Have you ever thought how your camera performs face detection?
In one of my last articles devoted to Computer Vision I told you about pattern detection. The question is "what if the pattern is a face?"
Task of face detection in the image is often the first step in the process of solving the problem of higher level - facial recognition. In addition, information about the presence and the number of persons in the image may be useful in the automatic accounting system which counts the number of visitors; crossing control systems in offices, airports and subways; automated systems to prevent accidents; intelligent interfaces "man-computer"; in a photographic technique for automatic focusing on the human face.
Existing algorithms for face detection can be divided into four categories:
- Empirical method;
- The method of feature invariant approaches;
- Template Matching Methods;
- The method of detection by external signs, educable systems.
The empirical approach (Knowledge-based top-down method)
This method involves the creation of an algorithm that implements a set of rules, which the image must have to be recognized as a human face.
The most simple rules:
- The central part of the face has a homogeneous brightness and color;
- The difference in brightness between the central part and the upper part of the face is significant;
- A face has got two symmetrically placed eyes, nose and mouth, sharply differing in brightness relative to the rest of the face.
The method of powerful zoom used to smooth the noise and to reduce the computational operations decreases the image.
In this image, it is easier to identify the area of homogeneous brightness distribution (estimated area of face location), and then check the availability of sharply differing brightness areas: such areas can be a considered as "face"
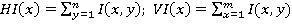
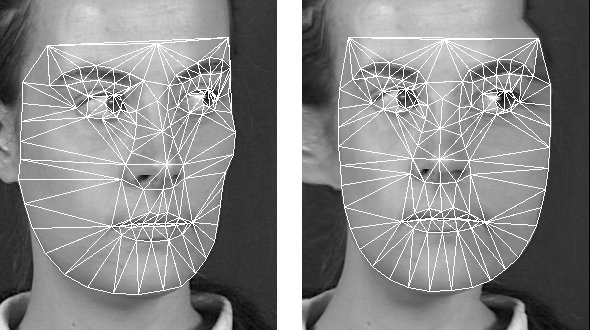
Feature invariant approaches
It forms the second family of methods of face detection. Supporters of the approach try to identify patterns and properties of the face image implicitly, find the invariant features of faces, regardless of the angle and position.
The main stages of the algorithms:
- Detection of overt signs on the face: the eyes, nose, mouth;
- Detection: face boundaries, shape, brightness, texture, color;
- Association of all detected invariant features and their verification.
The method of face detection in complex scenes involves finding the correct geometrical locations of facial features. For this Gaussian derivative filter with a plurality of different scales and orientations is used. After that the search of matches with identified characteristics and their relative position is made using random listing.
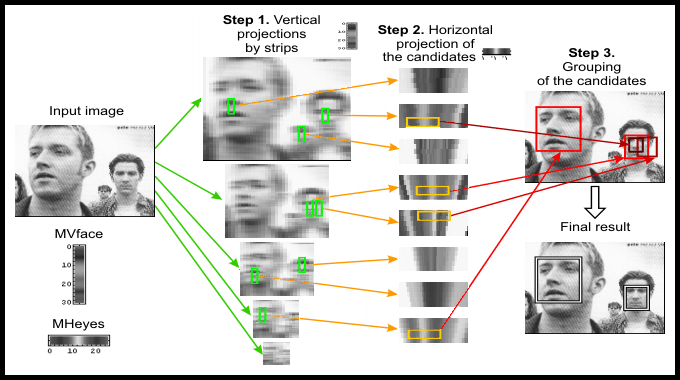
Methods of this group have the ability to recognize a face in different positions. But even with a small noise or illumination the percentage of reliable detection sharply decreases.
Template Matching Methods
Templates define a standard image of the face, for example, by describing the properties of the individual areas of the face and their possible mutual arrangement. Face Detection using a template is a test of the areas of the image and finding matches with a given template.
Features of the approach:
- Two types of templates:
a) non-deformable
b) deformable - Templates are pre-programmed, uneducable
- Correlation is used to locate the face in the image
Face detection method using the three-dimensional forms is to use the template in the form of pairs of brightness relationships in two areas. To locate a face position you must pass through image and compare it with a predetermined template. And this should be done at different scales.
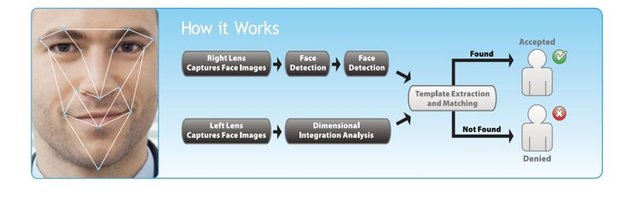
The advantages of this method are its relative ease of implementation and good results with images that have a rear background. A major disadvantage is a need for an alignment of template near the image of the face.
Method of detection by external signs
These are the methods in which it is necessary to teach system, by processing test images.
Image (or a fragment) is associated in some way with the calculated vector, which is used for image classification into two classes - face / non-face.
The basic principles of the methods:
Scholasticism: Each window is scanned and represented by a vector value
Block structure: Image is divided into overlapping or non-overlapping areas of various sizes and algorithm that counts the weight of vector is used.
To teach algorithms a library of manually prepared “face” and “not face" images is required.
It is worth noting that the most important task is to highlight the strong classifiers. They will have the highest priority for checking features found in the image.
Here are the basic methods of performing these tasks:
- Neural network: Multilayer Perceptrons;
- Principal Component Analysis (PCA);
- Hidden Markov model;
- Active Appearance Models;
- Viola-Jones method
The most perspective in terms of high performance and low frequency of false results and a large percentage of true face detections is considered a Viola-Jones method.
The basic principles on which the method is based, are as follows:
- the integral representation of the image, allowing you to quickly calculate the necessary facilities is used;
- boosting to select the most suitable characteristics for the desired object on the part of the image is used;
- all the signs are input to the classifier, which gives the result "true" or "false";
- cascades of signs are used to quickly get rid of windows where a face has been found.
- Haar features by which the desired object is searched are used;
In this method the integral representation of the image is used - it is a matrix that matches size of the original image. In each element the sum of the intensities of all the pixels located above and to the left of the element are kept in it.
Matrix elements are calculated using the following formula: 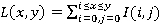 where I (i, j) - the brightness of the original image pixel. Each matrix element L [x, y] represents the amount of pixels in the rectangle from (0,0) to (x, y).
where I (i, j) - the brightness of the original image pixel. Each matrix element L [x, y] represents the amount of pixels in the rectangle from (0,0) to (x, y).
In the standard method of Viola - Jones rectangular signs are used, they are called wavelets:
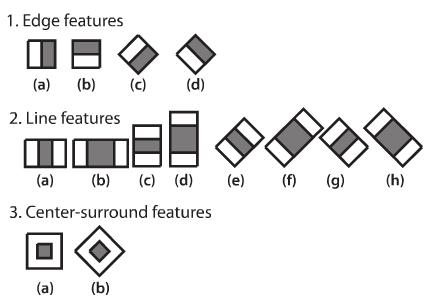
The teaching of classifiers is very slow, but the search for the face is very fast. The algorithm works well and recognizes facial features at a slight angle, approximately 30 degrees.
There are a lot of different methods, some are faster, others provide a fascinating percentage of successful matches, some are really slow or even could mix up a hand with a face - so all methods have their pros and cons and because of it, they will be being developed in the next few years and maybe we'll get the one that would be convenient for industrial and individual purposes.
Follow me, to be the first to learn about my publications devoted to popular science and educational topics
With Love,
Kate

Easy explained, thankx!
THANKS :)
This is a really neat post! Thanks for sharing @krishtopa