Quantum Cryptography and China's Quantum Satellite : A New Era of Hack-Proof Communication
Hello friends, today I bring to you a topic about a technology which is going to revolutionize our world in near future. This new technology based on Quantum Mechanics is going to change the technology on which we communicate with each other over the internet. This technology is believed to provide hack-proof communication system. Various experiments on it are going on across the world and it is believed that very soon it will be used in wide scale for commercial purpose. Let us visit to know more about it.

“Quantum”- this word has become a popular word in the science and technology community. In most of the new topics of discussion you’ll find a mention of it like Quantum Mechanics, Quantum Field Theory, Quantum Gravity, Quantum Computers and now Quantum Cryptography.
All these names owes to the achievement in developing the Holy Grail in physics : “Quantum Mechanics”. Quantum Mechanics gave birth to the many new technologies e.g. the transistor which is the fundamental building unit of a computer processor, LASER, the photoelectric cells(solar cells), the LCD and LED (used in LED displays and LED lights) and what not!! Many aspects of Quantum Mechanics are still not clearly understood and we still don't know how those aspects can be used for human interests. The latest use of Quantum Mechanics is the Quantum Computers and Quantum Cryptography which are in development stage and a rigorous race to develop these two technologies for commercial use is underway. For now let us concentrate our discussion on Quantum Cryptography. A new post on Quantum Computers will follow soon.
What is Cryptography ?
Cryptography, if I say in laymen’s language, is the study of techniques to protect a communication from an undesired third party. Cryptography deals with various aspects of information security like Confidentiality, Data Integrity, Authentication and Non-Duplication. Wikipedia defines Cryptography as :
Cryptography is about constructing and analyzing protocols that prevent third parties or the public from reading private messages.
Anyone doesn’t want their communication to be read by an unauthorized person. It is a matter of big concern when it comes to Military Communications, Business and E-commerce, Electronic Machines like PCs and Mobile Phones and especially for us in Digital Currencies. Cryptography is what makes our Steemit account and our digital transactions secure.
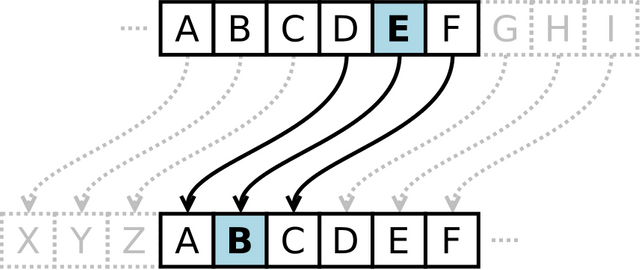
Since ancient times people have used various cryptographic techniques for private communications. The most basic one which I remember is Caesar Cipher. This technique was used by Julius Caesar for his private affairs. It is a kind of substitution cipher where an alphabet or number is replaced by a fixed number of position down the alphabet or number. If we take a right shift of 4, “A” will be replaced by “E”, “M” will be replaced by “Q”, “Y” will be replaced by “C” and so on and the original message words gets converted to a meaningless word. For example, if we take a right shift of 3, the word “STEEMIT” becomes “VWHHPLW”.
In later times some other techniques encryption techniques followed like the Vignere Cipher. However these cryptographic techniques were pen and paper based. In World War I and World War II Rotor Cipher Machines were extensively used for encrypting and decrypting the secret military messages. Encryption is the process of converting a meaningful word into a meaningless junk of letters based on some rules such that an unauthorized person cannot read the message. Decryption is the process of retrieving the original message from the meaningless junk of letters. The most popular rotor machine was the Enigma Machine used by the Nazi Germany during World War II.

The machine had 26 keys where each key was labeled an alphabet which were connected with wires to 26 bulbs which were also labeled with an alphabet. On pressing a key a bulb connected to the key lights up. But between the keys and the lights there are three rotors with a scale of 26 numbers. So on pressing the key “P” lights up the alphabet “B”, the rotor moves one position and hence pressing the same key "P" again lights up a different alphabet. Now, one round of the first rotor moves the second rotor by one position. Similarly, one complete rotation of the second rotor moves the third rotor by one position. This mechanism made it extremely difficult to decrypt the message. There must be a same machine with the same configuration with the receiver who will then type the encrypted message in the machine and recover the original message. Simon Singh who authored the book "The Code Book : The Science of Secrecy from Ancient Egypt to Quantum Cryptography" and who now owns the Enigma Machine used in World War II shows how the Enigma Machine works in the World Science Festival meet in 2013 :
With the advent of digital computers the era of modern cryptography began. A diverse range of cryptographic techniques evolved since then. Modern cryptography incorporates the concepts of Information Theory, Computer Science, Mathematics, Electronics and Physics. These cryptographic techniques are based on algorithms which are designed on assumptions of computational hardness. Computational hardness refers to the inability of a computer to carry out certain calculations with ample computational resources (e.g. time, memory space etc.). Such algorithms are hard to be broken by an adversary. Modern cryptosystems are of two types : Symmetric and Asymmetric.
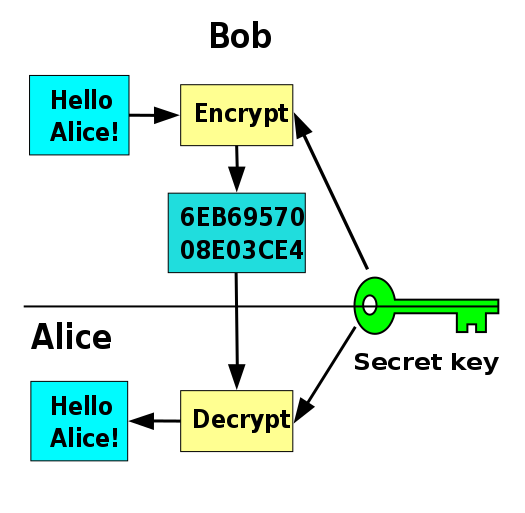
In Symmetric Cryptosystems, the same key( a secret key) is used for both encryption and decryption. The sender encrypts the original message to an intelligible junk of letters and sends to the intended recipient. The recipient then decrypts the received junk of letters using the same secret key and retrieves the original message. Examples of most commonly used symmetric protocols are the DES (Data Encryption Standard) and the improved version of it, AES (Advanced Encryption Standard).
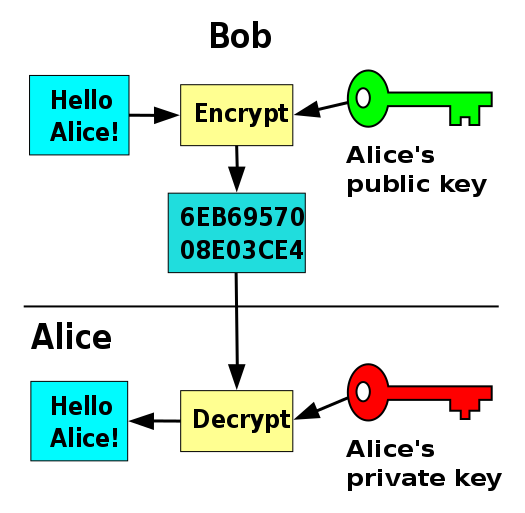
In Asymmetric Cryptosystems also known as Public Key Cryptography two keys are used : a public key for encryption and a private key for decryption. The sender encrypts the message using the public key and sends it. Now only that recipient who has a private key paired to this public key can decrypt the encrypted message. The most popular asymmetric protocols are the RSA algorithm and the Elliptic Curve Cryptography.
RSA :
The name RSA was derived from the names of its developers namely Ron Rivest, Adi Shamir and Leonard Adleman. RSA ensures its security on the basis of the difficulty to factorize a large number. The public and private keys are generated in a process which involves the multiplication of two large prime numbers. Multiplying two large prime numbers is easy but, retrieving the two prime numbers from the product is not feasible with a normal computer.
But, as the computers are gaining more computing power day by day, more efficient factorizing algorithms are being developed which can break the RSA keys. One way to tackle this problem is to increase the key length. RSA keys are generally 1024 to 2048 bits long. Experts believe that in the near future with increasing computing power key with length 1024 bits could be easily broken. For this reason, governments and industries are moving to minimum of 2048 bit long keys.
ECC :
Elliptic Curve Cryptography(ECC) is gaining popularity nowadays as an alternative for RSA. It can create faster, smaller and more efficient cryptographic keys. ECC generates its keys through the properties of the elliptic curve equation instead of the method of multiplying two large prime numbers in the RSA algorithm. ECC can also work in combination with other public key encryption systems like RSA and Diffie-Hellman Technique. ECC can provide proper security with a key length of only 164 bit which other systems like RSA would have needed a 1024 bit long key. Most of the today’s hardware are ECC compatible and it needs lower computing power and consumes less battery making it more suitable for mobile apps than RSA.
Threat of Quantum Computers
The advent of Quantum Computing is posing a threat to the present day cryptosystems. Quantum Computer is believed to be the computing giant which is still in its infancy. With the same length of inputs Quantum Computers are believed to be exponentially faster than even the fastest supercomputers on earth. It is believed that with the exponential computing power of Quantum Computers the keys of the public key cryptosystems can be easily broken. Researchers are working on developing Quantum–Proof Cryptographic Protocols.
Quantum Cryptography
Quantum Cryptography is the most favorable candidate in this concern. Quantum Cryptography is the study of exploiting quantum mechanical properties of nature to perform cryptographic tasks. One of the major applications of Quantum Cryptography is the Quantum-Key-Distribution(QKD) Protocol which offers information-theoretically-secure solution to the key exchange protocol.
Quantum Key Distribution Protocol
Quantum Key Distribution Protocol is a hot topic in the information security field. Heisenberg’s Uncertainty Principle and the No Cloning Theorem is the working principle of this protocol. Heisenberg’s Uncertainty Principle states that any measurement on a quantum system disturbs the system. On the other hand, No Cloning Theorem states that any unknown quantum state cannot be copied. It can only be teleported and in this process the original quantum state is destroyed. Hence, any eavesdropping on the system will be traced by both the sender and the receiver thus confirming its security.
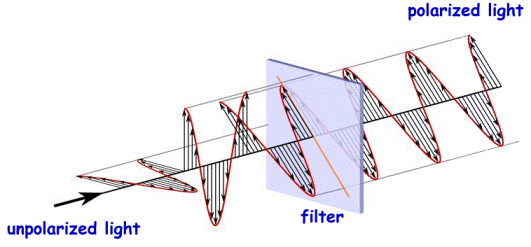
Quantum Cryptography was first proposed by Stephen Wiesner in the early 1970s and introduced the concept of quantum conjugate coding. His paper “Conjugate Coding” was rejected by IEEE Information Theory Society but was published later in the SIGACT news in the year 1983. His paper demonstrated how to store or transmit two messages by encoding them in two conjugate observables e.g. the linear and circular polarization of light, so that either one, but not both of the messages may be received and decoded.
Furthering his idea Charles H. Bennet and Gilles Brassard in the year 1984 proposed an secure communication technique based on Wiesner’s idea of “conjugate observables” which is now known as the BB84 protocol. It is the first of the two quantum key exchange protocols developed till date. The other one known as the E91 protocol was developed by Artur Ekert in the year 1991 which uses the Quantum Entanglement to share the private key. Both of these two ideas are now being studied extensively and have been employed in small scale in various areas. Let us discuss these two protocols.
BB84 Protocol
The protocol uses polarization of photons to encode the secret key. Alice and Bob uses two channels : a classical channel(usually a telephone line or internet) and a quantum channel(usually an optical fiber). The protocol is as follows :
Step 1 :
Alice randomly prepares linearly polarized photons at angles 0o, 90o, 45o and 135o that are Eigen states of the horizontal-vertical basis(⊕) and the diagonal basis(⊗). She sends the randomly prepared states to Bob through the quantum channel and records the sequence of the prepared states. She denotes the photons polarized at angles 0o, 90o, 45o and 135o as H, V, D and A and assigns a value 0 for the states H and D and a value 1 for the states V and A. Hence, Alice creates a random sequence of bits. Now, she records the three sequences: first, the sequence of the polarization basis; second, the polarization states of the photons and last, the assigned values for the polarization states. The recorded sequence is shown below :
.png)
Step 2 :
Bob can analyze the polarizations of the photons sent by Alice by measuring their polarizations in the bases ⊕ and ⊗. Bob chooses the bases at random and measures the polarizations of each photons and writes down the sequence of the bases used by him to measure. He also records the results of the measurement. Like Alice, Bob also assigns a value 0 to the states H and D and 1 to the states V and A. The sequence obtained by Bob is :
.png)
It is to be noted that if Alice and Bob use the same basis for a photon they will both get the same result. In the other cases, Bob has a probability of Screenshot (66).png of obtaining the same result. As a whole there is a 75% probability that Bob will measure the values correctly.
Step 3 :
Now, Bob tells Alice over the classical channel the sequence of the bases used by him and Alice compares Bob’s sequence with that of hers.
Alice to Bob :.png)
Bob to Alice :%20-%20Copy.png)
It is to be noted that Bob tells Alice only the sequence of the bases uses by him for the measurement, not the results of his measurement. In such case, even if Eve listens to their communication through the classical channel, he can know only the sequence of the bases used by Bob. This information is not sufficient for Eve to know the sequences of polarization states sent by Alice.
Step 4 :
Alice now tells Bob, which of the bases he used wrongly and the two discards the cases in which Bob used the wrong bases.
.png)
.png)
After discarding, they get the same subsequence of bits. The sequence of bits obtained after the discarding is:
This sequence is the secret key that the two can now use to encrypt and decrypt their secret messages and communicate over the classical channel securely. In practical situation a large number of photons are used and thus the length of the key generated will be much longer than what we got in our example.
Now, if Eve measures the photons sent by Alice using his choice of random bases, he gets a sequence of polarization states and he has to send the states obtained by him to Bob because he cannot clone the states and his interception changed the states of the photons. Now Bob measures new sequence of the states and sends the results to Alice. Alice discovers that even at the positions where Bob used the same bases as hers, he didn’t get the same state as sent by her thus making them alert of the Eavesdropping. In this way the BB84 protocol ensures a theoretically unhackable communication system. Readers can watch the video on BB84 Protocol prepared by the youtube channel "Creature Mann" below :
E91 Protocol
In this protocol instead of Alice sending the photons to Bob, there is a central source (e.g. satellite distributing the entangled photons to various locations on earth) creating entangled pairs of particles of which each of them gets one particle from each pair. Like BB84 Protocol, E91 Protocol also uses two channel : a classical channel(a telephone line or internet) and a quantum channel(usually free space).
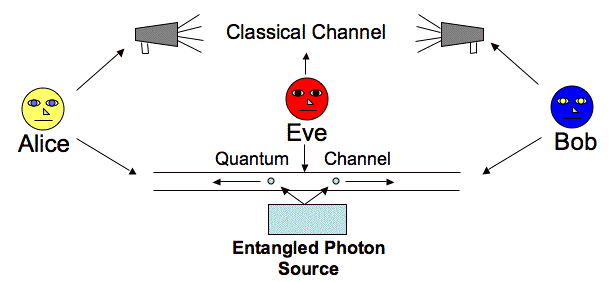
Ekert used the spin singlet states of the photons to explain the creation of entanglement. Quantum entanglement is the inability to define the quantum state of one particle without referring to the quantum state of another particle which may be at any distance apart. Although the state of the individual photon is not known, the quantum state of the entangled pair is well defined. According to the protocol, the source emits the pairs of spin Screenshot (66).png particles(e.g. the photons) in singlet states :
This equation means that in the state I (first bracket), particle A has an up spin and particle B has a down spin. In state II (second bracket), particle A has a down spin and particle B has up spin. This state is called the Superposition of the States, where the combined state of the two particles is well defined, but the state of the individual particle is unknown. It means that even if it is known that one particle is spinning up and the other one is spinning down, it is impossible to know which particle is spinning in which direction until a measurement is made.
Alice and Bob chooses one of three coplanar axes to measure the spins. The three bases can be mathematically expressed by defining the vectors ai (i=1,2,3) for Alice and bj(j=1,2,3) for Bob. If the photons are travelling in the z-direction, then the vectors ai and bj lies in the x-y plane. By measuring the angles from the vertical x axis, the vectors ai and bj can be defined with the angles ϕ1a=0о, ϕ2a=45о, ϕ3a=90о and ϕ1b=45о, ϕ2b=90о, ϕ3b=135о. The superscripts a and b represent the orientation of Alice and Bob’s measuring bases respectively.
.png)
The Orientation of Alice and Bob's Measuring Bases [Source]
It is clear that the probability that Alice and Bob choose the compatible bases is 1/3 to measure the spin of the incoming photons. If they choose compatible bases and Alice measures a spin up particle, the system collapses to state I and the probability that Bob will measure a spin down particle is 100%. Similarly, if Alice measures a spin down particle it is 100% sure that Bob will measure a spin up particle. But, when the two measures in incompatible bases things become really interesting. For example, if Alice measures a spin up particle in the 45о basis, there is an equal probability that Bob will measure a spin up or spin down particle in the 90о basis. It is as if Bob’s particle knows how Alice’s particle was measured and orients itself accordingly such that, if Alice measures in a basis compatible with Bob, Bob’s particle will compliment Alice’s particle’s spin and if she measures in a basis incompatible to that of Bob, Bob’s particle will result in a random spin.
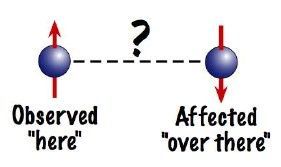
Quantum Entanglement : Spooky Action at a Distance [Source]
There must be something through which they become aware of the action taken on the other one. This phenomenon proved the existence of entanglement and it defied the classical understanding of locality and realism. The “Spooky action at a distance” that Einstein ridiculed is indeed a reality.
Now, if Alice and Bob choose compatible bases, their measurement results will be anti-correlated, meaning Alice’s particle will be spin up and Bob’s particle will be spin down and vice versa. Now, Alice and Bob communicates through the classical channel and discusses at which point of time they measured the incoming streams of particles with the compatible bases (but not the results of their measurement) and discards the cases with incompatible bases. Now, Bob will compliment his results as his results are anti-correlated to that of Alice. Now both of them have the same results and they will assign a value 0 to spin down particle and a value 1 to spin up. In this way the two has the same sequence of 0’s and 1’s which is their secret key. Using this key they can now encrypt and decrypt their messages and communicate through the classical channel safely.
If Eve tries to intercept the particles coming from the source, she must choose a basis to measure it which he does at random. In this process he disturbs the system. If Eve measures the particle in a basis incompatible to that of Alice and Bob, her result will be random she will recreate her detected particle and send it to Bob. As Eve’s interception made the state of the particle random, Bob's measurement result won’t anti-correlate with that of Alice even if Alice and Bob are using the same basis. This will alert them of the eavesdropping caused by Eve. The mathematical check for the eavesdropping can be done as follows:
The Correlation Coefficient of Alice’s (ai) and Bob’s (bj) measurements in reference to the vectors ai and bj is defined as:
.png)
Where, P± is the probability of getting ±1 along ai and ±1 along bj. Now, let us define a quantity S which is the sum of all the correlation coefficients for which Alice and Bob used incompatible bases as:
.png)
John Bell proved using local realism that the value of S ≤ 2 . However, Quantum Mechanics yields a value,
.png)
It means that if the two particles were truly entangled and defied the rules of local realism, Bell’s Theorem should be violated. Therefore publicly announcing the results of their measurements Alice and Bob can calculate a value of S. If the entangled state was not disturbed by an eavesdropper, the value of S should be equal to 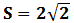.png) and they can be sure that their measurement results in the compatible bases were anti-correlated and that secret key is secure. Otherwise, it will imply to an eavesdropping and they will abort the operation and start over.
and they can be sure that their measurement results in the compatible bases were anti-correlated and that secret key is secure. Otherwise, it will imply to an eavesdropping and they will abort the operation and start over.
China’s Quantum Satellite
Based on BB84 protocol and E91 protocols Quantum Networks has been built at various places in the world but limited to only a short distance because due to the disturbance caused by the atmosphere destroys the state of the photon particles being exchanged. On the ground, through air or optical fibers they cannot go much further than 200 km. Satellite is a perfect alternative for it, as the photons will have to travel much of its distance through vacuum which will reduce the disturbance on the states of the photons significantly. This is what China did.
China launched a satellite called Micius named after the ancient Chinese philosopher and scientist of the same name in August, 2016 and placed it in the sun-synchronous orbit so that it passes over the same point on earth at the same time each day. In the satellite there is a Sagnac Effect interferometer which generates a sequence of entangled photons whose polarizing states are entangled. One photon from each entangled pair is then directed to two separate ground based receiving stations at Xinjiang Astronomical Observatory near Urumqi and Xinglong Observatory near Beijing which are 2500 km apart from each other. The team reported that simultaneously measuring more than 1000 photon pairs they found that the photons had opposite polarisations more often than expected by chance confirming spooky action at a record distance of 1200 km(the previous record distance being 1.3 km performed in 2015). Readers can watch the video on China's Quantum Satellite posted by the YouTube channel "Science Magazine" below :
It was a giant leap for such efforts. It will open up an era of unhackable Quantum Internet spread across the globe by setting up receiving stations across the globe. China now plans to carry out the experiment at a longer distance from China to Austria in Europe. Along with this experiment the Chinese team teleported a photon from ground to the satellite Micius 500 km above the ground station.
After this achievement other countries has also inched towards space based quantum cryptographic experiments. Australia is also in a mission to send quantum information between two satellites. The Indian space agency ISRO has teamed up with the Raman Research Institute(RRI) in Bangalore to develop space based quantum cryptographic technologies link. The Canadian Space Agency (CSA) has also announced funding for a small quantum satellitelink. The European and U.S. teams have also plans to set up quantum instruments in ISS to test various quantum experiments.
There are many small scale quantum networks based on BB84 and e91 protocol, already working at various regions of the world. Their small scale is limited by the destruction of the quantum states of the particles caused by the disturbances in the atmosphere or optical fiber. Some of the well-known networks are: the DARPA Quantum Network, the SECOQC Network, the SwissQuantum Network, the Tokyo QKD Network, etc.
There are currently four companies providing quantum key distribution systems : ID Quantique(Geneva), MagiQ technologies Inc(Newyork), QuintessenceLabs(Australia) and SeQureNet(Paris). Some other companies working on this field are: Toshiba, IBM, HP, Mitsubishi, NEC and NTT. In 2004 using QKD first bank transaction was carried out at Vienna, Austria.
With this new technology a network of satellite will one day bring the world into the world of Quantum Internet which will connect the Quantum Computers that will be built across the world in the future. It is clearly visible that the future of internet will be based on these quantum principles only.
References :
- Youtube : The Enigma Machine Explained by the Channel "World Science Festival"
- Youtube : Enigma Machine by the Channel "Numberphile"
- Quantum Teleportation and Quantum Cryptography by Urtzi Las Heras
- BB84 Protocol by Wikipedia
- Ekert Protocol for Quantum Key Distribution
- The Ekert Protocol by Nicolina Ilic
- BBC News : China's Quantum satellite in Big Leap
- Science Magazine : China’s Quantum Satellite Achieves ‘Spooky Action’ at Record Distance
- MIT Technology Review : First Object Teleported From Earth to Orbit
- The Indian Express : ISRO Sets Forward to Build Secure Quantum Communications Network
- Wikipedia
I hope you enjoyed learning about Quantum Cryptography. If you love dreaming and learning science then please follow me, @tech-mac
If you are interested in various domains of Science and Mathematics then join the @steemstem project, team to support high quality STEM(Science,Technology, Engineering and Mathematics) related contents. Join them in steemit.chat to interact with the science authors from all over the world.
Thank you for reading my content !!

This is a great post! Super nice information. I think you could maybe get more credits for it (which it deserves in my opinion) by dividing this into two or more posts? For absolute nitwits like me, this was quite a read. But thanks for sharing, I will definitely follow you from now on!
Thanx a lot for that... :)
Following you too!!
nice post
Thanx.. :)
absolutely brilliant post and well explained for newbies to the topic. Next step: Universal Internet ;>)
d

Thanx a lot.. :)