Neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer and Parkinson strangely linked to viral infections
(Wikimedia Commons https://bit.ly/3R0BrSP)
Last year, scientists found that multiple sclerosis was linked to the Epstein-Barr virus.
However, this was not the first time scientists have found a link between viral infection and neurodegeneration.
Now, a team of researchers of the NIH led by Andrew Singleton has found even more correlations between viral infections and neurodegenerative diseases: Alzheimer's and Parkinson's.
Scientists have already found links between viruses and neurodegenerative disorders, like herpes and Alzheimer's disease, and the flu and Parkinson's disease.
A year ago, the results of a study were published, the authors of which analyzed the data of ten million military personnel.
Researchers watched them for 20 years and during this time 955 people developed multiple sclerosis.
It turned out that the risk of developing this disease was associated with infection with the Epstein-Barr virus in history: 800 out of 995 people with sclerosis were infected.
THE STUDY
Now Singleton’s team has found even more correlations of viral infections with neurodegenerative disorders:
- Alzheimer's disease
- Parkinson's disease
- amyotrophic lateral sclerosis
- multiple sclerosis
- dementia
- vascular dementia
To do this, the authors of the new work studied health care data from FinnGen, a large Finnish biobank.
There were 26,000 people with neurodegenerative disorders found there, and scientists tested whether these people were infected with any virus.
They were able to find 45 pairs of viral infections and neurodegenerative disorders that were significantly related to each other.
The scientists then turned to the UK Biobank, the UK's largest database, and analyzed data from 106,000 people, 20,000 of whom had neurodegenerative disorders.
Here, 22 associations were reproduced, and it was on them that the researchers focused.
For example, the flu increased the risk of various dementias 5 times.
And when the flu spilled over into pneumonia, it was associated with all the diseases they were looking for, except for multiple sclerosis.
Dementia had the most associations with several infections at once: encephalitis, viral warts, influenza and pneumonia.
Even intestinal infections and chickenpox have been correlated with several neurodegenerative disorders.
Alzheimer's disease and encephalitis, which is caused by many different viruses, were most strongly associated.
When the team compared with control, patients who had viral encephalitis had a 31-fold higher risk of Alzheimer's disease.
Almost all correlations found were associated with neurotropic viruses that can penetrate the central nervous system and infect neurons:
- herpes simplex virus
- some strains of influenza
- viruses that cause encephalitis
CORRELATION =/= CAUSATION
Based on data from the Finnish Biobank, the researchers assessed how the strength of the link between viruses and diseases changes over time: 1, 5 and 15 years after infection.
Neurodegenerative diseases take a long time to develop, and one would expect the link to be stronger in 15 years.
However, the researchers studied 16 pairs of associations, and for almost all pairs, the highest risk was within a year after infection with the virus, and then decreased.
After 5-15 years, only 6 of these couples remained at high risk.
The authors did not find any viral infections that would, on the contrary, reduce the risk of neurodegeneration.
If viral infections actually increase the risk of neurological disorders, vaccination should reduce this risk.
According to several studies, flu vaccination actually reduces the risk of Alzheimer's and Parkinson's.
However, scientists emphasize that their results do not say anything about causal relationships, only about correlation.
So, for some reason, a person may be more susceptible to viruses and neurodegeneration, and one does not necessarily follow from the other.
Or it may be that, on the contrary, developing neurodegeneration weakens the immune system and makes a person more susceptible to viruses.
Sources:
- Neuron: https://www.cell.com/neuron/fulltext/S0896-6273(22)01147-3#secsectitle0035
- NIH: https://www.nia.nih.gov/news/could-viral-illness-increase-chances-developing-alzheimers-or-other-neurodegenerative-disease
Wanna save your links for later?
Try this new tool: https://bit.ly/3Wb8Mwe
#science #neuroscience #virus #alzheimer #parkinson #news #nftmc
and
I'm always cautious about findings that come about from sifting through large databases like this. It's far too easy to mistake a spurious correlation for something meaningful. So (IMO), this is an important section in your article ;-)
Hehe, thanks. I mean, I chose this article because there are known strong correlations between herpes and alzheimer, and sometimes correlations don't mean causations but sometimes...
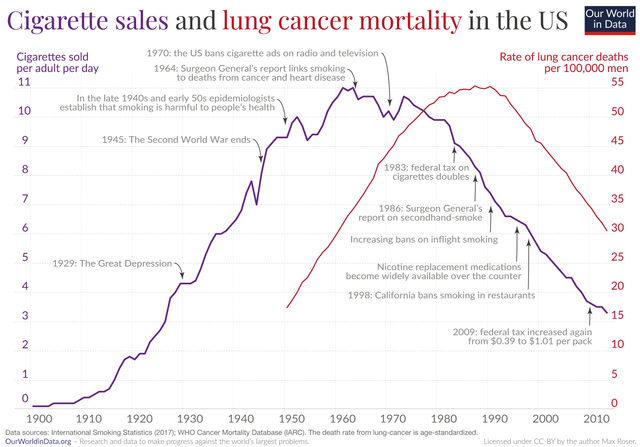
Yeah, but the tobacco studies took decades and the statistical techniques were more focused. And even with the certainty of the link between cigarettes and lung cancer, I still look at that graph and wonder, yeah, but how much of that decline is because modern medicine got better at treating lung cancer? What would the graph of lung cancer illnesses look like? Statistics are funny things... ;-)
With big data sweeps like the Alzheimer's one, it's too easy for researchers to find the correlation first and then use it to establish the hypotheses - which basically invalidates the finding unless they partition the data properly. Not saying that's what happened here, just that I'm cautious about accepting the results from this sort of study.