Bioinformatics experiments. Exp 1. Analysis of mechanisms of Cd+2 impact on MAPK-signalling through DUSPs (or “Catch me (Cd2+) if you can”). Part 1. Theory
Introduction
You can find detailed definitions of specific bioinformatics/biochemical terms used in this post at the bottom of the post. Short cues will be given throughout the text.
Cadmium (Cd+2) is widely used in manufacture.
Cadmium harms kidneys, lungs, circulatory system, and influences bone tissue metabolism.
A lot of diseases are partially due to cadmium (including carcinogenesis).
So, it’s going to be quite interesting to try to analyze how exactly cadmium could affect some signalling pathways of the cell and what outcome of this impact could be (cell death/prolifiration…)). We are going to try to analyze MAPK (Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinases) signalling pathway.
Cadmium relationship with MAPK-signalling
To enter the cell Cd2+ as free ions or as a part of proteins/peptides uses transitory proteins: free Cd2+ can get into the cell through ion channels or with the help of carrier proteins, and Cd2+ complexes enter the cell with the help of receptor-mediated endocytosis. Cd2+ possesses "ionic mimicry", i.e. it has similar properties to essential ions (which organisms need to stay alive). Similarly Cd2+ complexes demonstrate "molecular mimicry", i.e. they ares similar to endogenous (originating from within an organism) biomolecules.
Once in the cell, Cd2+ can replace some proteins' ligands, which leads to Cd2+ accumulation in the cell [2,3].
Cd2+ affects a lot of processes, happening in the cell: it inhibits DNA reparation, increases oxidative stress level in the cell, may lead to cell necrosis/apoptosis, affects MAPK-signalling and more [1].
Just imagine a big spider web for a second. This web probably consists of thousands of parts. Similarly, there’re thousands of biochemical pathways in the cell. When flies get into the web/trap, then the whole web react for that (so that a spider can “feel” that). Just like that, when something happens with 1 signalling pathway, then the whole network of metabolic pathways might react on that. World Wide Web could serve as an analogy in this case as well.

(the image source - pixabay)
In our case we will examine just 1 signalling pathway – MAPK-signalling pathway. What’s more, we are going to focus on just 1 “fragment” of this pathway – where DUSP phosphatases influence/regulate MAPK-signalling pathway.
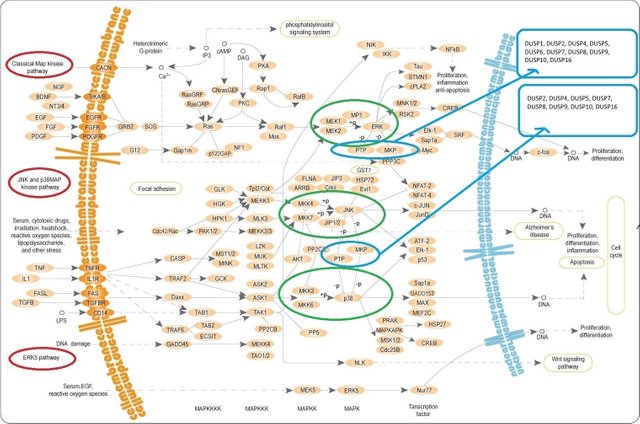
(the image is from Wikipedia. Public domain. The parts of this image with better resolution is below. I placed this, so that you could get an overall picture of MAPK pathway. Mitogen-activated Protein Kinase Phosphatases (MKPs) are highlighted with the blue ovals.
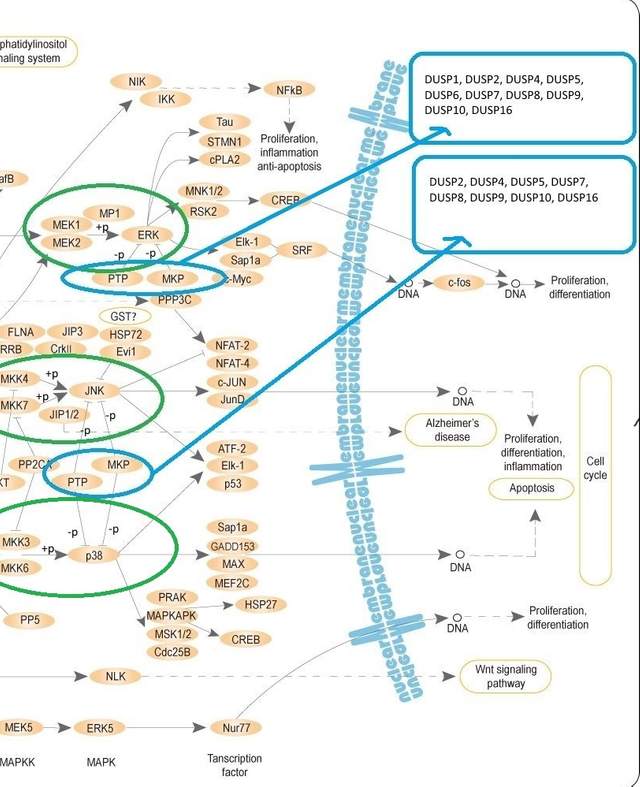
When you hover over/click on MKP element on KEGG (see below) we get a set of DUSPs. That's how we get the DUSPs list you can see on the right top corner)
|| Useful tip
|| Almost the same image is on KEGG.
But that image is interactive -> you can click/hover over different elements to get the list of proteins and detailed information about each of them.
The KEGG PATHWAY database is a collection of manually drawn graphical diagrams, called KEGG pathway maps, representing molecular pathways for metabolism, genetic information processing, environmental information processing, cellular processes, organismal systems, human diseases, and drug development.
KEGG
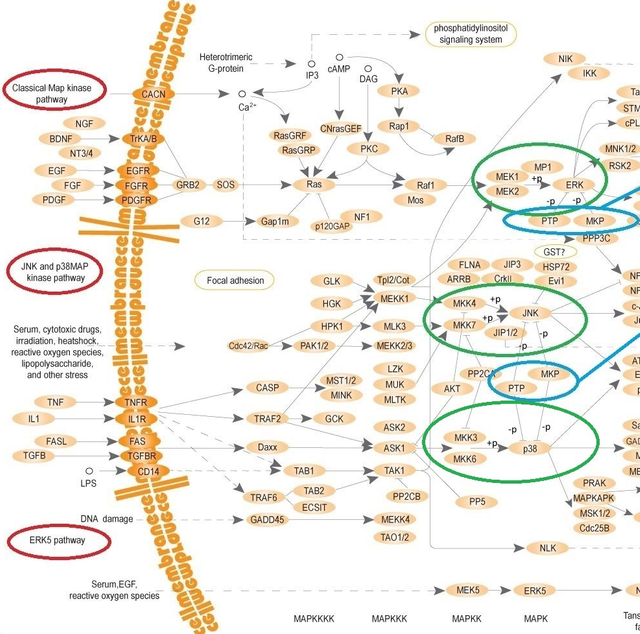
Аt first glance (especially to the untrained eye) all this might look scary.
Pay attention to ERK, JNK and p38 kinases (highlighted with the green ovals). These are kinases regulated by DUSP.
In response to signals (mitogens, heat shock, osmotic stress etc.), coming from the outside of the cell (left part of the image with the overall process), a special group of enzymes activates and passes the signal to the nucleus (right part of that image). It’s is a multilevel process, in which kinases consecutively phosphorylate (add phosphate group) the next members of a cascade, which leads to their activation. This signalling includes MAPK kinase kinases (MKKK or MEKK), MAPK kinases (MKK or MEK) and MAPK themselves.
|| Think of relay race where athletes (kinases) carry a baton (phosphate group) and pass it to the next members (MAPK signalling). And think of phosphatases as the obstacles those athletes might face during that relay race (so that they might lose that baton (phosphate group)).

As a result, a special group of genes activates. Activation of different groups of genes leads to different responses of the cell (proliferation (reproduction/division), cell death etc.).
|| This is to some extent similar to when your browser sends requests to Steemit, and then you get different responses based on what URL was in the address bar of the browser.
Malfunctioning MAPK-signalling pathways are partially responsible for development of some diseases, including diabetes, rheumatic arthritis, neurodegenerative diseases and more [4].
As you can see, there’re 4 main MAPK-signalling pathways (in mammalian cells):
classical Ras/MAPK pathway,
р38-pathway,
pathway with c-jun N-terminal kinases (or JNKs) 1, 2, 3
and ERK5-pathway
The key property of MAPKs is the necessity of phosphorylation of both Thr and Tyr residues of a conserved Thr-X-Tyr (T-X-Y, where X is any amino acid) motif (within the activation loop) for those MAPKs to be activated [6].
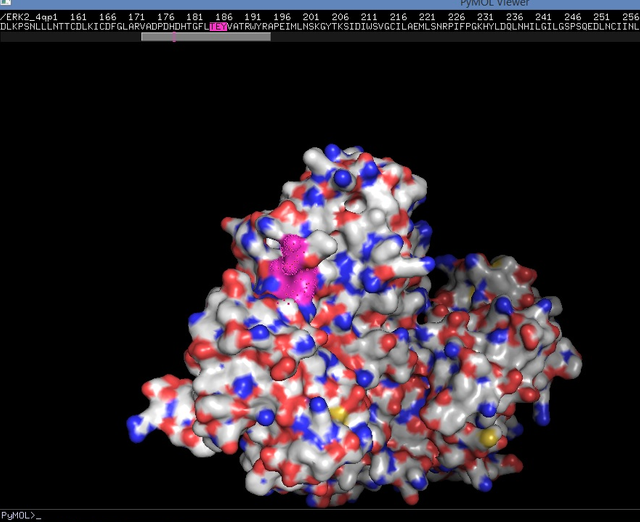
|| Useful tip
|| PDB (Protein Data Bank) is the central resource for 3-D structures of proteins/DNAs/RNAs
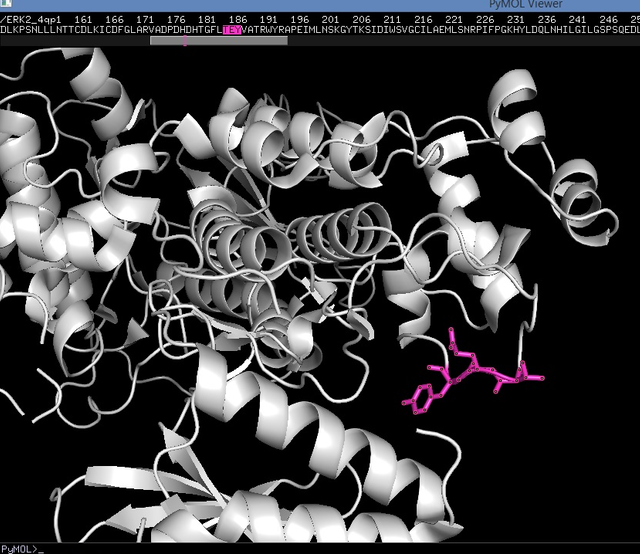
MKPs
MAPK activity is regulated by a number of factors, including specific phosphatases (enzymes that remove phosphate group from a protein), including DUSP phosphatases. Dephosphorylation of any residue (Thr or Tyr) may lead to MAPKs inactivation [5].
Protein Phosphatases are divided into 5 groups, 1 of which is Class I classical cysteine-based protein phosphatases.
Dual-specificity phosphatases (DUSPs) belong to this group. In its turn, DUSPs are categorized into 6 groups, 2 of which are
Mitogen-activated Protein Kinase Phosphatases (MKPs) (also known as classical DUSPs)
and atypical DUSPs
The last 2 groups are known MAPKs dephosphorylation. However, for the sake of simplicity we are going to analyse only MKPs.
This group is involved in regulation of ERK, JNK and p38 kinases (which we mentioned above).
They are called dual-specificity phosphatases because they can catalyse tyrosine, as well as serine/threonine residues.
All they catalyse substrates in a similar way – catalytically active Cys residue of MKP reacts with phosphate group of the substrate, which is then gets removed (thus inactivating MAPK).
The key feature of this group is that its members have specific conserved catalytic motif - (V)-HC-XX-X-XX-R-(S/T), where X - any amino acid, "(...)" means that this residue is optional, V - Valine (symbol Val or V),
H - Histidine (symbol His or H).
They have N-terminal non-catalytic domains (which help to define cell localization of the enzyme and bind to the substrate) and C-terminal catalytic domain with the (V)-HC-XX-X-XX-R-(S/T), mentioned above, and some others [7, [11]].
There’re 11 members of MKPs.

(The list was obtained with the help of HUGO)
|| HUGO
The resource for approved human gene nomenclature
HUGO
As for STYXL1 (the last MPK in the list), it was reported, that this enzyme is homologous to other MKPs, but is catalytically inactive (it has serine instead of cysteine in the catalytic site) [10]. Thus, we won’t analyse it.
MKPs family can be divided into 3 sub-families:
- DUSP1 ⁄ MKP-1, DUSP2 (PAC1), DUSP4 ⁄ MKP-2 и DUSP5 -> nucleus;
- DUSP6 ⁄ MKP-3, DUSP7 ⁄ MKP-X and DUSP9 ⁄ MKP-4 -> cytoplasm; ERK-specific;
- DUSP8 (M3 ⁄ 6), DUSP10 ⁄ MKP-5 and DUSP16 ⁄ MKP-7 -> nucleus/cytoplasm; JNK ⁄ p38-specific;
[7].
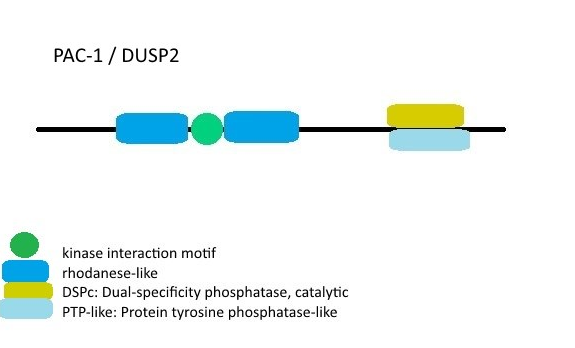
(Domain structure of DUSP2 as an example of MKPs [7, [11]]. The image was created by me with Paint. You can use it image if you want)
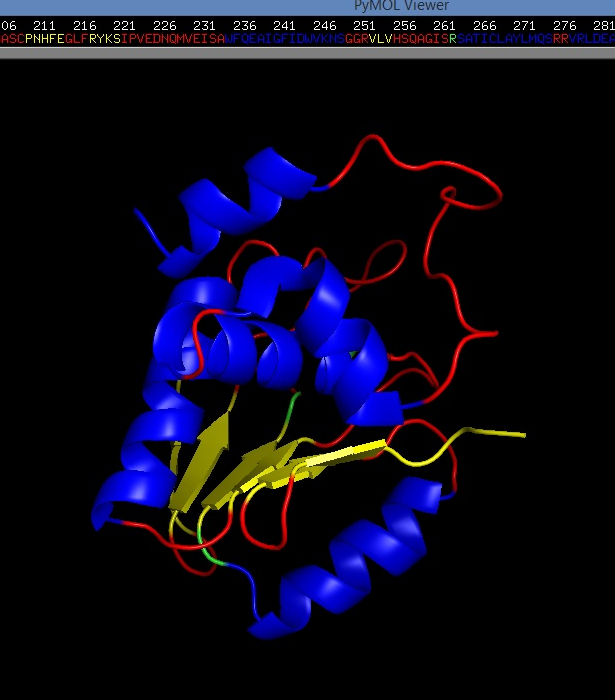
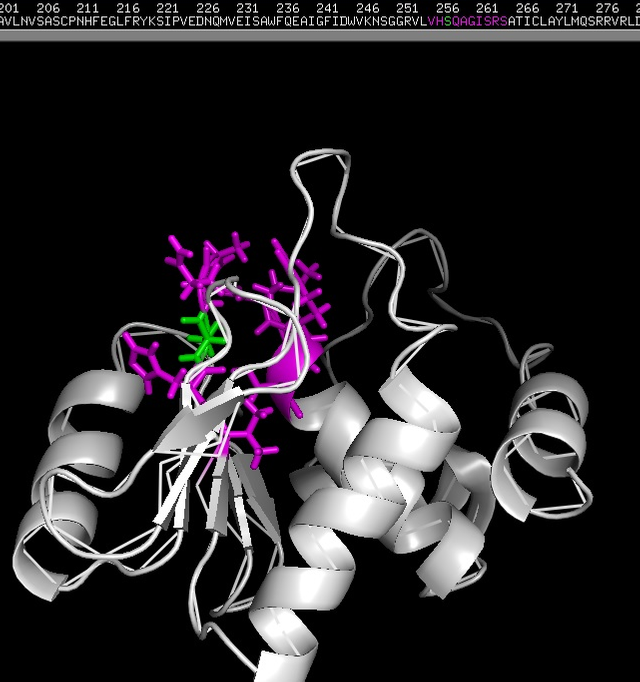
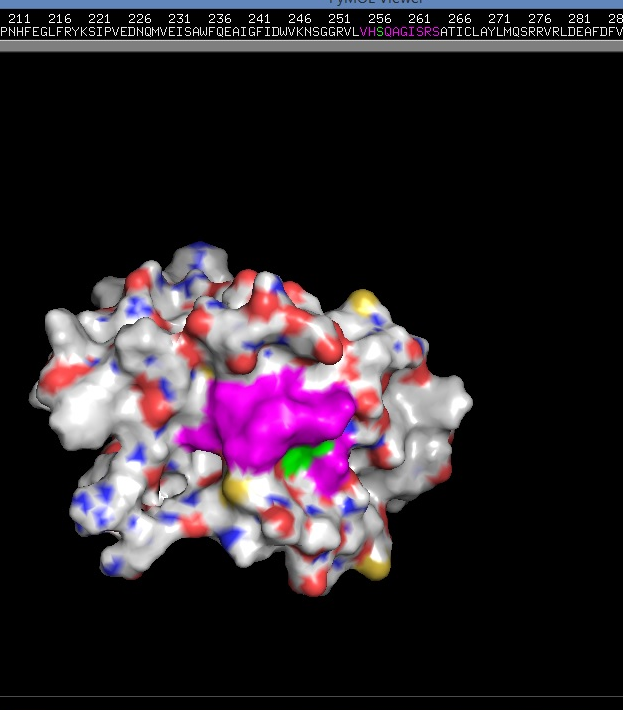
(DUSP2 catalytic domain (molecular representation (secondary structures)). 3D-structure (PDB-file) - 1M3G in this case - was obtained from PDB.
Where blue - alpha helix, gold - beta sheet, red - loops; [7, [11]]. The image was created by me with the help of PyMol - open source tool for molecules visualization/exploration. You can use the image if you want.)

3D-structure (PDB-file) - 1M3G in this case - was obtained from PDB. You can see that instead of Cys 257 (position) (C) in that (V)-HC-XX-X-XX-R-(S/T) motif (on the top) we see S (Ser) (highlighted with green) (this is also specified at PDB 1M3G entry). This is because of intentionally introduced by researches mutation, which somehow helps them to do NMR structural analysis (Nuclear Magnetic Resonance spectroscopy of proteins). [9]; The image was created by me with the help of PyMol - open source tool for molecules visualization/exploration. You can use the image if you want).
|| Useful tip
|| As for PyMol, you can download it at GitHub.
As for me, it's quite hard to undrstand how to install it there. So I followed instructions given at How to compile and install Pymol (windows & linux & MAC!) Updated to 1.8.2.0. Everything works great. But if you decide to install it from there, read carefully the commets section.
Glossary:
motif -
a distinctive sequence on a protein or DNA, having a three-dimensional structure that allows binding interactions to occur
[Oxford Dictionary of English, 3rd Edition, Oxford University Press 2010]
domain -
a distinct region of a complex molecule or structure
[Oxford Dictionary of English, 3rd Edition, Oxford University Press 2010]
ligand - substance that serve as a small addition to a larger molecule, which helps the latter to do its function;
(in case of proteins ligand binding often results in 3-D change of the protein)
endocytosis - a situation when a cell take substances by invaginating its membrane;
metabolism - chemical processes happening in organisms;
proliferation - rapid cell/organism devision;
kinase - a special enzyme which helps to transfer an ATP phosphate group to substrate;
mitogen - a substance which promotes mitosis;
phosphatase - enzyme that removes phosphate group from a protein;
residue - a monomer of polymeric chain;
References:
Sigel, Astrid, Sigel, Helmut, Sigel, Roland K. O. (Eds.).
Cadmium: From Toxicity to Essentiality. 2013, XXXVI, 560 p. 128 illus., 43 illus
Oh pretty nice! Resteem!
The image of the runner, might there be some copyright issues?
Hi. thanks for the interest.
I like your posts too.
As far as I know, there should not be copyright issues because Unsplash license states that:
A new source for copyright material on my list!
Thanks
This post has been voted on by the SteemSTEM curation team and voting trail. It is elligible for support from @curie and @utopian-io.
If you appreciate the work we are doing, then consider supporting our witness stem.witness. Additional witness support to the curie witness and utopian-io witness would be appreciated as well.
For additional information please join us on the SteemSTEM discord and to get to know the rest of the community!
Please consider setting @steemstem as a beneficiary to your post to get a stronger support.
Please consider using the steemstem.io app to get a stronger support.
Congratulations @alexbiojs! You have completed the following achievement on the Steem blockchain and have been rewarded with new badge(s) :
You can view your badges on your Steem Board and compare to others on the Steem Ranking
If you no longer want to receive notifications, reply to this comment with the word
STOPDo not miss the last post from @steemitboard:
Vote for @Steemitboard as a witness to get one more award and increased upvotes!
Hi @alexbiojs!
Your post was upvoted by Utopian.io in cooperation with @steemstem - supporting knowledge, innovation and technological advancement on the Steem Blockchain.
Contribute to Open Source with utopian.io
Learn how to contribute on our website and join the new open source economy.
Want to chat? Join the Utopian Community on Discord https://discord.gg/h52nFrV