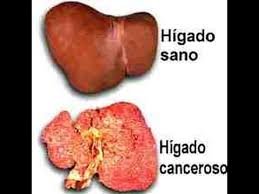
SYMPTOM
Symptoms of liver cancer may include any of the following:
Abdominal tenderness or pain, especially in the upper right quadrant
Tendency to bleeding or bruising
Enlargement of the abdomen
Yellowing of the skin or eyes (jaundice)
Unexplained weight loss
Tests and exams
The doctor will perform a physical examination and ask questions about the symptoms. The test may show a sensitive and enlarged liver or other signs of cirrhosis.
If your doctor suspects liver cancer, tests that may be ordered include:
CT scan of the abdomen
Abdominal ultrasound
Liver biopsy
Liver enzymes (liver function tests)
Magnetic Resonance of the Liver
Alpha-fetoprotein in serum
Some people who have a high chance of developing liver cancer may have blood tests and regular ultrasound scans to see if they are developing tumors.
To accurately diagnose hepatocellular carcinoma, a biopsy of the tumor is necessary.
TREATMENT
Treatment depends on how advanced the cancer is.
Surgery may be done if the tumor has not spread. Before surgery, the tumor can be treated with chemotherapy to reduce its size. This is done by injecting the medication directly into the liver with a catheter or by administering it intravenously (by IV).
Radiation treatments in the cancer area can also help. But in people who have cirrhosis in the liver or other liver diseases it is difficult to carry out radiation
Ablation (excision) is another method that can be used. Extirpate means to destroy. Types of ablation include the use of:
Microwave or radio waves
Ethanol (an alcohol) or acetic acid (vinegar)
Extreme cold (cryoablation)
A liver transplant may be recommended for certain people who have cirrhosis and cancer.
If the cancer can not be removed surgically or if it has spread beyond the liver, there is usually no likelihood of a long-term cure. Instead, treatment focuses on improving and extending life. In that case, the treatment is chemotherapy, which can be taken as pills or given through a vein (intravenously).
SUPPORT GROUPS
Stress caused by the disease can be alleviated by joining a cancer support group. Sharing with other people who have common experiences and problems can help you not feel alone.
EXPECTATIONS (PROGNOSIS)
If the cancer can not be completely removed, the disease is usually fatal within 3 to 6 months. However, survival may vary depending on how advanced the cancer is at diagnosis and how effective the treatment is.
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Call your healthcare provider if you have continued abdominal pain, especially if you have a history of liver disease.
PREVENTION
Preventive measures include:
Prevention and treatment of viral hepatitis can help reduce risk. Hepatitis B vaccine in childhood may reduce the risk of liver cancer in the future.
Do not consume excessive amounts of alcohol.
People with certain types of hemochromatosis (iron overload) may need liver cancer screenings.
People with hepatitis B or C or cirrhosis may be screened for liver cancer.