INTRODUCTION TO BLOCKCHAIN SIDECHAIN
To put it simply, they are additional chains that are linked to a specific blockchain in order to assist the primary blockchain in processing some data. We are all aware that most blockchains move slowly owing to network congestion, but if developers wish to make them move faster, they will have to compromise network security. Layer 2 scaling solutions were developed by the developers in order to increase network speed without jeopardizing network security.
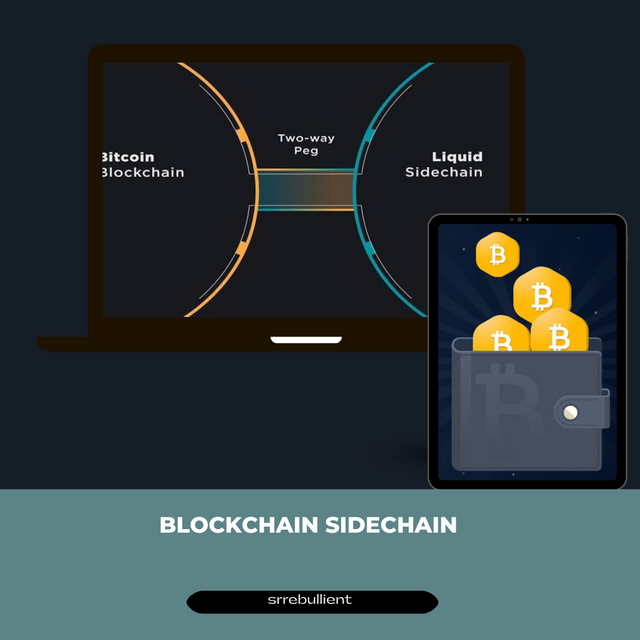
Sidechain is one of the many layer two solutions available. Because the side chain performs some of the functions of the main blockchain, it was developed differently. The performance of sidechains is excellent, but it is centralized. The security network will have to be put at danger, but it is far preferable to put the sidechain and main chain's security at risk. In contrast to the main chain, side chains use their own nodes and reward them with tokens for validating transactions.
There is a side chain component known as the two way peg. Technically, they use pegs to alternately move the main chain and the sidechain. Locking up and releasing are the separate terms for these actions.
Locking up your coins when you move them from the main blockchain to the sidecoin is crucial if you don't want to have a lot of free tokens on both the sidechain and the main chain. The smartcontract governs how your coin is locked up, so you don't need to be concerned. When you receive a duplicate of your coin, you lock it up on the main chain and release it on the sidechain. You will need to burn the coin you have on the sidechain in order to get your real coin on the main chain. Like the illustration I used earlier with the noodles, if you process all the transactions and data. Similar to the earlier analogy of the noodles, the main chain will become extremely clogged and slow if all transactions and data are processed at once, but if they are processed separately, the blockchain will not be overburdened.
- Federation
Since some Sidechains use code to lock up and release coin, it is actually the middle in the side chain that is in charge of doing so. Federal is not always necessary. The side chain organization, which controls the federation, is very helpful since it ensures that the quantity locked up on the main chain is the precise amount main chain.
- ROCKSTOCK
It was created as a Sidechain for Bitcoin in order to support smart contracts. Popular cryptocurrency exchanges, their federations assist in building a link from the Bitcoin blockchain to Rootstock. These indicate that anyone can transfer Bitcoin to Rootstock to obtain a Rootstock form of Bitcoin for use with certain smartcontract functions.
- POLYGON
As I mentioned before, there are various sidechains available, and Polygon is one of them because it is an Ethereum Blockchain sidechain. The extremely high Ethereum transaction price forced the creators to create Polygon, which was formerly known as Matic. Since they accomplish the same tasks, there is no distinction between Polygon and Ethereum; nonetheless, Polygon is significantly faster than Ethereum. People can transfer their assets from the Ethereum network to Polygon with the use of the Matic bridge, and the processing times for transactions on the two networks are considerably different as well.
https://twitter.com/EbullientSrr/status/1581220151273623555?s=19