HIV/AIDS Origin, Symptoms, Transmission, Treatment
HIV
The HIV virus attack certain types of white blood cells (CD4 + T lymphocytes) that are part of the immune system. As the immune system begins to weaken, the white blood cells become unable to resist and fight against disease germs. Germs that normally would be rapidly neutralized, remain in the body and multiply.
AIDS is not caused by HIV itself, as in the case of a viral disease common, but due to the inability of the immune system to fight infections. In medical terms, a number or a group of symptoms and diseases that tend to act together called syndrome. Hence the name of the disease AIDS, meaning Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome.
Article Contents
- The origin of HIV
- Pathogenic mechanism
- Symptoms
- Mode of transmission
- Treatment
- Prophylaxis
The origin of the virus HIV
The first cases of AIDS were diagnosed officially in the US. In 1981, according to the mode of propagation and other factors, doctors have concluded that the disease was caused by the emerging tiny germ, a type of virus. By 1983, scientists from the US and France have discovered independently virus which is believed to cause AIDS. The French have discovered virus called Virus Associate
Limfoadenopathy or VAL because adenomegaly causes (increase in size of lymph nodes in the body). American Researchers have given name Lymphatic virus III or HTLV III human cell, because of the way it attacks the body's cells. After several controversies regarding the appointment of viruses and the team of researchers who first identified viruses were found to be almost identical.
Finally, they were called HIV, the Human Immunodeficiency Virus.
Most researchers believe the virus originated in chimpanzees and monkeys in Africa. HIV viruses alike, called VIP (Primate Immunodeficiency Viruses) are features to monkeys. It is believed that HIV could be developed from these viruses, in experiments with blood and organs of monkeys or traditional ceremonies involving their sacrifice.
Genetic analysis and research on HIV's spread shows that the virus is under 100 years, but over 20. Probably appeared in a small group of people in a remote area, many years ago and spread with increasing travel .
Pathogenic Mechanism
Numerous studies have been undertaken to find out how HIV affects the immune system, but until the mid-90s, were not discovered the details. What is known is that some types of virus attacks cells in the body. These are white blood cells, called lymphocytes and other immune cells that normally help the body to defend against viruses, bacteria and other germs.
Usually when a specific type of germ enters the body, the immune system against it creates special molecules, called antibodies. Antibodies float in blood and body fluids sticking to microbes or destroying them, rendering them harmless.
To some extent, the same happens when HIV enters the body. The immune system produces antibodies against the virus.
At this stage, a blood or body fluid can show whether a person has HIV. The test does not detect the virus itself but antibodies against it. If antibodies are present, the test is positive, indicating the presence of viruses. Meanwhile, the viruses "sleepers" hide and constantly modify inside the cells, antibody untouched. After a while, the virus begins to multiply again, and the first physical symptoms of AIDS begin to appear.
Occasionally occur according to some that HIV does not cause AIDS. It is said that the virus is present only in people who have AIDS and even some unknown trigger causes both HIV and AIDS. However, most scientists and doctors believe that HIV causes AIDS.
Intensive research started in the '80s have made one of the most studied HIV virus known to date. Researchers found its detailed structure and drew a map of its genes. They concluded that there are several types of HIV, not just one. They change continuously, making it difficult for vaccine production.
Bodies of people affected by this disease can not fight germs; The disease most often emerges victorious from this fierce battle.
Retroviruses and HIV
Viruses are the simplest life forms. Many diseases, such as measles, mumps, colds and flu are caused by viruses. A typical virus has a central portion or core made of DNA-deoxyribonucleic acid. This sets the genes of a virus-acid chemical code needed to build more viruses identical with him. DNA core is covered by a shield similar to a mosaic composed of various protein molecules.
However, a virus can not multiply alone but needs a living cell, such as a cell in the body, to be his host. The virus enters the host cell, the host adds its genes and determine the chemical mechanism of the cell to manufacture hundreds of thousands of copies of itself. Then, these viruses go out of the host cell, destroy and are ready to infect other cells.
HIV is unusual, belonging to a group of viruses called retroviruses. They do not contain DNA, RNA instead shows. Inside the host cell, RNA is first converted into DNA, and then this DNA is used as code for virus multiplication.
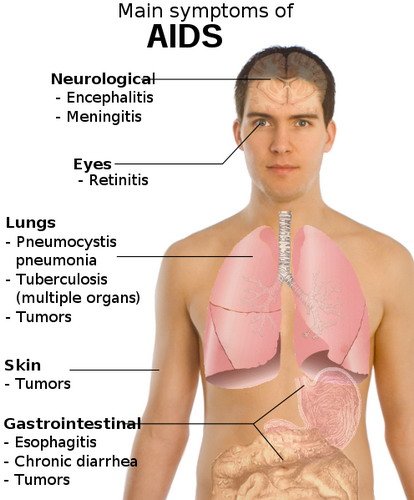
Symptoms
HIV is unusual because its main effects do not feel a period of time, generally between 5-10 years after it entered the body. When a person is infected with HIV, the virus multiplies rapidly. It can be detected in blood and cerebrospinal fluid. The person may not be affected at this stage or may have some flu-like symptoms such as runny nose and fever, rash, lymphadenopathy axillary or frequent headaches. These symptoms are often attributed to a cold.
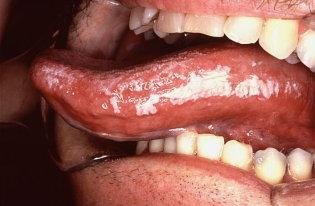
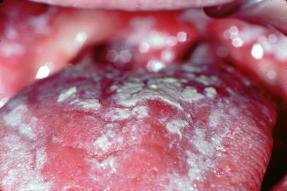
These symptoms and high levels of HIV in the body usually disappear after a few weeks, when the infected person feels well again. The virus is present but inactive. Unconscious person can transmit the virus to others. Eventually, perhaps after many years, HIV is reactivated and start to multiply again. Now is the time when AIDS occurs. Hairy leukoplakia, mouth sores often appear on language with AIDS.
Mouth sores appear as white spots on the tongue; leukoplakia consists of some white bumps along the tongue. At this stage, the immune system begins to fight, and the number of white blood cells begin to decline.
In some cases or in others gradually after a few weeks, begin to develop various diseases. These may be infections of the skin and mucous membranes.
Source
The body may succumb to infections, such as pneumonia or meningitis or encephalitis and tuberculosis. Such inflammation can cause confusion or mental problems (including dementia). Can also occur abnormal vision, diarrhea, digestive problems and wounds with excessive bleeding. Other diseases that may occur are different forms of cancer, Kaposi's sarcoma, which causes skin lesions. After a few weeks or months, the patient enters the last phase of the disease because various diseases overwhelm the body.
Means of transmitting
Compared with other viruses, HIV is transmitted relatively difficult. He can not survive outside the body, away from heat and liquid and therefore is not found in the air. This means that people can not infect inspired him. Under normal circumstances HIV can not be contacted by coughing, sneezing, insects like flies and mosquitoes or collective use towels, cutlery and other objects.
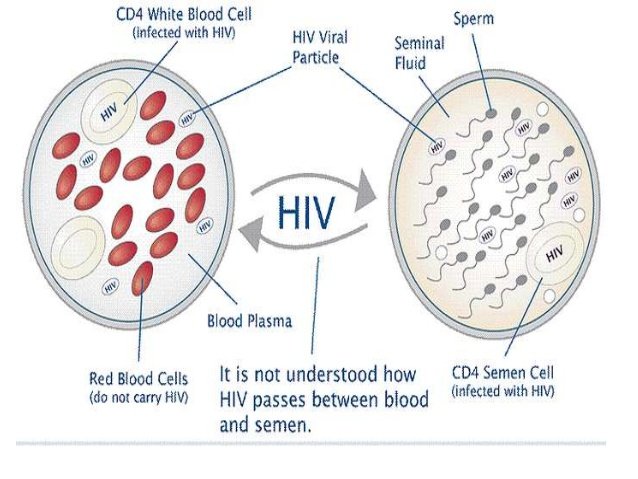
HIV can be transmitted in three ways, all involving the exchange of blood or body fluids. People can get the virus when blood or fluid (eg sperm) of the body of an infected person comes in contact with their own blood or liquid inside their bodies.
One way of HIV transmission is through sexual contact. It includes both heterosexual and homosexual ones. The virus is transmitted from one partner to another through body fluids.
The second way is the transplacental HIV is transmitted from infected mother to child in her womb. The virus can enter the baby's body before he was born, it develops in the womb or during birth.
A third way of contacting the virus is through blood or body fluids, usually by injection. Before the blood to be tested for HIV, some people donated blood. Some of you who received contaminated blood were infected. Currently, donated blood is carefully examined in order to prevent the spread of HIV through transfusions. The virus can be transmitted and by reusing unsterilized hypodermic needle or a sterile syringe already used by an infected person.
Treatments
As physicians and patients have gained experience related to the disease, there have been improvements in patient care and treatment of diseases and disorders caused by AIDS. For example, some types of pneumonia triggered by AIDS can be treated with antibiotics and antivirals. Skin inflammation caused by Kaposi's sarcoma were overcome by radiotherapy (radiation or X-ray treatment).
But currently no known cure against AIDS and no effective long-term treatment. Also, there is no vaccine (immunization) to prevent the evolution and spread of HIV, as there is polio, measles and other similar diseases. Despite ongoing efforts to search for drugs and vaccines against AIDS and occasional successes, progress proved to be slow and difficult.
Because viruses live and multiply inside the host cells, they are "targets" hard to reach. There are few effective antiviral drugs, compared to many antibiotics that kill bacteria. The drug zidovudine (AZT) slow evolution of AIDS in some people. But can have unpleasant or serious side effects: nausea, vomiting, weakness, and in some cases can damage the bone marrow. Some patients can not or prefer not to take this medicine.
Another scientific method is prevention of HIV to attach to the host cell surface. The points of attachment of the virus and the body cells are well perceived. Scientists are trying to create a drug that could interfere with the binding of the virus and the cell or block it and also hope that it will kill the virus the same time.
Prophylaxis
Many rumors have circulated since AIDS was first recognized as a disease. We now know that anyone can be infected with HIV. Young or old, gay or straight, white or black, male or female - the virus can affect anyone, depending on the circumstances. What is important is whether a person is involved in so-called "high risk activities". These activities include the use of unsterile needles and injecting drugs with frequent change of sexual partners or unprotected sex (without condom use).
Everyone can reduce their risk of HIV infection by avoiding those activities. This means avoiding drugs and safe sex. Protection consists in using condoms and limiting the number of sexual partners. It is important detailed knowledge of past sexual partner because of HIV infection may take years until the outbreak of AIDS. In this time, HIV infected person may look healthy and may not know that carries the virus, but being able to convey to others. HIV may lie in saliva, but is believed to not be transmitted through kissing.
Certainly, AIDS is a serious health threat to people. According to estimates, in the early 90s more than 10 million people had HIV. The World Health Organization show that this number reached 40 million in 2000. In the US, in 1991, a person with AIDS died every 12 minutes.
Almost all countries are affected by this disease, although HIV is found mainly in certain areas, such as North America, the Caribbean, Central Africa and Southeast Asia. Since most people living with HIV and AIDS will not survive, this is an enormous loss of lives and human resources. While scientists continue to seek treatment, defense is the only way to change personal habits, avoiding activities with high risk. To encourage safe sex campaigns have been launched worldwide.
Bibliography:
Nakagawa F., May M, Philips A, Life expectancy living with HIV 2013


If you have a computer or an Android phone, help in the search for a cure for HIV/AIDS by joining the World Community Grid.
Its very easy just:
1/ download BOINC from here https://boinc.berkeley.edu/download_all.php or for Android from the PlayStore.
2/ join the World Community Grid here https://www.worldcommunitygrid.org/discover.action
Its it safe? Yes very, I have been running BOINC for over 10 years with no issues, it will not slow down or harm your devices.
You can do research for many other humanitarian/scientific causes.
Finally if you are concerned about electricity cost, you can join team Gridcoin here https://gridcoin.us/ and earn some digital currency for the help you provide.