Petroleum
What is Petroleum?
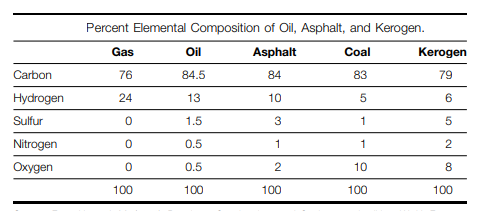
Petroleum is a naturally occurring substance consisting of organic compounds in the form of gas, liquid, or semisolid. Organic compounds are carbon molecules that are bound to hydrogen (e.g., hydrocarbons) and to a lesser extent sulfur, oxygen, or nitrogen.
Petroleum is also refer to has black gold
Petroleum is operationally defined as any hydrocarbon mixture that can be recovered through a drill pipe.
Origin of Petroleum
By referring to different grounds from two opposing theoritical hypothesis, petroleum origin and formation still become a polarized topic of scientists' debates. These theories are abiogenesis and biogenesis.
- Abiogenesis or inorganic origin of petroleum, is the theory which suggest that petroleum comes from the underneath part of the mantle very long time ago before the existence of life on earth.
- Biogenesis or organic origin suggests that petroleum is formed from biological matters, left behind by very ancient lives. These matters become subjected to high temperature under the absence of oxygen. Biogenesis is currently more accepted by many people due to how its supported by various valid grounds.
Engler Theory
According to this theory, petroleum is of animal origin. He suggested that petroleum is formed by the decay and decomposition of animals under high pressure and temperature. He suggested the following facts:
- Experiment the destructive distillation of fish oil and other animal fats under high pressure and temperature give a similar product to the natural petroleum.
- Presence of brine or sea water together with petroleum.
- Presence of optically active compounds, nitrogen and sulfur compounds and fossils in the petroleum area.
Disadvantages
It fails to explain the presence of chlorophyll, coal deposits in the vicinity of the oil fields.
Composition
Petroleum is composed of a great variety of molecules that range in molecular weight from methane (16g/mol) to the asphaltenes ( tens of thousands of g/mol).
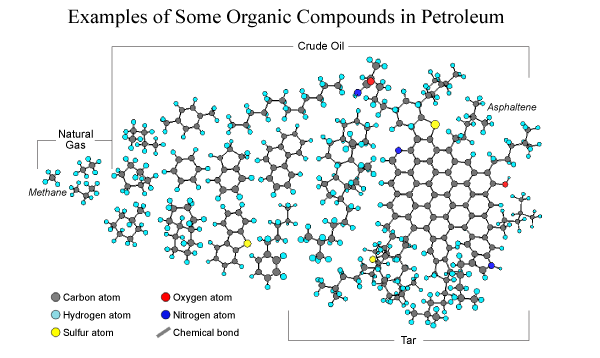
Compounds can be present as gases or liquids, and condensates. The condensates are hydrocarbons retrieved as gases or liquids that upon cooling change into liquids or solids.
- The gas phase includes low molecular weight hydrocarbons. These natural gases include methane, ethane, propane, and butane.
- The liquid phase is commonly referred to as crude oil. Although petroleum is primarily composed of wide range of more complex hydrocarbons, trace amounts of other chemicals are present. These include;
(1) gases, such as nitrogen, carbon iv oxide, hydrogen sulphide and helium
(2) trace metals, particularly vanadium, zinc, nickel and mercury
(3) organic compounds that contain nitrogen, sulfur, and oxygen. - The semisolid petroleum is tar, which is dominated by larger complex hydrocarbons and asphaltenes.
The major classes of hydrocarbons found in petroleum are the paraffins, isoparaffins, cycloparaffins, aromatics, and olefins
Petroleum Formation
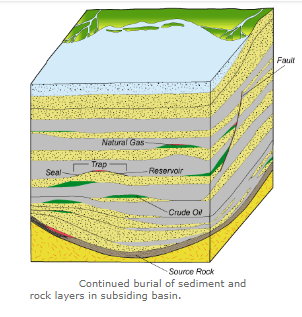
Petroleum formation takes place in the sedimentary basins, which are areas where the earth's crust subsides and the sediments accumulate within the resulting depression. As the sedimentary basin continues to subside, sediment accumulation continue to fill the depression. This results in a thickening sequence of sediment layers in which the lower sediment layers eventually solidify into sedimentary rocks as they experience greater pressures and temperatures with burial depth. The sediment layers that accumulate vary in character because the sources and the deposition settings of the sediments at least one of the sediment layers contain the remains of deceased plants or microorganisms.
As organic rich sediment layers are buried by deposition of overlying sediments in the subsiding basin, the sediments are compressed and eventually lithified into rocks referred to as black shale, bituminous limestone, or coal. Methane producing microorganisms referred to as methanogens may thrive under certain favorable conditions within the organic rich sediment layer during its early burial. These microorganisms consume portions of the organic matter as a food source and generate methane as a byproduct. This methane , which is typically the main hydrocarbon in natural gas, has a distinct neutron deficiency in its carbon nuclei (i.e., carbon isotopes), which allows microbial natural gas to be readily distinguished from methane generated by thermal processes later in basin. If the impermeable sediment layers, called seals, hinder the upward migration of microbial gas, the gas may be collected in underlying porous sediments, called reservoirs
Burial of the organic rich rock layer may continue in some subsiding basins to depths of 6,000 to 18,000 feet (1830 to 5490 m). At these depths, the organic rich rock layer is exposed to temperatures of 150 to 350 Fahrenheit (66 to 177 degree) for a few million to tens of millions years. The organic matter within the organic rich rock layer begins to cook during this period of heating and portions of it thermally decompose into crude oil and natural gas.
This process of cooking petroleum out of an organic rich rock layer involves the appropriate combination of temperature and time and is referred to as thermal maturation. If the original source of the organic matter is mostly higher plants (e.g., trees, shrubs, and grasses), natural gas will be the dominant petroleum generated with lesser amounts of crude oil generation. If the original source of the organic matter is plankton (e.g., algae, copepods, and bacteria), crude oil will be the dominant petroleum generated with lesser amounts of natural gas generation. Organic rich rock layer that have undergone this process of petroleum generation are considered to be thermally mature and referred to as source rocks.
Petroleum has a lower density than the water that occupies pores, voids and cracks in the source rock and the overlying rock and sediment layers. This density difference forces the generated petroleum to migrate upwards by buoyancy until sealed reservoirs in the proper configurations serve as traps that concentrate and collect the petroleum. Some of the generated natural gas may not migrate out and away from its source rock, but instead remains within microscopic pores and dissolved in the organic matter of its source rock. This retained natural gas has proven to be an economically significant resource that is referred to as shale gas.
Characterization Base on Standard
Crude oils quality are tell by API gravity (a measure of density) and sulfur content.
- API Gravity (Density): it indicate how light or heavy crude is. Lighter crude contain higher proportions of small molecules and its process in the refinery into gasoline, jet fuel, and diesel. Heavier crude contain higher proportions of large molecules and it can be used as heavy industrial fuels, asphalt, and other heavy products or be process into smaller molecules that can go into the transportation fuels products.
API gravity varies inversely with density (i.e., the lighter the crude , the higher its API gravity) and its measure in degree.
35 degree API indicates a typical light crude and 25 degree API indicate typical heavy crude.
- Sulfur content: sulfur in crude is undesirable, the higher the sulfur content in crude, the poor the quality and the lesser the sulfur content, the better the quality of the crude.
References
https://energy.usgs.gov/geochemistrygeophysics/geochemistryresearch/organicoriginsofpetroleum.aspx
http://booksite.elsevier.com/9780120885305/casestudies/01-Ch26-P088530web.pdf
https://www.researchgate.net/publication/226441668_The_Origin_of_Petroleum

http://connect.spe.org/blogs/donatien-ishimwe/2014/09/11/origin-and-formation-of-petroleum
https://www.theicct.org/sites/default/files/publications/ICCT05_Refining_Tutorial_FINAL_R1.pdf
https://energy.usgs.gov/GeochemistryGeophysics/GeochemistryResearch/OrganicOriginsofPetroleum.aspx