[The Governance of the TRON Ecosystem]-Steemit Crypto Academy | S4W7| Homework Post for @yohan2on
THE GOVERNANCE OF TRON ECOSYSTEM
SUPER REPRESENTATIVES, SR PARTNERS, And SR CANDIDATES. WHO ARE THEY?
Tron ecosystem is a decentralized blockchain designed for content creators in the entertainment industry. The blockchain enables producers to directly market and sell their creative work to customers, without the need for a middleman. Developers can also design DApps, Smart Contracts, and DApp coins that run on the Tron blockchain. Tronix (TRX), a native currency on the Tron blockchain, is used within the network and serves as the network's governance token.
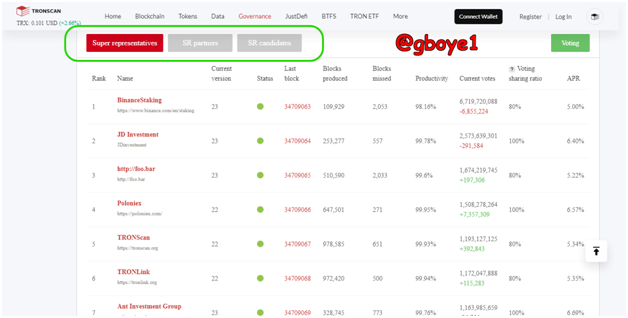
SUPER REPRESENTATIVES
The TronBlockchain's Super Representatives are nodes that have been voted on and chosen from among the super representative candidates. The Tronblockchain's super representatives are 27, and they are in charge of creating blocks, validating transactions, and gaining the voting rewards that go with it.
The super representatives voting takes place every six (6) hours, and the candidates with the highest number of votes in the range of 1 to 27 are chosen as super representatives, while those with votes in the range of 28 to 127 are referred to as superpartners.
Super representative are important because they are the book keepers of the Tron ecosystem, which is in charge of packaging and verifying all the transaction executed. This means they are in charge of maintaining the Tron Network on a regular and timely basis. Because of the critical role they play in the system, their background information is usually made public in the Tron Ecosystem so that interested voters can vote for their Super Representative. (Each user can vote for just one Super Representative.) Following the Super Representative voting, the Tron Foundation and Community provide technical support to the Network.
Holders of Tron Blockchain Tokens vote to elect the Super Representatives. Individual nodes that stake TRX tokens in their accounts are known as token holders, and each staking node is able to vote during the election process.
For validating a block of transactions, the super representative receives 32 TRX. Every 3 seconds, a new block is generated on the Tron Blockchain, implying that the supers earn around 336,384,000 TRX per year.
SR PARTNERS
Super representative partners (SR partners) are among the super representative candidates ranked 28 to 127. They're chosen automatically after the vote is over, and the super representative is chosen from the voting results. The SR partners should ideally be nodes that didn't make it to the top 27 slots during the voting process.
These sets have a restricted role in the network because they are unable to participate in block production or transaction packing. However, it's worth noting that the Super Representative Partner continues to be compensated for freshly created/produced blocks in the network. These 100 Super partners are rewarded based on their voting capacity in the system.
They've also been seen taking part in ecosystem voting activities aimed at improving Blockchain governance. They can also make proposals that are in line with the Super Representative's requirements.
SR CANDIDATES
The 147 nodes chosen by the whole Tronblockchain's token holders are referred to as super representative candidates. Every 6 hours, the voting is updated, and the super representatives are chosen as nodes with the highest votes in the range of 1 to 27, and the super representative partners are chosen as nodes with the corresponding votes in the range of 28 to 127.
The candidates ranked 128 to 147 will be placed on standby until the next voting round. Following each voting round, the selected SR candidates are awarded 115,200 TRX, which is divided among them in accordance with the number of votes they received. The super representative candidates will earn 168,192,000 TRX every year.
DIFFERENCE BETWEEN DPOS AND POS CONSENSUS MECHANISM
Different blockchains use DPos and PoS as consensus algorithms for transaction validation. Before I get into the specifics of the algorithms, let me first define consensus algorithms. The consensus algorithm is a set of well-implemented codes on the blockchain that serve the purposes of verifying transactions before recording them (as far as we know, no transaction on the blockchain is recorded until it has been verified), storing transactions in small interconnected units called blocks, and rewarding miners after successful completion.
DPOS (DELEGATED PROOF OF STAKE)
Delegated Proof-of-Stake (DPoS) is an internal arrangement by nodes in a blockchain to vote and select from a list of qualified nodes to take on various blockchain activities such as transaction validation and block generation. Although the DPoS consensus process is based on the concepts of proof-of-stake (PoS), the vote of selected nodes (delegates) provides more decentralization, allowing a larger number of Blockchain nodes to choose their preferred delegate.
Nodes vote for delegated nodes by staking their assets in a stake pool associated with the delegated node, resulting in the delegated node receiving a larger stake in the blockchain's token. The chosen delegates are rewarded from transaction fees, which are divided according to the percentage of tokens invested in the subaccounts by the voter.
POS (PROOF OF STAKE)
Proof-of-Stake (PoS) is a consensus mechanism that distributes blockchain responsibilities depending on the number of crypto assets owned by nodes, giving selected nodes extra rights and contributions. This consensus algorithm was developed in response to the issues with the proof-of-work consensus algorithm, which includes high operating costs and energy consumption.
Network nodes (users) allocate a percentage of their assets to a chosen node in the proof-of-stake consensus mechanism. The staked assets are used by the nodes to take on assigned on-chain obligations such as transaction validation, new protocol implementation, governance, guild line creation, and other tasks that help the blockchain develop and perform better.
HIGHLIGHT OF THEIR DIFFERENCES
Although DPoS and PoS both use staking assets to develop their protocols, there are some key differences:
• Proof-of-stake (PoS) is adaptive to the growth and expansion of a decentralized network, with nodes are chosen based on the number of assets staked. Because voting is required to pick nodes in the DPoS, it will scale poorly.
• Because of the randomized likelihood of selecting a new delegate node, DPoS is regarded to be more secure than PoS. These guards against 51 percent attacks on the Blockchain.
• Delegated proof-of-stake (DPoS) entrusts the performance of the blockchain to a limited group of delegates, which can have a positive impact such as preventing on-chain congestion and enhancing network throughout. Or in the case of a negative outcome, such as the possibility of assault schemes using forged voting nodes.
FREEZING AND STAKING TRX
Staking and voting in the Tron ecosystem are explained in detail below. We only require a TronLink wallet.
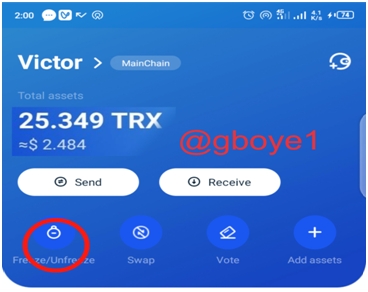
1.On your device, open the Tronlink wallet.
2.Click the Freeze option on the screen from your landing page.
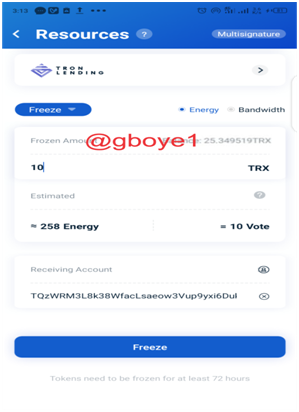
3.Enter the amount of TRX to be frozen on the resource page and click the Freeze button.
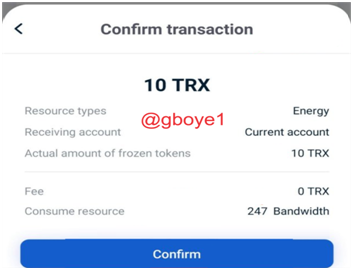
4.Confirm your transaction.
5.Then, to complete this transaction, enter your Password.
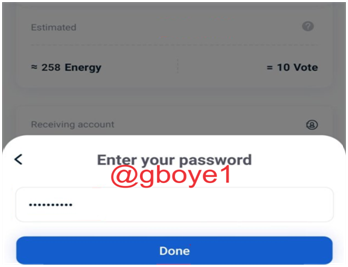
6.On the screen, we can see confirmation of frozen TRX assets.
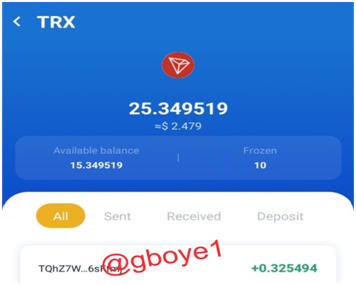
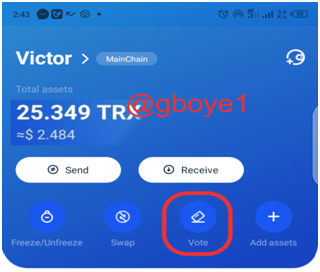
THE VOTING PROCESS
1.Select the Voting option from the initial landing page.
2.Select your favorite SRs from the list of options.
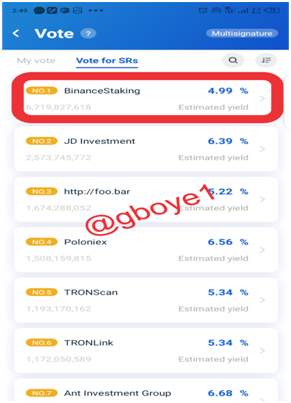
3.To continue, click the Vote Button.
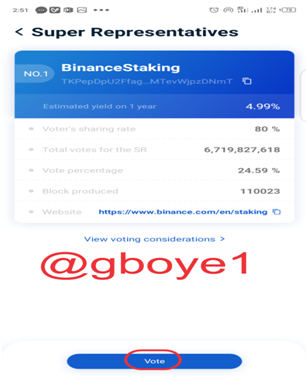
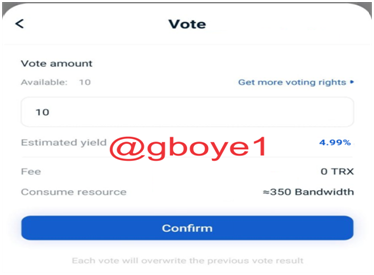
4.Click the confirm button after entering the number of votes for SR (10 votes).
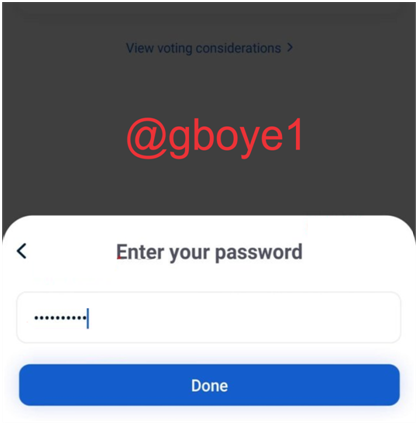
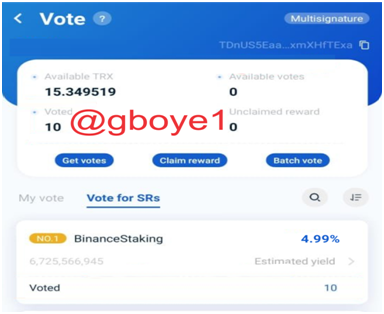
5.After you've entered your password, the process is finished.
CONCLUSION
Blockchain technology has revolutionized Defi in particular, and it is also altering other aspects of everyday life. With alternative consensus algorithms in place, the flaws of previous mechanisms such as PoW are mitigated by new mechanisms like PoS, DPoS, PoC, and PoB, among others. These new algorithms, like anything else, have flaws.
Hi @gboye1
Thanks for participating in the Steemit Crypto Academy
Feedback
Total| 6/10
Fairly done. For question 2, you needed to go deeper than that. You should have added an illustration for both algorithms. Otherwise, thanks for your effort.