We Just Detected Signals From The Very First Stars in Our Universe - And It's Not What We Expected

This is a HUGE minute for science.
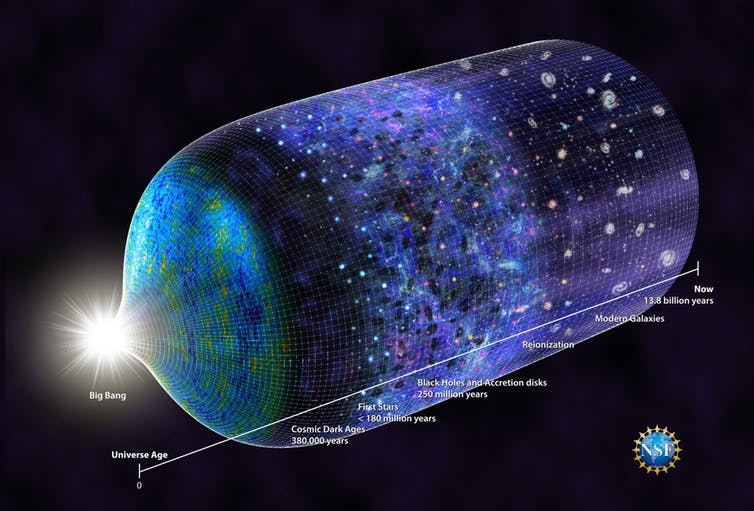
The Big Bang may have been splendid and sensational, yet instantly after it happened the Universe got to a great degree dull for quite a while.
Truth be told, researchers trust that it took up to 200 million years for the primary stars to rise up out of a dark soup of issue.
As present telescopes aren't sufficiently delicate to watch the light from these stars straightforwardly, cosmologists have been searching for backhanded confirmation of their reality.
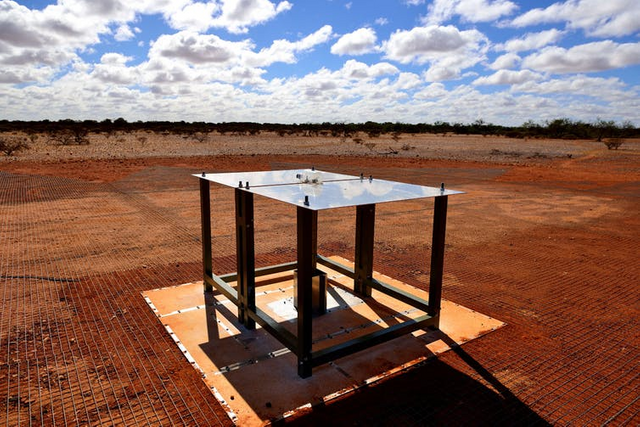
Presently a group of researchers has figured out how to get a black out flag from these stars with a radio reception apparatus the extent of a table best, called EDGES.
The noteworthy estimation, which opens another window on the early Universe, demonstrates that these stars developed around 180 million years after the Big Bang.
The discoveries, distributed in Nature, likewise proposes researchers may need to reexamine what "dull issue" - a secretive sort of imperceptible issue - is made of.
Models have demonstrated that the main stars that lit up the Universe would have been blue and fleeting, delivering a shower of bright light.
The soonest detectable flag of this astronomical day break has for quite some time been believed to be a "retention flag" - a plunge in shine at a specific wavelength - caused by this light going through and influencing the physical properties of billows of hydrogen gas, which is the most rich component in the Universe.

We know this dunk ought to be found in the radiowave part of the electromagnetic range, at a wavelength of 21 centimeters (8.2 inches).
Testing estimation
This was altogether anticipated by hypothesis.
Be that as it may, by and by, the flag is greatly testing to discover.
This is on the grounds that it covers with numerous different flags in this area of the range which are considerably more grounded -, for example, basic frequencies on the FM radio dial and radio waves from different occasions in our universe.
The reason the group in the end succeeded was incompletely down to the trial's touchy recipient and little recieving wire, which gives you a chance to cover an expansive zone of the sky all the more effectively.
To make certain that that any dunk in brilliance they discovered originated from starlight in the early Universe, the group took a gander at an impact known as the Doppler move - you will have encountered this as a bringing down of pitch when a siren goes by at speed.
Thus, as all worlds are retreating far from us because of the development of the Universe, light is moved to redder wavelengths. Space experts call this impact "redshift".
Redshift tells researchers how far away a specific gas cloud is from Earth and how far back in astronomical time the light from it was transmitted.
For this situation, any move in the plunge in splendor expected at 21 centimeters wavelength would give a sign of how the gas is moving and how far away it lies.
The group estimated a plunge that secured a scope of times in the universe - most drastically back to when the Universe itself was just 180 million years of age, contrasted with its great age today of 13.9 billion years. This was the light from the principal stars.
Dim issue turn
The story doesn't end there. The group was astonished to find that the abundancy of the flag was more than twice as huge as anticipated. This recommends the hydrogen gas was significantly colder than anticipated of the foundation radiation.
These discoveries, distributed in another paper in Nature, have tossed a spanner in crafted by the hypothetical physicists.
This is on account of the material science recommends that as of now in the Universe, it would have been anything but difficult to warm gas yet hard to cool it.
Keeping in mind the end goal to deliver the additional cooling expected to clarify the flag, the creators contend, the gas more likely than not cooperated with something considerably colder. Also, the main thing known in the early Universe colder than this infinite gas is dull issue.
Truth be told, scholars should now choose whether they ought to broaden the standard model of cosmology and molecule material science to clarify this impact.
We realize that dim issue is five times more typical than ordinary issue however we don't yet comprehend what it is made of.
A few alternatives for particles that could make up dull issue have been proposed, with the most loved competitor being the Weakly Interacting Massive Particle (WIMP).
The new research, nonetheless, proposes that the dim issue molecule would not be substantially heavier than a proton (which makes up the nuclear core alongside the neutron). This is well beneath masses anticipated for the WIMP.
The investigation likewise recommends that the dull issue is colder than anticipated, and opens the energizing plausibility of utilizing "21-centimeter cosmology" as another test of dim issue in the Universe.
Assist revelations with more delicate recipients and less difficulties from earthly radio impedance - which could be accomplished by setting an interferometer on the dull side of the moon - could divulge more insights about the idea of dim issue, possibly examining the speed at which it is moving.
The ConversationThis comes at a helpful time for radio space experts, who are building up the up and coming age of mammoth systems of radio telescopes or interferometers in Australia and South Africa called the Square Kilometer Array and additionally other bleeding edge tests committed to concentrate the astronomical sunrise.
Good content ... Keep going !!