A new way of understanding the universe! Gravitational waves!
For many years classical physics has tried to describe one of the most important enigmas, gravity, one of the main authors in trying to deduce this phenomenon was Isaac Newton, who described in a simple way that two objects can be attracted according to their mass and the distance between their centers, that is, if the mass increases its volume the force of attraction will increase, and if the distance between the two objects increases the force will decrease. However, this theory finds its own limit in scenarios where objects are supermassive, at that time Newton's theory does not make exact predictions.

FUENTE
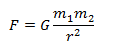
A simple interpretation of Newton's theory is to think of the following scenario: the sun and the earth are two masses which have a distance "x" separating them and each one of them has a certain mass, that is, the Earth is in the orbit around the sun due to the force of attraction that exerts one on the other, suppose the sun disappeared suddenly, the earth would be ejected immediately without direction in the vast universe, this because the sun has greater volume in mass.
FUENTE
It was not until 1905 when Albert Einstein in his theory of special relativity introduced concepts that revolutionized the way of understanding the universe. This theory is presented on the basis that the speed of light is the same in all inertial reference systems. This theory Einstein presents as "special" relativity because it only applies where the curvature of spacetime due to gravity is negligible.

FUENTE
The theory of special relativity is based on equations that clash with the common sense of people, among them we have: spatial contraction, time dilation and others.
Spatial contraction
Basically it represents a relativistic effect where the length of a body in motion contracts as the speed tends to the speed of light.
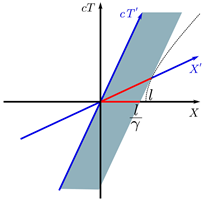
FUENTE
Dilation of time
This is a phenomenon posed by the theory of relativity, in which it is said that an observer at rest who has a clock exactly like another clock where the observer is in motion, will slow down the time the observer is in motion.
In this case the example of the twins is applied, where both have a clock exactly the same, one of them makes a space trip in which it goes at speeds close to the speed of light, and the other stays on the ground. On the way back the traveling twin is younger than the twin who stayed on the earth.
FUENTE
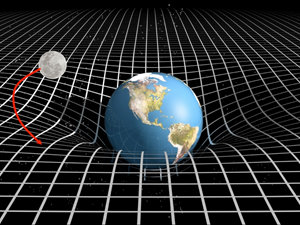
It was not until 1915-1916 that Albert Einstein introduced the concept of gravity in theory, calling it Theory of General Relativity. This is a theory of the gravitational field and the general reference systems. This theory generalizes the so-called theory of special relativity. The fundamental principles of this theory are: the principle of equivalence, the notion of the curvature of space-time and the principle of covariance.
Einstein basically postulated in this theory that at a certain point one can not distinguish experimentally between a uniformly accelerated object and a uniform gravitational object.
FUENTE
The theory of general relativity as well as special relativity share important aspects, among them is the principle that nothing travels faster than light. This explains that changes in the gravitational field can not occur everywhere instantaneously, they must propagate. These gravitational changes that propagate are called gravitational waves.
Gravitational waves is a physical phenomenon raised by Albert Einstein in 1916 in his theory of general relativity.
This phenomenon deals with fluctuations that are generated in the curvature of space-time which propagate in the form of waves moving away from their source.
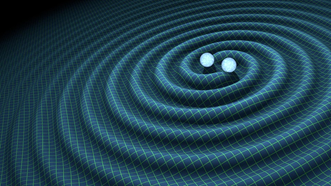
FUENTE
Gravitational waves originate when two or more massive bodies interact in space. Depending on the distance of these bodies from the earth, the waves when they reach the earth are weaker, they have lost strength. Since they are weak when they reach the earth it is difficult to detect them, scientists need very sensitive instruments to barely perceive these waves.
Gravitational waves represent a great importance for the understanding and explanation of many physical laws. This phenomenon can give information about the origin of the universe and how stars or black holes are formed or die.
On the other hand, for scientists this phenomenon could be a direct vision of seeing the universe a fraction of a second after the Big Bang.
What would happen if you had a particle with negative mass colliding with another?
First at all, I want to thank you for coment my post.
Regarding your question: According to Forward's analysis, there is a force of attraction between two positive masses, while in two negative masses the same force appears but in repulsion. That is to say, existing this force of replusion, there could not be a collision between two negative masses.