// Space NEWS // SpaceX authorized to reduce the number of satellites
The U.S. Federal Communications Commission (FCC), the equivalent of the Overseas Telecom Regulatory Authority, has authorized SpaceX to reduce the number of satellites in its domestic broadband constellation from 4,425 to 4,409 and to operate at an orbital altitude lower than previously authorized.

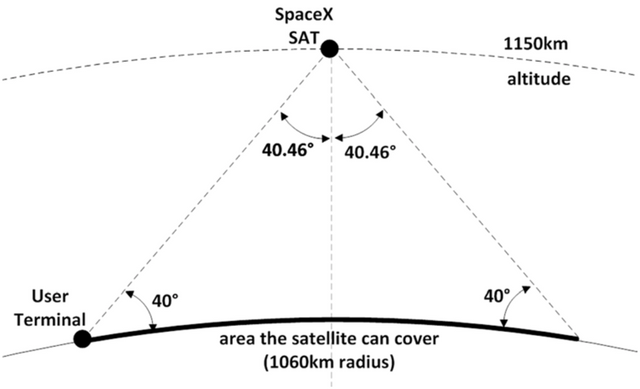
While originally planned to operate at an altitude of 1,150 km, 1,584 of Elon Musk’s SpaceX satellites will now operate at 550 km, with the necessary modifications to their operation also granted.
In addition, SpaceX has been authorized to use Ku-band gateway earth stations for less than 75 low-level non-geostationary satellites orbits (NGSO). “After review of the record, we conclude that grant of the SpaceX Modification Application will serve the public interest”, the FCC decided in a document made public last weekend.
“Grant of this modification will allow SpaceX to make efficient use of valuable spectrum resources more safely, quickly, and cost-effectively as it initiates a new generation of broadband services available to customers worldwide, including those in areas previously underserved or even totally unserved by other broadband solutions”.
After SpaceX requested in November 2018, competing suppliers OneWeb and Kepler filed petitions against SpaceX, citing a greater opportunity for interference. However, the FCC has pointed out that there will be a decrease in the number of SpaceX satellites.
Avoid interference and collisions
"We thus conclude that the number of spatial configurations that have the potential for generating interference between SpaceX and any other NGSO FSS system in the same processing round is expected to remain approximately unchanged. We consider this to be a fundamental element in assessing whether there would be significant interference problems as a result of granting the proposed modification”, the Commission said.
The gateways now using the 14-14.5GHz band will also use larger antennas with narrower beams, which, according to the FCC, will "be more capable of avoiding interference into satellites of other NGSO FSS systems”.
SpaceX also describes how it would avoid potential collisions – through a propulsion system so that it can manoeuvre satellites to avoid collisions – the FCC also noted that this risk was nul or near zero. The launch of global broadband satellites for homes was originally announced in November 2016, with SpaceX indicating that each unit would weigh 386 kg and measure 4x1.8x1.2m.
“The system is designed to provide a wide range of broadband and communications services for residential, commercial, institutional, governmental and professional users worldwide," said SpaceX management at the time.
However, the company has seen difficulties; last February, the Pentagon said it was planning an investigation into the certification granted to SpaceX’s Falcon launch vehicle family to
determine whether the US Air Force was following the right guidelines. SpaceX had been certified to launch military satellites in 2015.
“Our objective is to determine whether the U.S. Air Force complied with the Launch Services New Entrant Certification Guide when certifying the launch system design for the Evolved Expendable Launch Vehicle-class SpaceX Falcon 9 and Falcon Heavy launch vehicles,” U.S. Department Of Defense Deputy Inspector General Michael Roark said in the memo.
In January, SpaceX also announced what it called a "necessary cutback" while cutting 10% of its staff to deal with the "extraordinarily difficult challenges ahead".
Source : ZDNet

I've made a lot of articles with tools, explanations and advises to show you how to protect your privacy and to secure your computer, GO check them out!
This is my guide To Secure your PC after a fresh installation of Windows
If you think that your Phone or your PC has been hacked, you have to check it right now!
That's how you can be more Anonymous on the internet!
The Future of Cyber-Security, what to expect?
The best Crypto debit card – Wirex!
These are the best VPN to protect your numeric life: NordVPN, ExpressVPN and CyberGhost!
Your PC is slow? That's why!
Why is it important to Be Discreet on the Internet
Feel hot? Your Computer also!
How an Adware works?
That's how you should guard against Trojan!
What are the different Types of hackers?

Thanks for info
Posted using Partiko Android