Prosthetic dislocation of the hip, common complication after surgery.
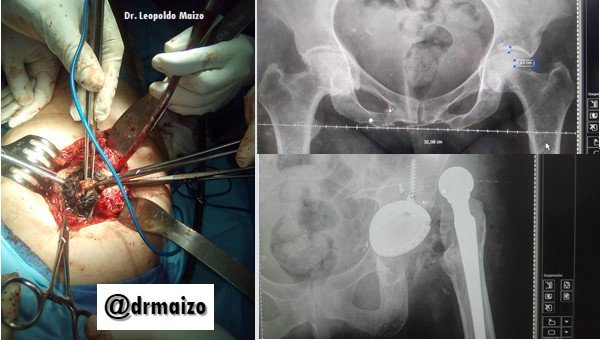
Prosthesis Hip Dislocation
Dislocation of the hip is the second most frequent complication of total hip arthroplasty, followed by aseptic loosening which is the second most frequent complication of TCA, occurring with an incidence of 2.4-3.9% in primary procedures and an incidence of up to 28% in revision surgeries. Hip dislocations can be classified into 3 groups: early, intermediate and late.
In general, early dislocations respond favorably to non-surgical treatment and have a low recurrence rate. In this case the need for revision surgery is much greater. The diagnosis of hip dislocation is relatively simple to make as the clinical picture is very typical. Once a hip dislocation has been identified, the first step is to make an attempt to reduce it in a closed manner.
Within the options we find the following: change of the modular components, trochanteric advances, revision of the orientation of the components and, ultimately, the use of constrained components. One of the most frequent problems for which the patient presents early recurrent instability is the inadequate orientation of the prosthetic components. ATC is one of the most useful and successful surgeries of the last 100 years, however, it requires a refined surgical technique, adequate planning and patient selection in order to meet expectations.

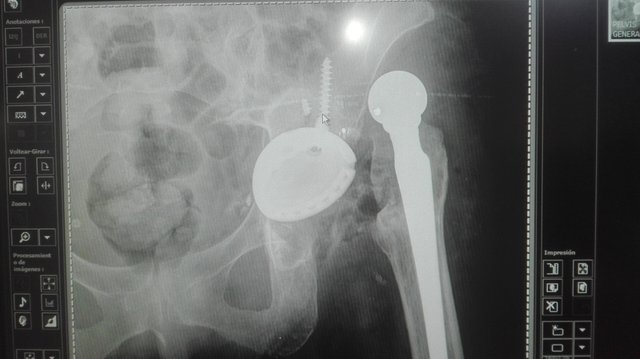
Causes
It seems that the posterolateral approach has a significantly greater risk than the rest of them, however, in the study conducted by Masonis and Bourne was observed that the risk of dislocation with this approach decreases significantly with capsular repair and reinsertion of short external rotator muscles, approaching significantly the same incidence as the anterolateral and direct lateral approaches.
The reconstruction of the offset is very important, as it will allow the biomechanics of the hip to be restored, as well as an adequate mobility of the hip, reducing the risk of dislocation. Otherwise, the prosthetic joint will not have an opposing force to that generated by gravity, the weight of the body and the adductor muscles of the hip having little containment capacity which will significantly increase the risk of dislocation.
Hyperlaxitude is a risk factor for TCA dislocation, as there is an increase in the arcs of motion, being more likely to pinch the ends of the arcs of motion.

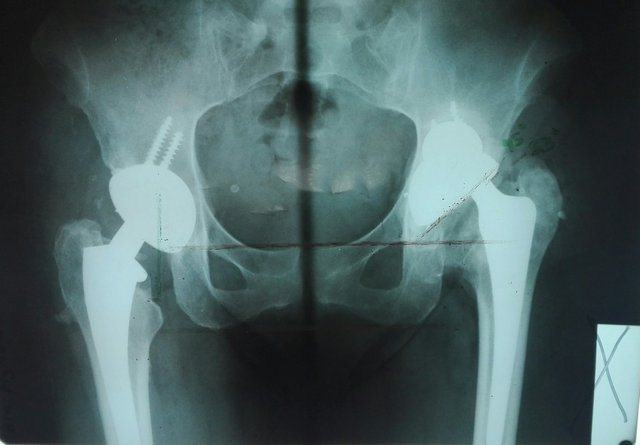
Diagnosis
On arrival at the emergency department, the patient must be evaluated clinically and with radiographic studies, generally requiring only an antero-posterior (AP) radiography of the pelvis and sometimes, a projection through the table, which is especially useful if there is doubt about the direction of dislocation, together with providing data regarding the orientation of the prosthetic components.
The diagnosis of hip dislocation is relatively simple to make, as the clinical picture is very typical. Most of the time the patient identifies that after excessive flexion or internal rotation (e.g. getting up from a chair), the prosthetic joint is out of place. They also have audible clicking, deformity, and difficulty mobilizing due to pain.
Generally, the patient goes to the doctor within the first hour of the event with a picture of intense pain in the groin and proximal thigh region, with the pelvic limb affected with shortening, flexion and internal rotation when the hip has been dislocated in the posterior direction (more frequent) and in external rotation and extension when it has been dislocated in an anterior position.
Dr. Leopoldo Maizo - Orthopedic Surgeon


Firma diseñada por @themonkeyzuelans, contáctalos vía Discord "themonkeyzuelans#9087"
Great projects from the Steemit community:
- My Fundition campaign: https://fundition.io/#!/@drmaizo/6f88ggj8h

.png)