SWALLOWING: THE ALMIGHTY TRANSPORT MECHANISM
The act of swallowing is part of our everyday life. We cannot stay a day without swallowing. this shows how important swallowing is for human survival. Nothing goes into the gastrointestinal tract through the mouth without passing the process of swallowing. I got to know more about swallowing when choked why drinking water. In physiological terms, the word swallowing can be called DEGLUTITION.
The act of swallowing is the process by which substance whether liquid or solid especially food and water are transported from the mouth through the oesophagus to the stomach. During this process, epiglottis is closed to avoid food substance from entering the wrong pathway which is the air passage. Eating and drinking which we do everyday are major part of swallowing. Swallowing is usually aided by saliva for easy movement. Before food substance to be swallowed are passed down oesophagus, they must be converted into bolus form. When food substance enters the air passage, it usually causes choking. The act of swallowing is always followed by digestion of the swallowed food substance. Swallowing is important in digestion mechanism because it aid the transport of food down the gastrointestinal tract.
GIT. Source:Wikimedia - CC BY-SA 3.0.
STAGES OF SWALLOWING
Swallowing involves three stages and they includes
Oral Stage
Pharyngeal Stage and
Oesophageal Stage
Only the initial or Oral stage of swallowing is voluntary action. The rest are series of pre programmed reflexes coordinated by the swallowing centre in the medulla oblongata in the pharyngeal and oesophageal stages.
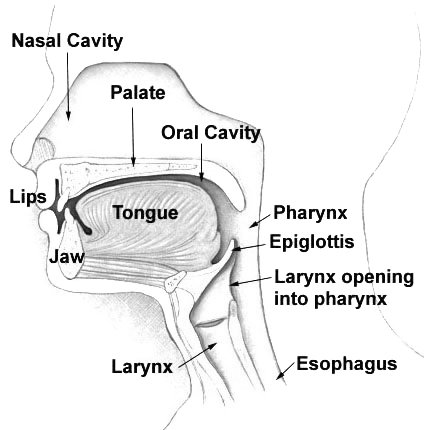
ORAL STAGE
This is the first stage of swallowing and it takes place in the mouth. It initiates the process of swallowing. Food substance on entry into the mouth are broken down by teeth in the process called mastication. In mastication, food substance are being moistened BT the saliva and are moved around in the oral cavity by the tongue. The end product of mastication is bolus and ready to be propelled posteriorly into the pharynx.
The tip of the tongue presses on the hard palate separating the bolus from the rest and the jaw shuts. The bolus is propelled into the oropharynx as the tongue elevate and presses the bolus against the hard palate rapidly backward. It is hard to swallow without closing your mouth. This stage of swallowing is voluntary meaning that you can control it and it involves cranial nerve, trigeminal, facial and hypoglossal nerve.

Mouthfeel. Source:Wikimedia - CC BY-SA 3.0.
PHARYNGEAL STAGE
This is the second stage and it take place in the pharynx. The oropharynx is connected with the nasopharynx which is air passage and the oesophagus. Food substance is suppose to enter the oesophagus through the pharynx. So for pharyngeal stage to work properly, the other part of pharynx related to air passage must be closed. that's why is advised ni talk while eating food.As soon as bolus enters the oropharynx, the nasopharynx is closed by reflex action by contracting the superior constrictor muscle of the pharynx and elevation of soft palate. During this process, respiration is stopped and the glottis is closed by contraction of laryngeal muscle.
The bolus is propelled through the pharynx by peristalsis which start from the superior constrictor muscle to the inferior constrictor muscle of the pharynx. The upper pharyngeal sphincter relaxes to receive the bolus into the oesophagus. As soon as the bolus enters the oesophagus, the sphincter contract and the nasopharynx open leading to resumption of respiration. This stage is involuntary action and gravity play little part in the upright position. Your position don’t actually affect your swallowing.
OESOPHAGEAL STAGE
This is the last stage of swallowing and it takes place in the oesophagus. It is involuntary action under the control of neuro muscle. Bolus enters the oesophagus and is propelled first by the striated muscle then followed by the smooth muscle. The movement of bolus in this stage is slower. The oesophagus is about 20cm in length and except during swallowing, it is closed at both end by sphincters.
The upper third of oesophagus is a striated muscle under cholinergic control of the vagus n. The lower oesophageal sphincter is not a true sphincter and factors responsible for it’s sphincteric actions include
- Acute angle of entry of the oesophagus into the stomach which gives it flap valve effect.
- Tonic vagal contraction of the smooth muscle of the lower oesophageal sphincter.
- A “pinch-cock” action of the crura of the diaphragm around the oesophagus.
- Intra abdominal location of gastro oesophageal junction
In this oesophageal stage, there is primary and secondary peristalsis. Peristalsis is a radial contraction and relaxation of muscle in a sequence that produce wave which propel bolus into the stomach in anterograde direction. Primary peristalsis propel the bolus into the stomach but in a situation were the primary peristalsis fails to empty the oesophagus, the secondary peristalsis follows until the oesophagus is emptied.
CONTROL OF SWALLOWING
Swallowing is a neuromuscular activities which consist of three stages with arch stages being control by neurological mechanism. Swallowing involves both skeletal and smooth muscle which are coordinated by Autonomic nervous system. The oral stage is voluntary and is controlled by cerebral cortex.
The pharyngeal and oesophageal stages is controlled by swallowing centre on the medulla oblongata and pons. Both are involuntary in nature and control of oesophageal peristalsis is both intrinsic and extrinsic.
nervous control. Source:Wikimedia - CC BY-SA 3.0.
DYSPHAGIA
This is problem associated with swallowing. Dysphagia simply mean difficulty in swallowing and it does not always indicate medical condition because most of them are temporary and goes away on it’s own. Severity of dysphagia varies and when very severe, solid and liquid food may not pass Down the oesophagus leading to vomiting. Dysphagia can be caused by many factors such as:
Acid Reflux: this is when stomach content are thrown back to oesophagus and stomach content is acidic in nature. This will lead to heartburn and burping.
Goitre: goitre is disease of the thyroid gland and it is the abnormal enlargement of thyroid gland located at the base of neck. Although it is painless but can make breathing and swallowing difficult by obstructing the passage.
Carcinoma of the oesophagus: cancer tumour on the oesophagus can obstruct the passage
Failure of the nervous control
TYPES OF DYSPHAGIA
There are two types of difficulty in swallowing and they include oropharyngeal and oesophageal dysphagia. Oropharyngeal dysphagia occurs in the pharynx and is mainly caused by disorder of nerves and muscle. It always come with choking. The oesophageal dysphagia occurs in the oesophagus and is caused by spasms in oesophagus and narrowing of oesophagus. This comes with the feeling that something stuck in your throat.
Dysphagia can be controlled and treated by
Diet modification
Postural modification
Surgery to remove obstacles
Drug prescription to treat acid reflux
REFERENCE
meaning of swallowing ~wikipedia
Phases of swallowing ~wikipedia
Coordination of swallowing ~wikipedia
Swallowing difficulty
If you write STEM (Science, Technology, Engineering, and Mathematics) related posts, consider joining #steemSTEM on steemit chat or discord here. If you are from Nigeria, you may want to include the #stemng tag in your post. You can visit this blog by @stemng for more details. You can also check this blog post by @steemstem here and this guidelines here for help on how to be a member of @steemstem. Please also check this blog post from @steemstem on proper use of images devoid of copyright issues here.
