Fibromyalgia Syndrome; the cause of chronic pain and fatigue
Fibromyalgia(FM), formerly known as fibrositis, is common muskuloskeletal syndrome that causes pain in the connective tissues, muscles, joints and ligaments, as well as an assortment of other symptoms such as sleep disorders, fatigue, abdominal cramp, morning stiffness and depression.
Fibro; meaning fibrosus tissues (tendons, ligaments)- my meaning; muscles - algia; meaning pain.
Insidance
According to the American College of Rheumatology, fibromyalgia is 7 times more common in women than in men. It’s estimated that as Many as %3 -%6 of the USA population has fibromyalgia.
Although it can ocur at any age, it’s more common in 20 through 40 year olds and most common in women of childbearing age. It has shown some familial patterns, suggesting that it may have a genetic basis.
Also, the incidence of fibromyalgia in well-trained active people is much lower than in the general population.
• Primer FM: its cause is unknown, its a commonly seen Fibromyalgia type, also known as the idiopathic FM.
• Sekonder FM: Type of FM that occurs with the causes of illness, injuries, or surgeries.
Etiology
There is no precise information on the etiology. According to studies;
• Causes related to physical or psychological traumas. (22%)
• Infection-related FM (18%)
• Other causes (60%): genetic factors, chronic sleep disorders, changes in pressure and climate, joint hypermobility.
Endocrinological and neurologic findings in FM patients;
• Serotonin in the cerebrospinal fluid is lower than normal.
Serotonin; When this hormone, which is necessary for deep sleep is secreted at a low level, it causes sleep disorders.
• If the growth hormone is secreted at a low level it causes irregular sleep rhythm..
• The value of substance p in cerebrospinal fluid is 3 times its normal value.
Substance p; is a neurotransmitter that causes increasing of the sense of pain.
• Decrease in cortisol level.
Symptoms of FM
• Chronic widespread pain: Though 2/3rds of FM patients suffer from widespread body pain, it typically focuses majorly on one or two regions (the main disturbing pain). These pain centers frequently move around to other parts of the body with biomechanical stress or traumas.
• The pain is burning and throbbing. And it is worse in the mornings. Though it reduces within the day, it starts to increase at night.
• Sleep disorders: Most fibromyalgia patients suffer from bad sleep. Problems of falling to sleep and waking up frequently are seen. Because they don't get deep sleep, they wake up unrested in the morning.
• Tiredness: Though its severeness differs it is the most common symptom of fibromyalgia.
• Tender points: They occur with muscle spasms or nodules.
18 tender points in 9 bilateral regions according to American College of Rheumatology classification criteria;;
(both side of the body): Occiput (2),Low cervical (2),Trapezius (2), Supraspinatus (2), Second rib (2), Lateral epicondyle (2), Gluteal (2), Greater trochanter (2), Knee (2).
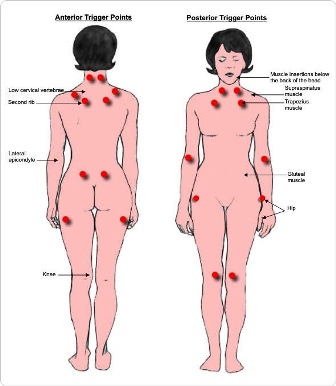
Diagnostic Criteria
the criteria for the Classification of Fibromyalgia by the American College of Rheumatology, (ACR) 1990
diagnostic criteria for fibromyalgia that includes common symptoms such as fatigue, cognitive problems and sleep disturbances, as well as pain
• History of widespread pain has been present for at least three months.
• Pain in both sides of the body pain above and below the waist. Pain is considered widespread when all of the following are present:
• Pain in 11 of 18 tender point sites on digital palpation
New ACR diagnostic criteria
Prognosis of fibromyalgia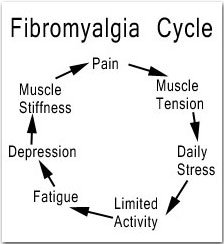
image source

• Remittent – intermittent: Symptoms may disappear and may rarely reappear.
• Fluctuating type: Symptoms don't completely disappear, the symptoms may abate or exacerbate time to time.
• Progressive type: Symptoms exacerbate over time..
The treatment
It is separated into 2 as pharmacological and non-pharmacological..
Pharmacological treatment:
• Antidepressants: they regulate sleep by increasing the serotonin level. Thus, aiming to decrease muscle spasms, pain, and tiredness..
• Analgesics
• Muscle relaxants
• Sleeping Pills
• Estrogen therapy: Estrogen replacement in menopausal women is known to regulate sleep.
Non-pharmacological treatment:
• Patient instructions, heat theraphy(hot pack), classical and friction massage, kconnective tissue massage, exercise, ergonomy education, relaxation exercises, biofeedback, acupuncture, dry needling, stress management therapy, psychological support, nutrition, and electrotherapy applications(TENS, Ultrasound, HVPC - high-voltage pulsed galvanic current)
• Because the exact cause of fibromyalgia is unknown, all the existing treatment methods are for symptoms. When pharmacological and non-pharmacological treatments are applied together, the chance of success of treatment increases..
)
references:
The information on this post is provided for educational and informational purposes only.
Health is wealth, have learnt something new today @myego13
You right! Thanks for reading.
Thank you, this has been really informative.
Thank you too. I hope it's helpfull.
👍
Pharmacological treatment seems what i needed.
according to my experience; both treatments should be combined for best solution.
Oh ok. I'll give it a shot.
Does fascia massage help that condition, or is that something different?
Myofascial release, deep tissue and trigger point I think we can apply the combination of them, more helpfull
I wrote on how i helped my wifes FM https://steemit.com/health/@mytips/how-i-helped-my-wife-s-fibromyalgia