The Chemistry of Glow Sticks
It's a party favorite that most people use at parties; glow sticks. Either on a birthday party, at holiday meetings or in marriage ceremonies, the glow sticks are an easy fun! In addition, glow sticks help to save lives in emergency situations such as natural disasters. Also, campers and divers often use these bars. I have wondered how these plastic tubes work, and after I did a little research on the subject, I wanted to share it with you.
If you are wondering what happens to these sticks and how they shine like that ... voila!
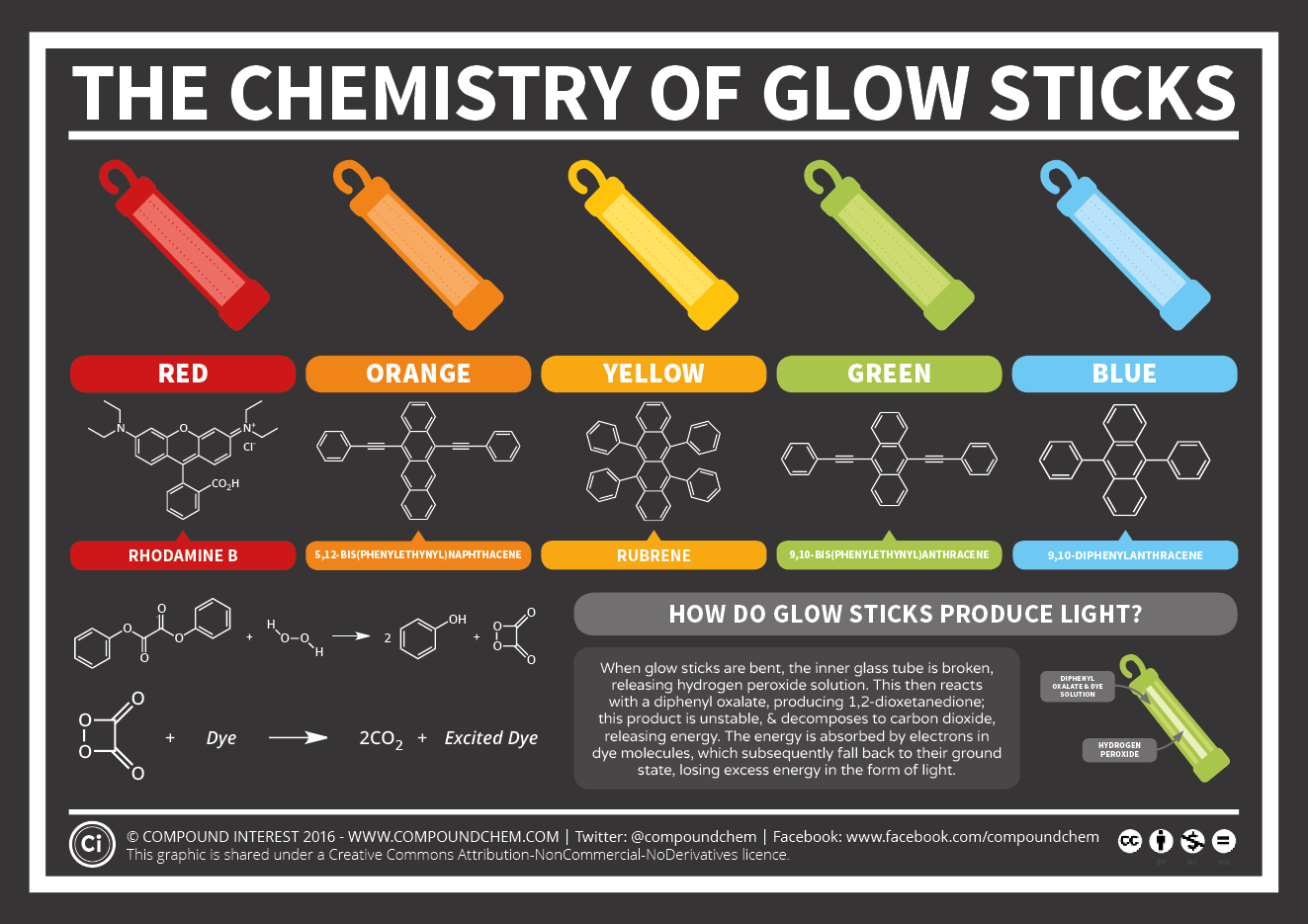
An exergonic reaction occurs when you bend a glow stick. Exergonic simply means "energy release". There are two different compartments inside the plastic tube and different chemicals in these parts. One of the commonly found solutions in the glow sticks is the diphenyl oxalate compound. This compound is used in combination with color-determining paint. Different colors can be used according to the desired color. Another solution is the hydrogen peroxide solution present in the glass cylinder which is on the inner side and constitutes the second chamber. The glass cylinder keeps the two solutions separate and prevents them from entering the reacting with each other. When the glow stick is crushed, the glass cylinder is broken and the hydrogen peroxide and diphenyl oxalate solutions enter the reaction. These two solutions are mixed and the reaction which gives rise to phosphor light is realized.
As a result of this reaction, the diphenyl oxalate compound is oxidized by hydrogen peroxide and forms the 1,2-dioxoetanedione compound which is unstable with other products. This highly unstable compound is poised to decompose to release carbon dioxide and energy. Exactly the dye molecules used at this point participate in the game, and although not involved in the reaction itself, the electrons in the molecule absorb the energy released by the decomposition of 1,2-dioxetanedion and pass to an upper energy level. Electrons lose their excess energy when they return to their original energy levels (the fundamental energy level), and this energy loss occurs as light (photon) emission. This process is called "chemiluminescence".
The energy of the emitted light depends on the structure of the dye molecule, and the differences in structure allow different colors to be obtained. During the reaction, the hydrogen peroxide and diphenyl oxalate gradually decrease as the amount of dye molecules remains constant. When one of these two molecules is consumed, the reaction ends and the light is no longer emitted from the stick.
Perhaps you noticed the text on the phosphor stick package. It says that the sticks must not be cut and the chemicals inside must not be removed. There is a chemical cause in this case. In addition to being harmful to the hydrogen peroxide present in the glass cylinder, the reaction between the diphenyl oxalate and the hydrogen peroxide results in a small amount of phenol as a by-product. This may cause undesirable effects such as irritation and dermatitis when in contact with skin.
One last thing more, reactions occurring in the phosphorus stick, like many chemical processes, can also be thermally affected. Low temperature reaction will slow down while high temperature will increase reaction speed. If you want the light to run out longer, you can hold the stick in a freezer.
Have a nice weekends.
Glow sticks are great. Many uses for them, just have to be creative.