Mining 101
PART ONE: AN OVERVIEW
Blockchain miner defined:
A blockchain miner is an individual or group who use computational hardware to validate and include new transactions within a blockchain network. In doing so miners are rewarded with Cyrptocurrency. In layman’s term a miner can be described as a person who runs a program on their computer in return for Cyrptocurrencies.Using a personal laptop to mine Cyrptocurrencies:
Mining on personal hardware (laptops, CPU’s, cellular devices ) is a great way to learn and get a taste of mining. Emphasis must be placed on “taste” as it is no longer profitable to mine Cyrptocurrencies on personal hardware. With the mining industry genesis in 2009, personal hardware such as laptops and computers were used to profitably validate and include transactions in return for Bitcoin (BTC). As more computers joined the network the difficulty to validate and include transactions increased. Early adopters were prospers and monopolies were established based on economies of scale. As bitcoin gained traction alternative Cyrptocurrencies utilising different protocols began to emerge. This created the incentive for miners and startup companies to build effective and efficient mining rigs. In order to mine profitably one is required to build a GPU rig or purchase an ASIC miner. It’s important to decide on the Cyrptocurrency you will mine before purchasing hardware to ensure it is compatible. Other important considerations include the networks protocol, total hash rate difficulty and block rewards.The mining process:
Miners compete against one another to solve a mathematical problem based on a cryptographic hash algorithm. When a miner finds a solution, the transactions within the block are considered to be confirmed and the miner is rewarded. Miners receive two forms of remuneration namely solved block rewards and transaction fees. The mining process for BTC can be seen below:
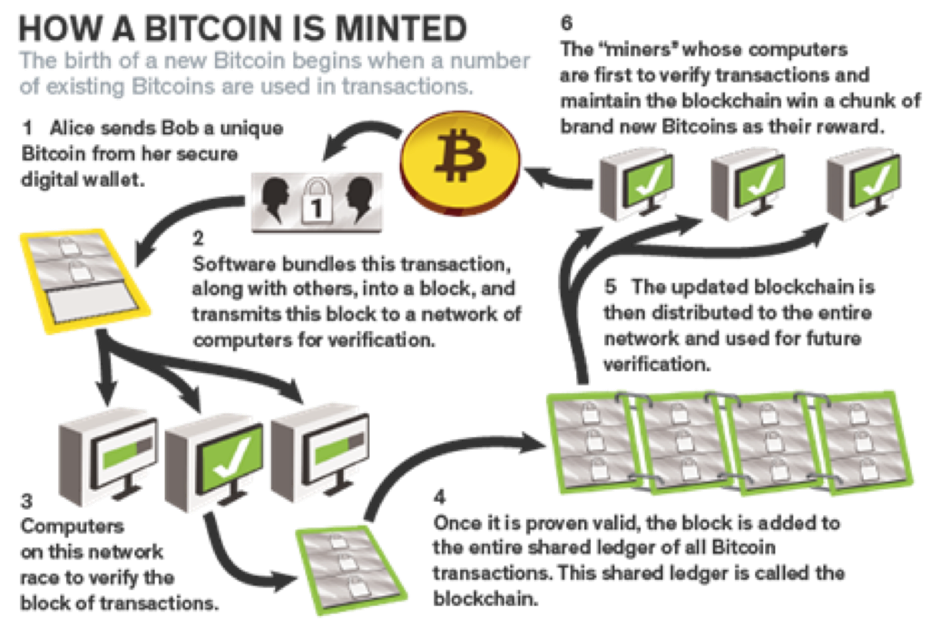
BTC protocol dictates that its reward structure decreases every 210 000 blocks, approximately four years. A miner who finds the block on the BTC network receives 12.5 BTC. Miners also receive remuneration in the form of transaction fees. The transaction fees offset the decreasing block rewards. The incentive to mine ensures global participation resulting in a decentralized network. Miners essentially run computer hardware 24/7 dedicated to a blockchain network in return for Cyrptocurrencies.
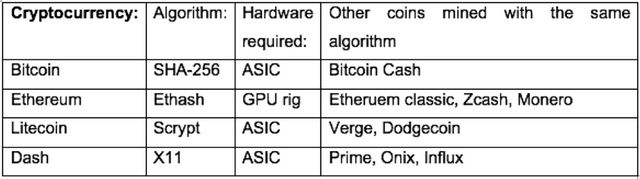
- Protocols: (SHA-256, Ethash, Script, X11)
Two primary protocols exist namely proof of work and proof of stake. Furthermore, these protocols make use of different algorithms. A short video of the difference between proof of work and proof of stake can be seen below:
With the emergence of alternative Cryptocurrencies individuals and groups have adopted different protocols to run their blockchain networks on. The protocol dictates the type of mining that is to be done, rewards to be paid and network difficulty adjustments. Furthermore the algorithm will influence the hardware and software a miner requires to have a profitable operation. It is important to note that hardware purchased for one cryptocurrency may not be compatible to mine another.
- Difficulty:
The complexity for solving an algorithms on a blockchain network have a positive correlation to the network hash rate. In other words and increase in computing power (hash rate) causes an increase in the difficulty to solve and validate blocks.
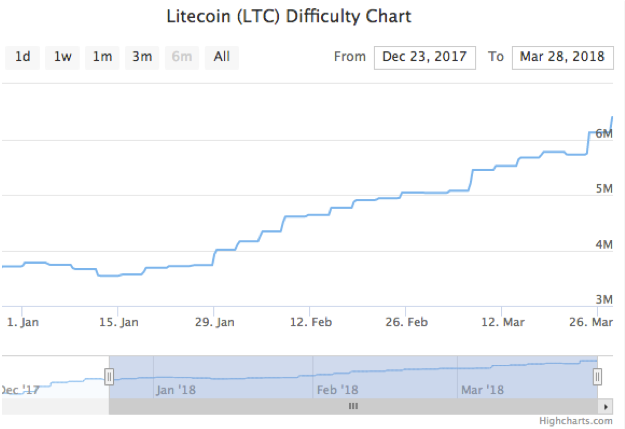
Source: CoinWarz LTC difficulty has almost doubled in the first quarter of 2018. Coupled by a decrease in price very few hardware products in the current market will breakeven and ultimately make a profitable return.
Source: CoinWarz
LTC difficulty has almost doubled in the first quarter of 2018. Coupled by a decrease in price very few hardware products in the current market will breakeven and ultimately make a profitable return.
- Hash rate:
The hash rate is the speed of the computer hardware that is completing an operation on the blockchain network. It is a measure of the processing power on a blockchain network. A higher hash rate results in a higher chance of a miner finding the next block and being rewarded. This is explained simply in the video below:
MARCH 30, 2018
https://steemit.com/@a-0-0